Abstract
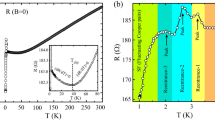
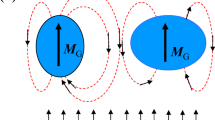
Superconducting non-granular quasi-one-dimensional (1D) NbN nanowires and relatively wide granular wires of the same material exhibit similar magneto-transport behavior arising from different physical origin. Both types of wires exhibit a broad transition into the superconducting state with non-vanishing resistance well below Tc, and negative magnetoresistance (nMR) decreasing in magnitude with temperature. A distinct behavior between the two wires is revealed in their response to increasing current. In V-I measurements, the 1D wires exhibit finite initial slope, i.e., zero critical current, at all temperatures below the transition, while the granular wires exhibit a nonzero critical current that depends on temperature. Also, the two wires differ from each other in the current dependence of the nMR. In the 1D wires, at low temperature, the nMR decreases monotonically with the current, while in the granular wires the nMR initially increases with the current. The different current response of the two types of wires indicates the different physical origin of their behavior: That of the 1D wires is attributed to fluctuations of the order parameter, while that of the granular wires reflects the response of an inhomogeneous chain of Josephson junctions.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Langer, J.S., Ambegaokar, V.: Intrinsic resistive transition in narrow superconducting channels. Phys. Rev. 164(2), 498–510 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.164.498
McCumber, D.E., Halperin, B.I.: Time scale of intrinsic resistive fluctuations in thin superconducting wires. Phys. Rev. B 1(3), 1054–1070 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.1.1054
Giordano, N.: Evidence for macroscopic quantum tunneling in one-dimensional superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 61(18), 2137–2140 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.61.2137
Xiong, P., Herzog, A.V., Dynes, R.C.: Negative magnetoresistance in homogeneous amorphous superconducting Pb wires. Phys. Rev. Lett. 78(5), 927–930 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.927
Lau, C.N., Markovic, N., Bockrath, M., Bezryadin, A., Tinkham, M.: Quantum phase slips in superconducting nanowires. Phys Rev Lett 87(21), 217003–217004 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.87.217003
Tian, M., et al.: Dissipation in quasi-one-dimensional superconducting single-crystal Sn nanowires. Phys Rev B Condens Matter Mater Phys 71(10),(2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.71.104521
Duan, J.-M.: Quantum Decay of One-Dimensional Supercurrent: Role of Electromagnetic Field. (1995)
Voss, J.N., et al.: Eliminating quantum phase slips in superconducting nanowires. ACS Nano 15(3), 4108–4114 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c08721
Tian, M., Kumar, N., Chan, M.H.W., Mallouk, T.E.: Evidence of local superconductivity in granular Bi nanowires fabricated by electrodeposition. Phys Rev B Condens Matter Mater Phys 78(4),(2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.78.045417
Cirillo, C., et al.: Quantum phase slips in superconducting Nb nanowire networks deposited on self-assembled Si templates. Appl Phys Lett 101(17),(2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4764066
Trezza, M., Cirillo, C., Sabatino, P., Carapella, G., Prischepa, S.L., Attanasio, C.: Nonlinear current-voltage characteristics due to quantum tunneling of phase slips in superconducting Nb nanowire networks. Appl Phys Lett 103(25),(2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4851240
Levi, D., Shaulov, A., Koren, G., Yeshurun, Y.: Magnetoresistance anomalies in ultra-thin granular YBa2Cu 3O7-δ bridges. Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications 495, 39–43 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.2013.07.012
Shapiro, B.Y., Shapiro, I., Levi, D., Shaulov, A., Yeshurun, Y.: Negative magnetoresistance slope in superconducting granular films. Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications 501, 51–54 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.2014.04.001
Levi, D., Shaulov, A., Frydman, A., Koren, G., Shapiro, B.Y., Yeshurun, Y.: Periodic negative magnetoresistance in granular YBa2Cu 3O7-δ nanowires. Epl 101(6),(2013). https://doi.org/10.1209/0295-5075/101/67005
Arutyunov, K.Y., Golubev, D.S., Zaikin, A.D.: Superconductivity in one dimension. Phys. Rep. 464(1–2), 1–70 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physrep.2008.04.009
Tian, M., Kumar, N., Xu, S., Wang, J., Kurtz, J.S., Chan, M.H.W.: Suppression of superconductivity in zinc nanowires by bulk superconductors. Phys. Rev. Lett. 95(7), 4–7 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.076802
Patel, U., et al.: Magnetoresistance oscillations in superconducting granular niobium nitride nanowires. Phys Rev B Condens Matter Mater Phys 80(1),(2009). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.80.012504
Shani, L., et al.: DNA origami based superconducting nanowires. AIP Adv 11(1),(2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0029781
Sofer, Z., Shaulov, A., Yeshurun, Y.: Current dependence of the negative magnetoresistance in superconducting NbN nanowires. Sci. Rep. 12(1), 22027 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-26475-6
Lehtinen, J.S., Kemppinen, A., Mykkänen, E., Prunnila, M., Manninen, A.J.: Superconducting MoSi nanowires. Supercond Sci Technol 31(1),(2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6668/aa954b
Baumans, X.D.A., et al.: Thermal and quantum depletion of superconductivity in narrow junctions created by controlled electromigration. Nat. Commun. 7, 3–10 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10560
Masuda, K., et al.: Thermal and quantum phase slips in niobium-nitride nanowires based on suspended carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett 108(22),(2016). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4952721
Zgirski, M., Riikonen, K.P., Touboltsev, V., Arutyunov, K.Y.: Quantum fluctuations in ultranarrow superconducting aluminum nanowires. Phys Rev B Condens Matter Mater Phys 77(5), 1–6 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.77.054508
Arutyunov, K.Y.: Negative magnetoresistance of ultra-narrow superconducting nanowires in the resistive state. Physica C: Superconductivity and its Applications 468(4), 272–275 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physc.2007.08.027
Tinkham, M.: Introduction to Superconductivity, 2nd edn., no. 207. Dover Publications. (2004)
Newbower, R.S., Beasley, M.R., Tinkham, M.: Fluctuation effects on the superconducting transition of tin whisker crystals. Phys. Rev. B 5(3), 864–868 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.5.864
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the help of Gili Cohen-Taguri in GIXRD measurements. Thanks are also extended to Avital Fried and Lidor Geri for help in fabricating the NbN films.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors conceived the concept and designed the experiment, analyzed the data and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sofer, Z., Shaulov, A., Sharoni, A. et al. Probing the Difference Between Amorphous and Granular Superconducting Nanowires in Transport Measurements. J Supercond Nov Magn 37, 729–735 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-024-06719-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-024-06719-4