Abstract
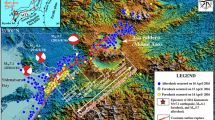
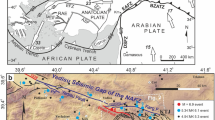
The early 2014 Cephalonia Island (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) earthquake sequence comprised two main shocks with almost the same magnitude (moment magnitude (Mw) 6.0) occurring successively within a short time (January 26 and February 3) and space (Paliki peninsula in Western Cephalonia) interval. Εach earthquake was induced by the rupture of a different pre-existing onshore active fault zone and produced different co-seismic surface rupture zones. Co-seismic surface rupture structures were predominantly strike-slip-related structures including V-shaped conjugate surface ruptures, dextral and sinistral strike-slip surface ruptures, restraining and releasing bends, Riedel structures (R, R′, P, T), small-scale bookshelf faulting, and flower structures. An extensional component was present across surface rupture zones resulting in ground openings (sinkholes), small-scale grabens, and co-seismic dip-slip (normal) displacements. A compressional component was also present across surface rupture zones resulting in co-seismic dip-slip (reverse) displacements. From the comparison of our field geological observations with already published surface deformation measurements by DInSAR Interferometry, it is concluded that there is a strong correlation among the surface rupture zones, the ruptured active fault zones, and the detected displacement discontinuities in Paliki peninsula.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubouin J (1959) Contribution a l’ étude géologique de la Grèce septentrionale, les confins de l’Epire et de la Thessalie. Ann Geol Pay Hellen 10:1–525
Aubouin J, Dercourt J (1962) Zone preapulienne, zone ionienne et zone du Gavrovo en Peloponncse occidentale. B Soc Geol Fr 4:785–794
Benekos G, Derdelakos K, Bountzouklis C, Kourkouli P, Parcharidis I (2015) Surface displacements of the 2014 Cephalonia (Greece) earthquake using high resolution SAR interferometry. Earth Sci Inform. doi:10.1007/s12145-015-0205-7
BP Co (1971) The geological results of petroleum exploration in Western Greece. Inst Geol Subsurf Res Athen 10:73
BP Co, Bergmann H, Braune K, Dremel G, Hatzopoulos Ε, Hug E, Uliczny E (1985) Geological map of Greece, Cephalonia Island (northern and southern part) sheet, scale 1:50000. Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Athens, Greece
Georgiadou-Dikaioulia E (1967) The Neogene of Kephallinia. PhD Thesis, University of Athens
Hollenstein C, Müller MD, Geiger A, Kahle H-G (2008) Crustal motion and deformation in Greece from a decade of GPS measurements 1993–2003. Tectonophysics 449:17–40
Karakostas Ch, Lekidis V, Makra K, Margaris B, Morfidis K, Papaioannou Ch, Rovithis M, Salonikios T, Savvaidis A, Theodoulidis N (2014a) The earthquake of 26/1/2014 (M6.1) in Cephalonia (Greece): strong ground motion, soil behaviour and response of structures (preliminary report). Earthquake Planning and Protection Organization - Institute of Engineering Seismology and Earthquake Engineering. Thessaloniki, Greece. http://www.slideshare.net/itsak-eppo/20140126-kefaloniaeq-report-en Accessed April 2014
Karakostas Ch, Lekidis V, Makra K, Margaris B, Morfidis K, Papaioannou Ch, Rovithis M, Salonikios T, Savvaidis A, Theodoulidis N (2014b) Strong ground motion of the February 3, 2014 (M6.0) Cephalonia earthquake: effect on soil and built environment in combination with the January 26, 2014 (M6.1) event. Earthquake Planning and Protection Organization - Institute of Engineering Seismology and Earthquake Engineering. Thessaloniki, Greece. http://www.slideshare.net/itsak-eppo/20140203-kefaloniaeq-report-en Accessed April 2014
Lagios E, Sakkas V, Papadimitriou P, Damiata BN, Parcharidis I, Chousianitis K, Vassilopoulou S (2007) Crustal deformation in the Central Ionian Islands (Greece): results from DGPS and DInSAR analyses (1995–2006). Tectonophysics 444:119–145
Lekkas E (1996) Neotectonic Map of Greece. Cephalonia—Ithaki sheet, scale 1:100.000. University of Athens
Lekkas E, Mavroulis S (2015) Earthquake environmental effects and ESI 2007 seismic intensities of the early 2014 Cephalonia (Ionian Sea, western Greece) earthquakes (January 26 and February 3, Mw 6.0). Nat Hazards. doi:10.1007/s11069-015-1791-x
Lekkas E, Kolyva M, Antonopoulos G, Kopanas I (1997) Earthquakes in Zakynthos: interpretation attempt of earthquakes descriptions and correlation with the existing geological structure. Ann Geol Pay Hellen, 1, XXXVII:1033–1073
Lekkas E, Danamos G, Mavrikas G (2001) Geological structure and evolution of Cefallonia and Ithaki Islands. Bull Geol Soc Greece XXXIV/1:11–17
Lekkas E, Kyratzi A, Ganas A, Mavroulis S, Alexoudi V, Avramea V, Gkountromichou Chr, Ioakeimidou A, Kerpelis Pl, Kourou A, Lalechos S, Manousaki M, Bakas K, Panoutsopoulou M (2014a) The earthquakes (Mw 6.0) on January 26th and February 3rd, 2014: the seismotectonic and geodynamic setting as parameters controlling structural damage. In: Earthquake Planning and Protection Organization and Technical Chamber of Greece (Eds), Proceedings of the Conference “The 2014 Cephalonia earthquakes”, June 6th, 2014, Argostoli, Cephalonia, 5
Lekkas E, Mavroulis S, Alexoudi V (2014b) The geodynamic and seismotectonic setting of Cephalonia (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) as factor controlling the distribution of earthquake environmental effects and structural damage induced by early 2014 earthquakes (January 26th and February 3rd, Mw 6.0). In: Proceedings of the International Workshop on Seismic Hazard and Earthquake Engineering, September 24–25, 2014, Cephalonia, Greece, 5–6
Mandl G (1987) Tectonic deformation by rotating parallel faults: the “bookshelf” mechanism. Tectonophysics 141:277–316
Papadopoulos GA, Karastathis VK, Koukouvelas I, Sachpazi M, Baskoutas G, Agalos A, Daskalaki E, Minadakis G, Moshou A, Mouzakiotis A, Orfanogiannaki K, Papageorgiou A, Spanos D, Triantafyllou I (2014) The Cephalonia, Ionian Sea (Greece), sequence of strong earthquakes of January–February 2014: a first report. Res Geophys. doi:10.4081/rg.2014.5441
Papazachos BC, Papazachou CB (1989) The earthquakes of Greece. Ziti Publ., Thessaloniki, Greece, pp 356. (in Greek)
Papazachos BC, Papazachou CB (1997) The earthquakes of Greece. Ziti Publ., Thessaloniki, Greece, pp 304
Papazachos BC, Papazachou CB (2003) The earthquakes of Greece. Ziti Publ., Thessaloniki, Greece, p 286. (in Greek)
Renz C (1955) Die vorneogene Stratigraphie der normalsedimentaren Formationen Griechenlands. - Inst Geol subsurf Res, Athènes, p 637
Royden LH, Papanikolaou DJ (2011) Slab segmentation and late Cenozoic disruption of the Hellenic arc. Geochem Geophys Geosyst . doi:10.1029/2010GC003280
Sorel D (1976) Etude Néotectonique des îles Ioniennes de Céphalonie et de Zante et de l’ Elide Occidentale (Grèce). Thèse 3e cycle, Orsay, Université Paris Sud, p 200
Stavropoulos A (1988) Geological map of Greece, Ithaki-Atokos sheet, scale 1:50000, Institute of Geology and Mineral Exploration, Athens, Greece
Underhill JR (1989) Late cenozoic deformation of the Hellenide foreland, western Greece. Bull Geol Soc Am 101:613–634
Valkaniotis S, Ganas A, Papathanassiou G, Papanikolaou M (2014) Field observations of geological effects triggered by the January–February 2014 Cephalonia (Ionian Sea, Greece) earthquakes. Tectonophysics 630:150–157. doi:10.1016/j.tecto.2014.05.012
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the two anonymous reviewers whose suggestions and comments improved the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lekkas, E.L., Mavroulis, S.D. Fault zones ruptured during the early 2014 Cephalonia Island (Ionian Sea, Western Greece) earthquakes (January 26 and February 3, Mw 6.0) based on the associated co-seismic surface ruptures. J Seismol 20, 63–78 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-015-9510-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10950-015-9510-3