Abstract
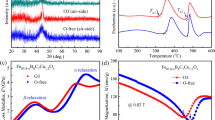
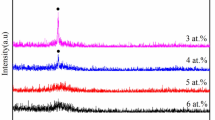
Low amorphous forming ability (AFA) and weak thermal stability become the main obstacles in adjusting α-Fe crystallization behaviors and fabricating uniform α-Fe grains with nanosize and high density–inserted amorphous matrix, which effectively improve magnetic properties in Fe-rich amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys, as Fe content is over 85 at.%. In this study, the role of micro-alloyed P has been investigated in novel Fe-rich Fe86B13-xPxCu0.4Hf0.6 alloys; its relationship of appropriate micro-alloyed P and its positive role on controlling crystallization and optimizing magnetic properties have been researched systemically. Minor P less than x = 1.5 is beneficial for optimizing AFA and thermal stability and obtaining the ΔTx value over 140 K; different P also guide the discrepant crystallization behaviors and result in easily precipitating concomitant Hf3P2 phase during α-Fe crystallization. Ultimately, it has been founded that the Fe86B12.5P0.5Cu0.4Hf0.6 ribbons with entire amorphous structure become easier to be controlled for fabricating the uniform α-Fe/amorphous dual-phase structure; its Bs (saturation magnetization tensity) value reaches to the maximum of about 1.91 T as crystallized near Tp1. Meanwhile, the related Hc (coercivity) value can be decreased effectively from 17.1 to 3.1 A/m after an auxiliary annealing process was operated applying the magnetic field of 0.1 T. These novel-type Fe86B13-xPxCu0.4Hf0.6 alloys with uniform α-Fe/amorphous dual-phase structure show an excellent soft magnetic property and exhibit competitive advantages with the high Bs-oriented Si-steels.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sahingoz, R., Erol, M., Gibbs, M.R.J.: Observation of changing of magnetic properties and microstructure of metallic glass Fe78Si9B13 with annealing. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 271, 74–78 (2004)
Chau, N., Luong, N.H., Chien, N.X. et al.: Influence of P substitution for B on the structure and properties of nanocrystalline Fe73.5Si15.5Nb3Cu1B7-xPx alloys. Phys. B. 327, 241–243 (2003)
Kubota, T., Makino, A., Inoue, A.: Low core loss of Fe85Si2B8P4Cu1 nanocrystalline alloys with high Bs and B800. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, S416–S419 (2011)
Dan, Z.H., Qin, F.X., Zhang, Y. et al.: Mechanism of active dissolution of nanocrystalline Fe-Si-B-P-Cu soft magnetic alloys. Mater. Charact. 121, 9–16 (2016)
Takenaka, K., Setyawan, A.D., Sharma, P. et al.: Industrialization of nanocrystalline Fe-Si-B-P-Cu alloys for high magnetic flux density cores. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 479–483 (2016)
Zhai, X.B., Wang, Y.G., Zhu, L. et al.: Effect of heating rate on atom migration, phase structure and magnetic properties of the Fe82Si2B11P4Cu1 alloy. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 499, 337–343 (2018)
Li, X.L., Liu, J.B., Qu, C.G. et al.: Effect of Nb on the precipitation of α-Fe, glass forming ability and magnetic properties of Fe85B10P5 alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 694, 643–646 (2017)
Silveyra, J.M., Illeková, E.: Effect of air annealing on Fe-Si-B-M-Cu (M=Nb, Mo) alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 610, 180–183 (2014)
Ohta, M., Yoshizawa, Y.: High Bs nanocrystalline Fe84-x-yCuxNbySi4B12 alloys (x =0.0–1.4, y =0.0–2.5). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 2220–2224 (2009)
Wang, Y.C., Zhang, Y., Makino, A. et al.: First principle study on the Si effect in the Fe-based soft magnetic nano-crystalline alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 730, 196–200 (2018)
Pradeep, K.G., Herzer, G., Raabe, D.: Atomic scale study of Cu clustering and pseudo-homogeneous Fe-Si nanocrystallization in soft magnetic FeSiNbB(Cu) alloys. Ultramicroscopy. 159, 285–291 (2015)
Dan, Z.H., Zhang, Y., Takeuchi, A. et al.: Effect of substitution of Cu by Au and Ag on nanocrystallization behavior of Fe83.3Si4B8P4Cu0.7 soft magnetic alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 683, 263–270 (2016)
Zhou, L., Wang, G.T., Yuan, H., Yang, Y.Z.: Effect of Hf addition on the glass forming ability, thermal and magnetic properties in the (Fe86B13Cu1)100-xHfx alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 501, 167–172 (2018)
Parsons, R., Li, Z., Suzuki, K.: Nanocrystalline soft magnetic materials with a saturation magnetization greater than 2 T. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 485, 180–186 (2019)
Li, X.L., Liu, J.B., Qu, C.R. et al.: Effects of Nb the precipitation of α-Fe, glass forming ability and magnetic properties of Fe85B10P5 alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 694, 643–646 (2017)
Wang, G.T., Zhou, L., Yuan, H. et al.: Hf optimizes the glass forming ability and controls the crystallization behavior in Fe-rich Fe-B-Cu alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 527, 740–747 (2020)
Xu, J., Yang, Y.Z., Yan, Q.S. et al.: Effects of the substitution of Si by P on the crystallization behavior, soft magnetic properties and bending ductility of FeSiBCuPC alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 816, 534–532 (2020)
Xu, J., Yang, Y.Z., Yan, Q.S. et al.: Effect of microalloying on crystallization behavior, magnetic properties and bending ductility of high Fe content FeSiBCuPC alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 777, 499–505 (2019)
Fan, X.D., Zhang, T., Jiang, M.F. et al.: Synthesis of novel FeSiBPCCu alloys with high amorphous forming ability and good soft magnetic properties. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 503–504, 36–43 (2019)
Fu, C.Q., Xu, L.J., Dan, Z.H.: Annealing effect of amorphous Fe-Si-B-P-Cu precursors on microstructure evolution and redox behavior of nanoporous counterparts. J. Alloy. Compd. 726, 810–819 (2017)
Wu, Z.Y., Fan, X.A., Li, G.Q. et al.: Evolution from amorphous to nanocrystalline and corresponding magnetic properties of Fe-Si-B-Cu-Nb alloys by melt-spinning and spark plasma sintering. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 187, 61–66 (2014)
Xu, J., Yang, Y.Z., Li, W. et al.: Effect of P addition on glass forming ability and soft magnetic properties of melt-spun FeSiBCuC alloy ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 417, 291–293 (2016)
Li, Z.Z., Wang, A., Chang, C.T. et al.: FeSiBPNbCu alloys with high glass-forming ability and good soft magnetic properties. Intermetallics. 54, 225–231 (2014)
Quyang, G.Y., Chen, X., Liang, Y.F. et al.: Review of Fe-6.5 wt%Si high silicon-a promising soft magnetic material for sub-kHz application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 481, 234–250 (2019)
Jafari, S., Beitollahi, A., Yekta, B.E. et al.: Atom probe analysis and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Fe84.3Si4B8P3Cu0.7. J. Alloys Compd. 674, 136–144 (2016)
Bayri, N., Izgi, T., Gencer, H. et al.: Crystallization kinetic of Fe73.5-xMnxCu1Nb3Si13.5B9 (x = 0, 1, 3, 5, 9) amorphous alloys. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 355, 12–16 (2009)
Li, W., Xie, C.X., Yang, Y.Z. et al.: Glass formation and soft magnetic properties in Dy-containing Fe-Si-B alloys by adjusting B/Si mole ratio. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 489, 1–5 (2018)
Xu, J., Yang, Y.Z., Li, W. et al.: Effect of Si addition on crystallization behavior, thermal ability and magnetic properties in high Fe content Fe-Si-B-P-Cu-C alloy. Mater. Res. Bull. 97, 452–456 (2018)
Takeuchi, A., Inoue, A.: Classification of bulk metallic glasses by atomic size difference, heat of mixing and period of constituent elements and its application to characterization of the main alloying elements. IEEE Trans. Magn. 12, 2817–2829 (2005)
Liu, T., Wang, A.D., Zhao, C.L. et al.: Compositional design and crystallization mechanism of high Bs nanocrystalline alloys. Mater. Res. Bull. 112, 323–330 (2019)
Minic, D.M., Thermochim, B.A.: Mechanism and kinetics of crystallization of α-Fe in amorphous Fe81B13Si4C2 alloy. Acta Materialia. 474, 41–46 (2008)
Blázquez, J.S., Conde, C.F., Conde, A.: Non-isothermal approach to isokinetic crystallization processes: application to the nanocrystallization of HITPERM alloys. Acta Mater. 53, 2305–2311 (2005)
Onodera, R., Kimura, S., Watanabe, K. et al.: Crystallization kinetics of high iron concentration amorphous alloys under high magnetic fields. J. Alloy. Compd. 604, 8–11 (2014)
Lin, W.D., Yang, Y.Z., Xu, J. et al.: Effect of Nb, Si and Cu on the crystallization process and magnetic properties of FeNbBP alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 735, 1195–1199 (2018)
Pang, L.L., Inoue, A., Zanaeva, E.N. et al.: Nanocrystallization, good soft magnetic properties and ultrahigh mechanical strength for Fe82-85B13-16Si1Cu1 amorphous alloy. J. Alloy. Compd. 785, 25–37 (2019)
Liu, W.L., Wang, Y.G., Chen, F.G.: Investigation of microstructure and magnetic properties of Fe81Si4B12-xP2Cu1Mx (M=Cr, Mn and V; x =0, 1, 2, 3) melt spun ribbons. J. Alloy. Compd. 622, 751–755 (2015)
Jafari, S., Beitollahi, A., Yekta, B.E. et al.: Three-dimensional atom probe analysis and magnetic properties of Fe85Cu1Si2B8P4 melt spun ribbons. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 401, 1123–1129 (2016)
Xie, L., Wang, A.D., Yue, S.Q. et al.: Significant improvement of soft magnetic properties for Fe-based nanocrystalline alloys by inhibiting surface crystallization via a magnetic field assisted melt-spinning process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 483, 158–163 (2019)
Makino, A., He, M., Kubota, T. et al.: New excellent soft magnetic FeSiBPCu nanocrystallized alloys with high Bs of 1.9T from nanohetero-amorphous phase. IEEE Trans. Magn. 45, 4303–4305 (2009)
Sharma, P., Zhang, X., Zhang, Y. et al.: Competition driven nanocrystallization in high Bs and low core loss Fe–Si–B–P–Cu soft magnetic alloys. Scripta Mater. 95, 3–6 (2015)
Lashgari, H.R., Chu, D., Xie, S.S. et al.: Composition dependence of the microstructure and soft magnetic properties of Fe-based amorphous/nanocrystalline alloys: a review study. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 391, 61–82 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L.B., Wang, G.T., Zhou, L. et al. Micro-Alloyed P Optimizes AFA, Thermal Stability, Crystallization Behaviors, and Magnetic Properties of the Novel Fe-Rich FeBCuHf Alloys. J Supercond Nov Magn 34, 3267–3277 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-06004-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-021-06004-8