Abstract
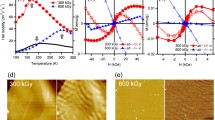
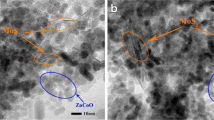
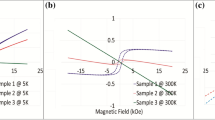
MoS2 is a typical two-dimensional material with promising optical and electrical properties. The realization of ferromagnetism in MoS2 is important for its applications in semiconductor spintronics. A facile technique should be developed to induce the ferromagnetism in MoS2, and the possible extrinsic contribution should be avoided. In this paper, flower-like MoS2 nanostructures were fabricated by the hydrothermal method. X-ray diffraction spectra show the 1 T/2H mixed phases of as-prepared MoS2 nanostructures, which changes to pure 2H structure after the O plasma treatment. Raman spectra confirm the existence of Mo–O bonding, which is further confirmed by the X-ray photoelectron spectra after the O plasma treatment. Magnetization measurements at 300 K show the weak ferromagnetism in the as-prepared MoS2, with saturated ferromagnetic magnetization of 0.0012 emu/g. After the O plasma treatment, the weak ferromagnetism is strongly enhanced with saturated ferromagnetic magnetization of 0.0343 emu/g. First principle calculation has been performed to disclose the possible origin of ferromagnetism. Significant overlapping between the density of states of O and Mo, or O and S has been observed. The magnetic contribution from Mo and S is negligible, while O takes the main role for the enhanced ferromagnetism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidt, G., Ferrand, D., Molenkamp, L.W., Filip, A.T., van Wees, B.J.: Phys. Rev. B 62, R4790 (2000)
Ohno, H.: Science 281, 951 (1998)
Coey, J.M.D., Venkatesan, M., Fitzgerald, C.B.: Nat. Mater. 4, 173 (2005)
Barla, A., Schmerber, G., Beaurepaire, E., Dinia, A., Bieber, H., Colis, S., Scheurer, F., Kappler, J.-P., Imperia, P., Nolting, F., Wilhelm, F., Rogalev, A., Müller, D., Grob, J.J.: Phys. Rev. B 76, 125201 (2007)
Novoselov, K.S., Fal′ko, V.I., Colombo, L., Gellert, P.R., Schwab, M.G., Kim, K.: Nature 490, 192 (2012)
Wang, Y., Ou, J.Z., Balendhran, S., Chrimes, A.F., Mortazavi, M., Yao, D.D., Field, M.R., Latham, K., Bansal, V., Friend, J.R., Zhuiykov, S., Medhekar, N.V., Strano, M.S., Kalantar-zadeh, K.: ACS Nano 7, 10083 (2013)
Lin, J., Zhong, J., Zhong, S., Li, H., Zhang, H., Chen, W.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 103 (2013)
Andriots, A.N., Menon, M.: Phys. Rev. B 90 (2014)
Wang, J., Sun, F., Yang, S., Li, Y., Zhao, C., Xu, M., Zhang, Y., Zeng, H.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 109 (2016)
Hu, A., Wang, L., Xiao, W., Xiao, G., Rong, Q.: Comp. Mater. Sci. 107, 72 (2015)
Chen, N., Hu, C., Luo, X., Hong, A., Yu, T., Yuan, C.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 116, 073102 (2020)
Wang, B., Zhang, D., Wang, H., Zhao, H., Liu, R., Li, Q., Zhou, S., Du, J., Xu, Q.: AIP Adv. 10, 015243 (2020)
Saber, M.R., Khabiri, G., Maarouf, A.A., Ulbricht, M., Khalil, A.S.G.: RSC Adv. 8, 26364 (2018)
Wu, M., Zhan, J., Wu, K., Li, Z., Wang, L., Geng, B., Wang, L., Pan, D.: J. Mater. Chem. A 5, 14061 (2017)
Pradhan, G., Sharma, A.K.: Appl. Surf. Sci. 479, 1236 (2019)
Chae, S., Chae, S.S., Choi, M., Park, H., Chang, H., Lee, J.: and T. Il Lee, Nano Energy 56, 65 (2019)
Liu, Q., Li, X., He, Q., Khalil, A., Liu, D., Xiang, T., Wu, X., Song, L.: Small 11, 5556 (2015)
Wang, X., Ding, W., Li, H., Li, H., Zhu, S., Zhu, X., Dai, J., Sheng, Z., Wang, H., Zhu, X., Sun, Y., Dou, S.X.: J. Mater. Chem. A 7, 19152 (2019)
Zheng, Z., Cong, S., Gong, W., Xuan, J., Li, G., Lu, W., Geng, F., Zhao, Z.: Nat. Commun. 8, 1993 (2017)
Jiao, J., Du, K., Wang, Y., Sun, P., Zhao, H., Tang, P., Fan, Q., Tian, H., Li, Q., Xu, Q.: Mater. Chem. Phys. 240, 122169 (2020)
Li, B., Jiang, L., Li, X., Ran, P., Zuo, P., Wang, A., Qu, L., Zhao, Y., Chen g, Z., Lu, Y.: Sci. Rep. 7, 11182 (2017)
Zhao, Q., Zhai, C., Lu, Q., Zhang, M.: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 21, 232 (2019)
Ding, X., Cui, X., Sohail, A., Murmu, P.P., Kennedy, J., Bao, N., Ding, J., Liu, R., Wang, L., Chu, X., Vinu, A., Ringer, S.P., Yi, J.: Adv. Quantum Technol. 4, 2000093 (2021)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, W., Li, R., Wang, B. et al. O Plasma Treatment Enhanced Room Temperature Ferromagnetism in MoS2. J Supercond Nov Magn 35, 501–506 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-06083-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-06083-7