Abstract
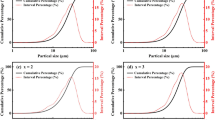
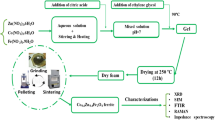
Y3Fe5O12 and Y2.8La0.2Fe5 − xAlxO12 (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, and 0.3) nanoferrites have been prepared by the sol-gel auto combustion route followed by sintering at 900 ° C for 3 h. The garnet phase formation has been confirmed by analyzing XRD patterns and also by noting intense bands for Fe-O vibrations in FTIR spectra. The XRD analysis has shown a decreasing trend for lattice parameter, X-ray density, and d-spacing due to the addition of smaller Al3+ ions at tetrahedral sites. The SEM study has shown agglomerated and branched morphology with an average branch width and branch length ranging between 90–140 nm and 537–437 nm, respectively. Enhanced values of saturation magnetization have been observed for all the samples due to the presence of 6.7% of La3+ ions in place of Y3+ ions. However, it decreased due to weakening of superexchange interaction with the addition of Al3+ ions at tetrahedral sites. These nanoferrite powders can be used as a substitute for costly rare earth garnets and also in many high-frequency microwave devices.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma, V., Saha, J., Patnaik, S., Kuanr, B.K.: Synthesis and characterization of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) nanoparticles - microwave material. AIP Adv. 7, 056405 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4973199
Mallmann, E.J.J., Sombra, A.S.B., Goes, J.C., Fechine, P.B.A.: Yttrium iron garnet: properties and applications review. Solid State Phenom. 202, 65–96 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/SSP.202.65
Pardavi-Horvath, M.: Microwave applications of soft ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 215–216, 171–183 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(00)00106-2
Ramesh, T., Raju, P., Shinde, R.S., Murthy, S.R.: Microwave hydrothermal synthesis and electromagnetic properties of nanocrystalline Y3-xDyxFe5O12 garnets for microwave antenna applications. Int. J. ChemTech. Res. 7(2), 539–546 (2014–2015)
Douglas Adam, J.: Ferrite devices and materials. IEEE Trans. Microwave Theory Techn. 50(3), 721–737 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/22.989957
Ganne, J.-P., Lebourgeois, R., Pat, M., Dubreuil, D., Pinier, L., Pascard, H.: The electromagnetic properties of Cu-substituted garnets with low sintering temperature. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 27, 2771–2777 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.11.054
Ali, W.F.F.W., Jaafar, H.H., Ain, M.F., Abdullah, N.S., Ahmad, Z.A.: Enhancement of YIG bandwidth efficiency through Ce-doping for dielectric resonator antenna (DRA) applications. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2428-7
Harris, V.G., Geiler, A., Chen, Y., Yoon, S.D., Wu, M., Yang, A., Chen, Z., He, P., Parimi, P.V., Xu, Z., Patton, C.E., Abe, M., Acher, O., Vittoria, C.: Recent advances in processing and applications of microwave ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321(14), 2035–2047, ISSN 0304-8853 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.01.004
Vincent, G.: Harris, modern microwave ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 48(3), 1075–1104 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMAG.2011.2180732
Chang, T.-H.: Ferrite materials and applications. Intech Open (2019). https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.84623
Praveena, K., Srinath, S.: Effect of Gd3+ on dielectric and magnetic properties of Y3Fe5O12. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 349, 45–50 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.08.035
Murthy, V.R.K., Raju, K.C.J., Viswanathan, B.: Characteristics of materials for microwave devices. Bull. Mater. Sci. 15, 213 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02927499
Geller, S., Gilleo, M.A.: Magnetic and crystallographic properties of substituted yttrium-iron garnet, 3Y2O3·xM2O3·(5−x)Fe2O3. Phys. Rev. 110, 73 (1958). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRev.110.73
Geller, S., Gilleo, M.A.: The crystal structure and ferrimagnetism of yttrium iron garnet, Y3Fe2(FeO4)3. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 3(1–2), 30–36 (1957). https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3697(57)90044-6
Mahour, L.N., Manjunatha, M., Choudhary, H.K., Kumar, R., Anupama, A.V., Damle, R., Ramesh, K.P., Sahoo, B.: Structural and magnetic properties of Al-doped yttrium iron aluminium garnet ceramics: 57Fe internal field NMR and Mössbauer spectroscopy study. J. Alloys Compd. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.213
Lax, B., Button, K.J.: Microwave ferrites and ferrimagnetics. McGraw-Hill, New York (1962)
Ramesh, T., Shinde, R.S., Murthy, S.R.: Nanocrystalline gadolinium iron garnet for circulator applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3668–3673 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.05.029
Lataifeh, M.S.: Room-temperature magnetization measurements of some substituted rare earth iron garnets. Appl. Phys. A. 92(3), 681–685 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4616-x
Wu, X., Wang, X., Liu, Y., Cai, W., Peng, S., Huang, F., Lu, X., Yan, F., Zhu, J.: Study on dielectric and magnetodielectric properties of Lu3Fe5O12 ceramics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 182903 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3259651
Nimbore, S.R., Shengule, D.R., Shukla, S.J., Bichile, G.K., Jadhav, K.M.: Magnetic and electrical properties of lanthanum substituted yttrium iron garnets. J. Mater. Sci. 41, 6460–6464 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-0365-4
Ahmad, H., Mohammad, N., Sirus, Z.: The theoretical investigation of the impact of substituting bismuth in yttrium iron garnet (YIG) on the Faraday rotation. World Appl. Sci. J. 19(3), 424–430 (2012). https://doi.org/10.5829/idosi.wasj.2012.19.03.3535
Musa, M.A., et al.: Structural and magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) and yttrium aluminium iron garnet (YAlG) nanoferrite via sol-gel synthesis. Results Phys. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2017.02.038
Musa, M.A., Azis, R.’a.S., Osman, N.H., Hassan, J., Dihom, M.M.: Structural and magnetic properties of yttrium aluminium iron garnet (YAlG) nanoferrite prepared via auto-combustion sol-gel synthesis. J. Aust. Ceram. Soc. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0126-7
Mohaidat, Q.I., Lataifeh, M., Hamasha, K., Mahmood, S.H., Bsoul, I., Awawdeh, M.: The structural and the magnetic properties of aluminum substituted yttrium iron garnet. Mater. Res. https://doi.org/10.1590/1980-5373-MR-2017-0808
Niyaifar, M., Beitollahi, A., Shiri, N., Mozaffari, M., Amighian, J.: Effect of indium addition on the structure and magnetic properties of YIG. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(7), 777–779 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.11.001
Dong, B., Yang, H., Cui, Y., et al.: J. Mater. Sci. 42, 3167 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-006-1063-y
Wu, M.: Nonlinear spin waves in magnetic film feedback rings. Solid State Phys. 62, 163–224 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-374293-3.00003-1
Sadhana, K., Murthy, R., Sarabu, Praveena, K.: Effect of Sm3+ on dielectric and magnetic properties of Y3Fe5O12 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 25, (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-014-2282-7
Xu, H., Yang, H.: Magnetic properties of Y3Fe5O12 nanoparticles doped Bi and Ce ions. Mater. Manuf. Process. 23(1), 1–4 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426910701524212
Cheng, Z., Yang, H.: Magnetic properties of Nd-Y3Fe5O12 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 18, 18 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9130-y
Sadhana, K., Ramana Murthy, S., Praveena, K.: Structural and magnetic properties of Dy3+ doped Y3Fe5O12 for microwave devices. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 34, 305–311 (2015)
Zeng, M.: CO-precipitation synthesis of iron-containing garnetsY3Al5 − xFexO12 and their magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 393, 370–375 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.05.082
Hapishah, A.N., Hashim, M., Syazwan, M.M., Idza, I.R., Rodziah, N., Ismayadi, I.: Phase, microstructure and magnetic evaluation in yttrium iron garnet (YIG) synthesized via mechanical alloying. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 15270–15278 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7407-3
Azadi Motlagh, Z., Mozaffari, M., Amighian, J.: Preparation of nano-sized Al-substituted yttrium iron garnets by the mechanochemical method and investigation of their magnetic properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 321, 1980–1984 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.12.025
Pal, M., Chakravorty, D.: Synthesis of nanocrystalline yttrium iron garnet by sol-gel route. Physica E. 5, 200–203 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1386-9477(99)00040-5
Shirsath, S.E., Jadhav, S.S., Mane, M.L., Li, S.: Ferrites obtained by sol-gel method. In: Klein, L., Aparicio, M., Jitianu, A. (eds.) Handbook of sol-gel science and technology. Springer, Cham (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19454-7_125-1
Anupama, A.V., Kumar, R., Choudhary, H.K., Sahoo, B.: Synthesis of coral-shaped yttrium-aluminium-iron garnets by the solution-combustion method. Ceram. Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.11.059
Akhtar, M.N., Sulong, A.B., Khan, M.A., Ahmad, M., Murtaza, G., Raza, M.R., Raza, R., Saleem, M., Kashif, M.: Structural and magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnet (YIG) and yttrium aluminum iron garnet (YAIG) nanoferrites prepared by microemulsion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.10.060
Cheng, Z., Cui, Y., Yang, H., et al.: J. Nanopart. Res. 11, 1185 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-008-9501-1
Cheng, Z., Yang, H., Yu, L., et al.: J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 19, 442 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-007-9357-7
Uhm, Y.R., Lim, J.C., Choi, S.M., Kim, C.S.: Magnetic properties of R-YIG (R = La, Nd, and Gd) derived by a sol-gel method. J. Magn. 21(3), 303–307 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4283/JMAG.2016.21.3.303
Opuchovic, O., Salak, A.N., Rehspringer, JL. et al. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. (2019) 90: 209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-04962-z
Bouziane, K., Yousif, A., Widatallah, H.M., Amighian, J.: Site occupancy and magnetic study of Al3+ and Cr3+ co-substituted Y3Fe5O12. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 2330–2334 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.04.163
Baños-López, E., Sánchez-De Jesús, F., Cortés-Escobedo, C.A., Barba-Pingarrón, A., Bolarín-Miró, A.M.: Enhancement in curie temperature of yttrium iron garnet by doping with neodymium. Materials. 11, (2018, 1652). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091652
Ortega, P.P.S., Ramirez, M.A., Foschini, C.R., Garcia, F.G., Cilense, M., Simoes, A.Z.: Synthesis, structure and magnetic properties of Y3Fe5-xAlxO12 garnets prepared by the soft chemical method. Process. Appl. Ceram. 8(4), 211–218 (2014). https://doi.org/10.2298/PAC1404211O
Grasset, F., Mornet, S., Demourgues, A., Portier, J., Bonnet, J., Vekris, A., Duguet, E.: Synthesis, magnetic properties, surface modification and cytotoxicity evaluation of Y3Fe5−xAlxO12 (0⩽x⩽2) garnet submicron particles for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 234, 409–418 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(01)00386-9
Fu, H.P., Hong, R., Wu, Y.J., Di, G.Q., Xu, B., Zheng, Y., Wei, D.: Preparation and Faraday rotation of Bi-YIG/PMMA nanocomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320, 2584–2590 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2008.04.129
Murumkar, V.D., Modi, K.B., Jadhav, K.M., Bichile, G.K., Kulkarni, R.G.: Magnetic and electrical properties of aluminium and chromium co-substituted yttrium iron garnets. Mater. Lett. 32, 281–285 (1997)
Bhalekar, A.R., Singh, L.N.: Structural, magnetic and ESR studies of Y3AlxFe5 − xO12 (0.0 ≤ x ≤ 1.2) nanoparticles synthesized by a sol-gel method. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 570, 82–93 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.06.002
Sanchez, R.D., Rivas, J., Vaqueiro, P., Lopez-Quintela, M.A., Caeiro, D.: Particle size effects on magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnets prepared by a sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 247, 92–98 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(02)00170-1
Nazlan, R., Hashim, M., Ibrahim, I.R., Idris, F.M., Ismail, I., Rahman, W.N.W.A., Abdullah, N.H., Zulkimi, M.M.M., Mustaffa, M.S.: Indium-substitution and indium-less case effects on structural and magnetic properties of yttrium-iron-garnet. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 85, 1–12 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2015.04.011
Lin, Q., He, Y., Xu, J., Lin, J., Guo, Z., Yang, F.: Effects of Al3+ Substitution on structural and magnetic behavior of CoFe2O4 ferrite nanomaterials. Nanomaterials. 8, 750 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8100750
Kumar, L., Kar, M.: Influence of Al3+ ion concentration on the crystal structure and magnetic anisotropy of nanocrystalline spinel cobalt ferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2042–2048 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.03.010
Kambale, R.C., Shaikh, P.A., Kamble, S.S., Kolekar, Y.D.: Effect of cobalt substitution on structural, magnetic and electric properties of nickel ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 478, 599–603 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.11.101
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank SAIF, Madras, for providing characterization facilities. Authors would also like to thank Prof. V. P. Jawanjal, Head, Department of Petrochemical Engineering, Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Vidyavihar, Lonere, for providing synthesis facility.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhalekar, A.R., Singh, L.N. Structural and Magnetic Studies of Al-Doped Y2.8 La0.2 Fe5 O12 Nanoferrites Prepared by a Sol-Gel Route. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 1859–1870 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05422-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-020-05422-4