Abstract
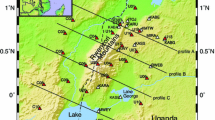
We investigated the primary mechanisms triggering the S-wave splitting (SWS) of seven unusually deep local earthquakes (between 50 and 60 km) which originated in the lithosphere beneath the Rwenzori region. We attempted to develop an understanding of the relationship between anisotropic structures in the lithosphere and tectonic deformation processes. A total of 12 out of 44 waveforms showed evidence of SWS on their polarization diagrams. The fast-wave direction (φ) and delay-time (δt) were estimated using the covariance matrix and the cross-correlation coefficient methods, respectively. We observed a clockwise rotation of φ-directions (NW - SE and ~ENE - WSW) at stations located in the rift valley. We related this pattern of φ-directions to anisotropic fabric, probably lattice-preferred orientation of preexisting olivine, whose a-axes are aligned with ESE absolute plate motion (APM) vector. At stations located outside the rift valley, however, we observed WNW - ESE and NNW - SSE patterns of φ-directions. We associated these patterns to the shape-preferred orientation of structures frozen in the lithosphere that are aligned with the present-day APM direction. We observed δt values ranging between 0.04 ± 0.01s and 0.43 ± 0.02 s, which decrease with distance away from the rift axis. This further supported our concept that the anisotropy observed at stations located on the moving plate is related to aligned melt inclusions frozen in the surrounding lithosphere. We further observed that the δt values increase linearly with ray-path length, which could indicate a fairly uniform anisotropy between 50-km and 60-km depth. Our study reported no evidence of multi-layer anisotropy beneath the Rwenzori region.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Supplementary data associated with this article is available in the Makerere University Institutional Repository at http://hdl.handle.net/10570/7597 under the name Earthquake data files. It is license-free with no restrictions attached.
References
Ayele A, Stuart G, Kendall J-M (2004) Insights into rifting from shear wave splitting and receiver functions: An example from Ethiopia. Geophys J Int 157(1):354–362
Bagley B, Nyblade AA (2013) Seismic anisotropy in eastern Africa, mantle flow, and the African superplume. Geophys Res Lett 40(8):1500–1505
Barruol G, Silver PG, Vanchez A (1997) Seismic anisotropy in the eastern United States: deep structure of a complex continental plate. J Geophys Res 102:8329–8348
Batte AG, Rümpker G (2019) Spatial mapping of b-value heterogeneity beneath the Rwenzori region, Albertine rift: evidence of magmatic intrusions. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 381:238–245
Batte AG, Rümpker G, Lindenfeld M, Schumann A (2014) Structurally controlled seismic anisotropy above small earthquakes in crustal rocks beneath the Rwenzori region, Albertine Rift, Uganda. J Afr Earth Sci 100:579–585
Booth DC, Crampin S (1985) Shear-wave polarizations on a curved wavefront at an isotropic free surface. Geophys J Int 83(1):31–45
Calais E, Ebinger C, Hartnady C, Nocquet J (2006) Kinematics of the East African Rift from GPS and earthquake slip vector data. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 259(1):9–22
Crampin S (1991) Wave propagation through fluid-filled inclusions of various shapes: interpretation in terms of extensive-dilatancy anisotropy. Geophys J Int 104:611–623
Crampin S, Evans R, Üçer SB (1985) Analysis of records of local earthquakes: the Turkish Dilatancy Projects (TDP1 and TDP2). Geophys J Int 83(1):1–16
Díaz J, Gallart J, Ruiz M, Pulgar J, López-Fernández C, González-Cortina J (2006) Probing seismic anisotropy in North Iberia from shear wave splitting. Phys Earth Planet Inter 158(2-4):210–225
Foley SF (1992) Vein-plus-wall-rock melting mechanisms in the lithosphere and the origin of potassic alkaline magmas. Lithos 28(3-6):435–453
Foley SF (2008) Rejuvenation and erosion of the cratonic lithosphere. Nat Geosci 1(8):503–510
Foley SF, Link K, Tiberindwa JV, Barifaijo E (2012) Patterns and origin of igneous activity around the Tanzanian craton. J Afr Earth Sci 62(1):1–18
Fouch MJ, Fischer KM, Parmentier EM, Wysession ME, Clarke TJ (2000) Shear wave splitting, continental keels, and patterns of mantle flow. J Geophys Res 105(B3):6255–6275
Fukao Y (1984) Evidence from core-reflected shear waves for anisotropy in the Earth’s mantle. Nature 309(5970):695–698
Gao SS, Davis PM, Liu H, Slack PD, Rigor AW, Zorin YA, Mordvinova VV, Kozhevnikov VM, Logatchev NA (1997) SKS splitting beneath continental rift zones. J Geophys Res-Solid 102(B10):22781–22797
Gao Y, Hao P, Crampin S (2006) SWAS: a shear-wave analysis system for semi-automatic measurement of shear-wave splitting above small earthquakes. Phys Earth Planet Inter 159(1-2):71–89
Gao SS, Liu KH, Abdelsalam MG (2010) Seismic anisotropy beneath the Afar Depression and adjacent areas: implications for mantle flow. J Geophys Res-Solid 115(B12)
Gashawbeza EM, Klemperer SL, Nyblade AA, Walker KT, Keranen KM (2004) Shear-wave splitting in Ethiopia: Precambrian mantle anisotropy locally modified by Neogene rifting. Geophys Res Lett 31(18)
Gripp AE, Gordon RG (2002) Young tracks of hotspots and current plate velocities. Geophys J Int 150:321–361
Homuth B, Löbl U, Batte AG, Link K, Kasereka CM, Rümpker G (2016) Seismic anisotropy of the lithosphere/asthenosphere system beneath the Rwenzori region of the Albertine Rift. Int J Earth Sci 105:1681–1692
Kaneshima S, Silver PG (1995) Anisotropic loci in the mantle beneath central Peru. Phys Earth Planet Inter 88:257–272
Karato S-I, Jung H (2003) Effects of pressure on high-temperature dislocation creep in olivine. Philos Mag 83(3):401–414
Keir D, Kendall JM, Ebinger C, Stuart G (2005) Variations in late syn-rift melt alignment inferred from shear-wave splitting in crustal earthquakes beneath the Ethiopian rift. Geophys Res Lett 32(23)
Kendall J-M, Stuart G, Ebinger C, Bastow I, Keir D (2005) Magma-assisted rifting in Ethiopia. Nature 433(7022):146–148
Kennett B, Engdahl E (1991) Travel times for global earthquake location and phase identification. Geophys J Int 105(2):429–465
Koehn D, Aanyu K, Haines S, Sachau T (2008) Rift nucleation, rift propagation and the creation of basement micro-plates within active rifts. Tectonophysics 458(1-4):105–116
Koehn D, Lindenfeld M, Rümpker G, Aanyu K, Haines S, Passchier C, Sachau T (2010) Active transsection faults in rift transfer zones: evidence for complex stress fields and implications for crustal fragmentation processes in the western branch of the East African Rift. Int J Earth Sci 99(7):1633–1642
Lienert BR, Havskov J (1995) A computer program for locating earthquakes both locally and globally. Seismol Res Lett 66(5):26–36
Lindenfeld M, Rümpker G (2011) Detection of mantle earthquakes beneath the East African Rift. Geophys J Int 186(1):1–5
Lindenfeld M, Rümpker G, Link K, Koehn D, Batte A (2012) Fluid-triggered earthquake swarms in the Rwenzori region, East African Rift—evidence for rift initiation. Tectonophysics 566:95–104
Link K, Koehn D, Barth MG, Tiberindwa JV, Barifaijo E, Aanyu K, Foley SF (2010) Continuous cratonic crust between the Congo and Tanzania blocks in western Uganda. Int J Earth Sci 99(7):1559–1573
Liu KH, Gao SS, Gao Y, Wu J (2008) Shear wave splitting and mantle flow associated with the deflected Pacific slab beneath northeast Asia. J Geophys Res-Solid 113(B1)
Long MD, van der Hilst RD (2006) Shear wave splitting from local events beneath the Ryukyu arc: Trench-parallel anisotropy in the mantle wedge. Phys Earth Planet Inter 155(3-4):300–312
Meissner R, Rabbel W, Kern H (2006) Seismic lamination and anisotropy of the lower continental crust. Tectonophysics 416(1-4):81–99
Montalbetti JF, Kanasewich ER (1970) Enhancement of teleseismic body phases with a polarization filter. Geophys J Int 21(2):119–129
Ochmann, N., Lindenfeld, M., Barbirye, P., and Stadtler, C. (2007). Microearthquake survey at the Buranga geothermal prospect, western Uganda. Paper presented at the Proceedings of Thirty-Second Workshop on Geothermal Reservoir Engineering.
Rümpker G, Ryberg T, Bock G, Group DS (2003) Boundary-layer mantle flow under the Dead Sea transform fault inferred from seismic anisotropy. Nature 425(6957):497–501
Savage M (1999) Seismic anisotropy and mantle deformation: what have we learned from shear wave splitting? Rev Geophys 37(1):65–106
Savage MK, Sheehan AF, Lerner-Lam A (1996) Shear wave splitting across the Rocky Mountain Front. Geophys Res Lett 23(17):2267–2270
Schmeling H, Wallner H (2012) Magmatic lithospheric heating and weakening during continental rifting: A simple scaling law, a 2-D thermomechanical rifting model and the East African Rift System. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 13(8)
Sharma K, Bala R, Kumar A, Kumar R (2016) Matlab codes (Qbody) to study attenuation of seismic body-waves. Int J Adv Res 4(1):107–117
Shih XR, Schneider JF, Meyer RP (1991) Polarities of P and S waves, and shear wave splitting observed from the Bucaramanga Nest Columbia. J Geophys Res 96:12069–12082
Shimshoni M, Smith SW (1964) Seismic signal enhancement with three-component detectors. Geophysics 29(5):664–671
Silver PG, Chan WW (1991) Shear wave splitting and subcontinental mantle deformation. J Geophys Res 96:16429–16454
Silver PG, Savage M (1994) The interpretation of shear wave splitting parameters in the presence of two anisotropic layers. Geophys J Int 119:949–963
Sleep N, Ebinger C, Kendall J-M (2002) Deflection of mantle plume material by cratonic keels. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 199(1):135–150
Stamps DS, Calais E, Saria E, Hartnady C, Nocquet JM, Ebinger CJ, Fernandes RM (2008) A kinematic model for the East African Rift. Geophys Res Lett 35(5)
Stamps DS, Kreemer C, Fernandes R, Rajaonarison TA, Rambolamanana G (2020) Redefining East African Rift System kinematics. Geology 49. https://doi.org/10.1130/G47985.1
Tepp G, Ebinger C, Zal H, Gallacher R, Accardo N, Shillington D, Gaherty J, Keir D, Nyblade A, Mbogoni G (2018) Seismic anisotropy of the upper mantle below the Western rift, East Africa. J Geophys Res-Solid 123(7):5644–5660
Tommasi A, Tikoff B, Vauchez A (1999) Upper mantle tectonics: three-dimensional deformation, olivine crystallographic fabrics and seismic properties. Earth Planet Sci Lett 168(1-2):173–186
Vinnik L, Makeyeva L, Milev A, Usenko AY (1992) Global patterns of azimuthal anisotropy and deformations in the continental mantle. Geophys J Int 111(3):433–447
Waldhauser F, Ellsworth WL (2000) A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: Method and application to the northern Hayward fault, California. Bull Seismol Soc Am 90(6):1353–1368
Walker KT, Nyblade AA, Klemperer SL, Bokelmann GH, Owens TJ (2004) On the relationship between extension and anisotropy: Constraints from shear wave splitting across the East African Plateau. J Geophys Res-Solid 109(B8)
Wallner H, Schmeling H (2010) Rift induced delamination of mantle lithosphere and crustal uplift: a new mechanism for explaining Rwenzori Mountains’ extreme elevation? Int J Earth Sci 99(7):1511–1524
Wölbern I, Rümpker G, Schumann A, Muwanga A (2010) Crustal thinning beneath the Rwenzori region, Albertine rift, Uganda, from receiver-function analysis. Int J Earth Sci 99(7):1545–1557
Wölbern I, Rümpker G, Link K, Sodoudi F (2012) Melt infiltration of the lower lithosphere beneath the Tanzania craton and the Albertine rift inferred from S receiver functions. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 13(8)
Zhu L, Kanamori H (2000) Moho depth variation in southern California from teleseismic receiver functions. J Geophys Res-Solid 105(B2):2969–2980
Acknowledgments
We, the authors, strongly acknowledge the financial support offered by the German Research Council for the financial aid they offered towards the completion of this research. We also wish to thank the Uganda National Council of Science and Technology, Uganda Wildlife Authority for their unconditional cooperation. We wish to recognize Paul Wessel and Walter, H.F. Smith, authors for the Generic Mapping Tools used.
Funding
The authors wish to declare the following funding sources:
•The German Research Council (DFG)
•The German Academic Exchange Services (DAAD)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have been intensively involved in the data collection phase, drafting the manuscript, and revising it critically for important intellectual content.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1320 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Batte, A.G., Schumann, A. & Twesigomwe, E.M. Seismic anisotropy accrued by seven unusually deep local earthquakes (between 50 and 60 km) in the Albertine Rift: implications of asthenospheric melt upwelling. J Seismol 25, 921–936 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-021-10007-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-021-10007-2