Abstract
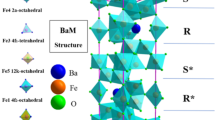
Praseodymium (Pr)–aluminum (Al)-co-doped M-type barium ferrite with Ba0.85Pr0.15Fe12-xAlxO19 (x = 0.0–1.0) was prepared by combining solid-phase sintering with high-energy ball milling. The samples were characterized using a thermogravimetric analyzer, X-ray diffractometer, field emission scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and vibrating sample magnetometer. Thermogravimetric analysis indicated that M-type barium ferrite was formed at 1250 °C. X-ray diffraction patterns showed that Al doping did not destroy the crystal structure of barium ferrite. Field emission scanning electron microscopy showed that the samples had a hexagonal crystal structure. The wave numbers of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy in the 597–607 and 452–459 cm−1 bands represent tetrahedral and octahedral clusters, respectively. With the increase in the amount of Al doping (x) from 0.0 to 1.0, the saturation magnetization (Ms) and residual magnetization (Mr) decreased continuously, and the magnetic anisotropy field (Ha) and coercivity (Hc) increased significantly.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, W., et al.: Structural, optical, dielectric, and magnetic properties of Sr0.7La0.3Zn0.3Fe11.7-xAlxO19 hexaferrite synthesized by the solid-state reaction method. J. Solid State Chem. 306, (2022)
Wang, Z., et al.: Preparation and magnetic properties of La-substituted strontium hexaferrite by microwave-assisted sol-gel method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 29, 981–984 (2016)
Schultz, L., Krabbes, G., Fuchs, G., Pfeiffer, W., Müller, K.: Superconducting permanent magnets and their application in magnetic levitation. Int. J. Mater. Res. 93(10), (2022)
Li, Q., et al.: Preparation of barium ferrite microtubules and the effect of the La-dope onto the property of barium ferrite microtubules. J. Inorg. Chem. 25(02), 312–316 (2009)
Ayon, S.A., Jamal, M., Nahin, A.M., Islam, M.S., Nishat, S.S., Sharif, A.: Enhanced dielectric stability and coercivity of band gap tuned Ba-Al Co-doped bismuth ferrite: an experimental and DFT+U investigation. J. Ceramics Int. 48(3), (2022)
Yi, S.: Study on the mechanism of high energy ball milling-microwave synergistic effect on mineral phase reconstruction and properties of barium ferrite. Inner Mongolia Univ. Sci, Technol (2021)
Kim, C.S., Leeand, S.W., An, S.Y.: Mössbauer studies of BaFe11.9Mn0.1O19 by a sol–gel method. J. Appl. Phys. 87, 6244 (2000)
Yang, Y., et al.: A study on structural, spectral, and magnetic properties of Pr-Bi co-doped M-type barium-strontium hexaferrites via the solid-state reaction method. Appl. Phys. A. 124, 12 (2018)
Zhang, W., et al.: Influence of La-Nb co-substituted Sr ferrite on microstructure, spectrum and magnetic properties of hexaferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 871, (2021)
Gu, Y., et al.: Structure and magnetic properties of M-type barium ferrite doped with lanthanum ion. Rare Earth. 33, 70–74 (2012)
Li , P., et al.: Structures, spectra, morphologies, and magnetic properties of Pr3+-substituted Ba hexaferrites. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 8(5), (2022)
Xu, T., et al.: Enhanced magnetic and electrical properties in cobalt ferrite ceramics by doping trace amount of aluminum. Rare metal Materials and Engineering. 42(S1), 197–200 (2013)
Guo, R., et al.: Influence of doping trace aluminum on structure and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering. 40(S1), 379–382 (2011)
Li, A., et al.: Effect of Al2O3 addition on the high permeability MnZn ferrites. J. Jilin University (Science Edition) 51(01), 132–134 (2013)
Godara, S.K., Kaur, V., Narang, S.B., Singh, G., Singh, M., Bhadu, G.R., Chaudhari, J.C., Babu, P.D., Sood, A.K.: Tailoring the magnetic properties of M-type strontium ferrite with synergistic effect of co-substitution and calcinations temperature. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 9(2), (2021)
Pornpen, M., Wirunya, K., Nattamon, K., Pongsakorn, J.: Study the effect of the substitution of Ba with Pr in barium ferrite powder on magnetic properties. Advanced Materials Research. 3482, 1025–1026 (2014)
Yi, S., et al.: Infrared fitting spectral analysis of barium ferrite precursor in high energy ball milling process. Spect. Spectral Analysis. 42(05), 1634–1641 (2022)
Olivares-Lugo, L.I., Sánchez-De, J.F., Rosales-González, O., Cortés-Escobedo, C.A., Barba-Pingarrón, A., Bolarín-Miró, A.M., Physica, B.: Evidence of magnetodielectric coupling in bismuth doped lanthanum ferrite obtained by high-energy ball milling. Phys. Cond. Matter. 643, (2022)
Semaida, A.M., Darwish, M.A., Karpenkov, D.Y., Trukhanov, A.V., Kostishyn, V.G., Korovushkin, V.V., Menushenkov, V.P., Savchenko, A.G.: Correlation between composition and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19/Co nanocomposite synthesized by the high energy ball-milling process key engineering materials. 6323, (2022)
Yi, S., et al.: Study on preparation of barium ferrite by mechanical alloying combined with microwave sintering. Nonferrous Metal Eng. 12, 22–27 (2022)
He, Q., et al.: Formation and properties of BaxFe3-xO4 with spinel structure by mechanochemical reaction of α-Fe2O3 and BaCO3. J. Alloys Compd. 486, 246–249 (2009)
Gao, J., et al.: Structure and microwave absorption properties of rare earth Gd3+ doped cobalt ferrite. Rare metal Materials and Engineering. 49(07), 2524–2529 (2020)
Xie, D., et al.: Preparation and XRD analysis of M-type barium hexagonal ferrit. Phys. Test. 3, 22–23 (2002)
Wang, C., et al.: ChemInform abstract: crystal structure of Sr6Y2Al4O15: XRD refinements and first-principle calculations. ChemInform 43, 40 (2012)
Liu, X.: Applications of Rietveld method in inorganic materials. Xiamen university. (2006)
El Sbakhy, F.S., et al.: Structural, spectral, Rietveld refinement and cation distribution of nanoferrite NiFe2O4 doped with Mn. Eur. Phys. J. Plus. 136, 5 (2021)
Qiu, H., et al.: Influence of Al3+ and Co2+ substitution on the microstructure and magnetic properties of NiCuZn ferrite material. Magnet. Mater. Devices. 50(05), (2019)
Gayathri, S., Jesurani, S., Ashok, K., John, P.A.: An investigation on the structural, spectral and magnetic properties of Nb-Zn doped Barium strontium hexaferrite nanocomposite powder synthesized by sol-gel method. Int. J. Adv. Res. (IJAR). 6(5), (2018)
Tang, J., et al.: Structure and magnetic analyses of hexaferrite Sr1-xLaxFe22+Fe163+O27 prepared via the solid-state reaction. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30(1), (2019)
Yang, Y., et al.: Structural, spectral, magnetic, and electrical properties of Gd-Co-co-substituted M-type Ca-Sr hexaferrites synthesized by the ceramic method. Appl. Phys. A. 125(1), (2019)
Li, Y., et al.: Fabrication of M-type ferrites with high La-Co concentration through Ca2+ doping. J. Alloys Compd. 734, (2018)
Yang, Y., et al.: Influence of Nd-NbZn co-substitution on structural, spectral and magnetic properties of M-type calcium-strontium hexaferrites Ca0.4Sr0.6-xNdxFe12.0-x(Nb0.5Zn0.5)xO19. J. Alloys Compd. 765, (2018)
Han, P., et al.: Application of Peakfit in FT-IR spectrum fitting and chemical composition analysis of M-type ferrite. J. Shenyang Institute of Technology. 40(06), 66–70 (2021)
Zhang, W., et al.: Structure, spectra, morphology, and magnetic properties of Nb5+ ion-substituted Sr hexaferrites. Magnetochemistry. 8(5), (2022)
Wen, L., Liang, W., Zhang, Z.: Mineral infrared spectroscopy. Chongqing University Press, Chongqing (1988)
Weng, S., Xu, Y.: Fourier Transform infrared spectrum analysis. Chemical Industry Press, Beijing (2016)
Liu, M., et al.: Research on densification and magnetic properties of LaCo-substituted M-type barium Ferrit. J. Synthetic Crystals. 44(06), 1485–1489 (2015)
Vinaykumar, R., Mazumder, R., Bera, J.: Characterization of SrCo1.5Ti1.5Fe9O19 hexagonal ferrite synthesized by sol-gel combustion and solid state route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 429, 359–366(2017)
Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y., El Sayed, H.S., Baykal, A.: Structural and magnetic properties of Ce-Y substituted strontium nanohexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 44, 12511–12519 (2018)
Zhao, F., et al.: Effect of calcination technology and rare earth doping on the micro/nano structure of barium ferrite. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 42(S1), 60–63 (2013)
Du, Y., et al.: Structural and magnetic properties of Sr0.8La0.2Co0.2Fe11.8-xAlxO19 hexaferrite particles prepared via sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 469, (2018)
Alam, R.S., Moradi, M., Rostami, M., Nikmanesh, H., Moayedi, R., Bai, Y.: Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of doped Ba-hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 381, 1–9 (2015)
Almessiere, M.A., Slimani, Y., Baykal, A.: Impact of Nd-Zn co-substitution on microstructure and magnetic properties of SrFe12O19 nanohexaferrite. Ceram. Int. 45(1), 963–969 (2019)
Topal, U., Ozkan, H., Sozeri, H.: Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystaline BaFe12O19 obtained at 850 °C by using ammonium nitrate melt. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 284, 416–422 (2004)
Wang, C., et al.: Microstructure and electromagnetic properties of Cu-Ti Co-doped M-type BaFe12O19 hexaferrites. Rare Metal Mater. Eng. 47(S1), 179–184 (2018)
Guo, R., et al.: Study on magnetic properties of different rare earth doped M-type barium ferrite ultrafine powders. Funct. Mater. 605(06), 598–599 (2001)
Jia, P., et al.: Study on preparation and properties of Co-Cu Co-doped M-Type barium ferrites. J. Inner Mongolia Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.). 52(06), 617–623 (2021)
Chen, H., et al.: Synthesis and characterization of Ti-Mn-Cu substituted M-Type barium ferrite. Chemistry and Adhesion. 04, 248–250 (2007)
Ma, X.: Preparation and magnetic properties of high coercivity M-type ferrite powders. Lanzhou University. (2016)
Sun, Y., et al.: Effect of grain size distribution on coercivity in nanometer materials. Journal of Shandong University of Technology (Natural Science Edition). 24(03), 17–19 (2010)
Manaf, A., Buckley, R.A., Davies, H.A., Leonowicz, M.: Enhanced magnetic properties in rapidly solidified Nd-Fe-B based alloys. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 101(1), (1991)
Wei, F.L., Lu, M., Yang, Z.: The temperature dependence of magnetic properties of Zn-Ti substituted Ba-ferrite particles for magnetic recording. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 191, 249–253 (1999)
Funding
The study received funding support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 51764045), Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology Plan Project (grant no. 2021GG0438), and Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation (2020MS05048, 2020BS05029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Pengwei Li: conceptualization, methodology, software, investigation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Ji Li: resources, supervision. Yonglun Wang: methodology, software. Kai Yao: investigation, validation. Shuo Shan: validation. Xing Suo: validation. Saiai Ma: validation.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Li, J., Wang, Y. et al. Structural, Spectral, and Magnetic Properties of Praseodymium–Aluminum-Co-doped M-Type Barium Hexaferrites. J Supercond Nov Magn 36, 327–341 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06445-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-022-06445-9