Abstract
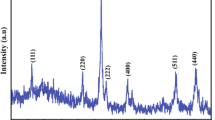
Tricobalt tetroxide (Co3O4) nanoparticles were synthesized by co-precipitation method. The structure, morphology, purity, real compositions, and functional groups of the prepared nanoparticles were determined by X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscope (TEM), energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis, and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, respectively. The results confirm the formation of pure spinel structure of the Co3O4 nanoparticles with space group Fd3m and average spherical particle size of 58 nm. The optical properties were explored by ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy (UV–vis) and photoluminescence spectroscopy (PL). Two absorption peaks were aroused in ultraviolet and visible ranges accompanied by two band gap energies and an Urbach energy. Moreover, two emission peaks in agreement with the calculated band gap energies were observed in the PL spectrum. A weak ferromagnetic behavior was investigated by magnetic hysteresis (M-H) loop at room temperature. The electrical conductivity was measured in the temperature range 313–573 K. A normal semiconductor behavior was detected. The dielectric properties were studied under the variation of temperature and frequency. Then, the dielectric constant, dielectric loss, ac conductivity, relaxation process, and Nyquist plots were discussed.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thota, S., Kumar, A., Kumar, J.: Optical, electrical and magnetic properties of Co3O4 nanocrystallites obtained by thermal decomposition of sol–gel derived oxalates. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 164, 30–37 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2009.06.002
Seidov, Z., Açıkgöz, M., Kazan, S., Mikailzade, F.: Magnetic properties of Co3O4 polycrystal powder. Ceram. Int. 42, 12928–12931 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.05.063
Ibrahim, E.M.M., Abu-Dief, A.M., Elshafaie, A., Ahmed, A.M.: Electrical, thermoelectrical and magnetic properties of approximately 20-nm Ni-Co-O nanoparticles and investigation of their conduction phenomena. Mater. Chem. Phys. 192, 41–47 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2017.01.054
Gunnewiek, R.F.K., Mendes, C.F., Kiminami, R.H.G.A.: Synthesis of spinel cobalt oxide nanoparticles using a modified polymeric precursor method. Adv. Powder Technol. 27, 1056–1061 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2016.03.013
Packiaraj, R., Devendran, P., Venkatesh, K.S., Asath bahadur, S., Manikandan, A., Nallamuthu, N.: Electrochemical investigations of magnetic Co3O4 nanoparticles as an active electrode for supercapacitor applications. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 32, 2427 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4963-6
Liu, B., Zhang, X., Shioyama, H., Mukai, T., Sakai, T., Xu, Q.: Converting cobalt oxide subunits in cobalt metal-organic framework into agglomerated Co3O4 nanoparticles as an electrode material for lithium ion battery. J. Power Sources. 195, 857–861 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2009.08.058
Pal, J., Chauhan, P.: Study of physical properties of cobalt oxide (Co3O4) nanocrystals. Mater. Charact. 61, 575–579 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchar.2010.02.017
Ravi Dhas, C., Venkatesh, R., Jothivenkatachalam, K., Nithya, A., Suji Benjamin, B., Moses Ezhil Raj, A., Jeyadheepan, K., Sanjeeviraja, C.: Visible light driven photocatalytic degradation of Rhodamine B and Direct Red using cobalt oxide nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 41, 9301–9313 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.03.238
Tharayil, N.J., Raveendran, R., Vaidyan, A.V., Chithra, P.G.: Optical, electrical and structural studies of nickel-cobalt oxide nanoparticles. IJEMS. 156(Dec. 2008), (2008)
Lu, J., Moon, K.-S., Xu, J., Wong, C.P.: Synthesis and dielectric properties of novel high-K polymer composites containing in-situ formed silver nanoparticles for embedded capacitor applications. J. Mater. Chem. 16, 1543–1548 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1039/B514182F
Huang, X., Jiang, P.: Core–shell structured high-k polymer nanocomposites for energy storage and dielectric applications. Adv. Mater. 27, 546–554 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201401310
Koseoglu, Y., Kurtulus, F., Kockar, H., Guler, H., Karaagac, O., Kazan, S., Aktas, B.: Magnetic characterizations of cobalt oxide nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25, 2783–2787 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-011-1265-7
Shafiu, S., Baykal, A., Sözeri, H., Toprak, M.S.: Triethanolamine assisted hydrothermal synthesis of superparamagnetic Co3O4 nanoparticles and their characterizations. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 27, 2117–2122 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2562-8
de Alba, J.R., Martínez, J.R., Guerrero, A.L., Ortega-Zarzosa, G.: Effect of the silica cover on the properties of Co3O4 nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 29, 2651–2658 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3595-y
Wadekar, K.F., Nemade, K.R., Waghuley, S.A.: Chemical Synthesis of Cobalt Oxide (Co3O4) Nanoparticles Using Co-Precipitation Method, vol. 7, p. 3 (2017)
Makhlouf, S.A., Bakr, Z.H., Aly, K.I., Moustafa, M.S.: Structural, electrical and optical properties of Co3O4 nanoparticles. Superlattice. Microst. 64, 107–117 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2013.09.023
Allaedini, G., Muhammad, A.: Study of influential factors in synthesis and characterization of cobalt oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanostructure Chem. 3(77), (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-8865-3-77
Bindu Duvuru, H., Alla, S.K., Shaw, S.K., Meena, S.S., Gupta, N., Prasad, B.B.V.S.V., Kothawale, M.M., Kumar, M.K., Prasad, N.K.: Magnetic and dielectric properties of Zn substituted cobalt oxide nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45, 16512–16520 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.05.185
Rani, S., Sharma, Y., Varma, G.D.: Mixed magnetic phases in Co3O4 nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. AIP Conf. Proc. 1591, 526–528 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4872662
Sharifi, S.L., Shakur, H.R., Mirzaei, A., Hosseini, M.H.: Characterization of cobalt oxide Co3O4 nanoparticles prepared by various methods: effect of calcination temperatures on size, dimension and catalytic decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. Int. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 9, 51–58 (2013)
Prabaharan, D.D.M., Sadaiyandi, K., Mahendran, M., Sagadevan, S.: Precipitation method and characterization of cobalt oxide nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 123(264), (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0786-8
Sumathi, S., Nehru, M.: Synthesis, characterization, and influence of fuel on dielectric and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 29, 1317–1323 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3416-3
Ahmad, Z., Atiq, S., Abbas, S.K., Ramay, S.M., Riaz, S., Naseem, S.: Structural and complex impedance spectroscopic studies of Mg-substituted CoFe2O4. Ceram. Int. 42, 18271–18282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.08.154
Joshi, J.H., Kanchan, D.K., Joshi, M.J., Jethva, H.O., Parikh, K.D.: Dielectric relaxation, complex impedance and modulus spectroscopic studies of mix phase rod like cobalt sulfide nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull. 93, 63–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2017.04.013
Alsayed, Z., Badawi, M.S., Awad, R.: Characterization of zinc ferrite nanoparticles capped with different PVP concentrations. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 4925–4933 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-019-07288-2
Moro, F., Yu Tang, S.V., Tuna, F., Lester, E.: Magnetic properties of cobalt oxide nanoparticles synthesised by a continuous hydrothermal method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 348, 1–7 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.07.064
Al Boukhari, J., Zeidan, L., Khalaf, A., Awad, R.: Synthesis, characterization, optical and magnetic properties of pure and Mn, Fe and Zn doped NiO nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. 516, 116–124 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemphys.2018.07.046
Sharrouf, M., Awad, R., Marhaba, S., El-Said Bakeer, D.: Structural, optical and room temperature magnetic study of Mn-doped ZnO nanoparticles. Nano. 11, 1650042 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1142/S1793292016500429
Tharayil, N.J., Sagar, S., Raveendran, R., Vaidyan, A.V.: Dielectric studies of nanocrystalline nickel–cobalt oxide. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 399, 1–8 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2007.03.037
Diallo, A., Beye, A.C., Doyle, T.B., Park, E., Maaza, M.: Green synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles via Aspalathus linearis: physical properties. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 8, 30–36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1080/17518253.2015.1082646
De-Sheng, X., Yu, G., Wen-Jing, L., Ming-Su, S., Zai-Wen, L.: Photoluminescence property of Co3O4 nanowires. Chin. Phys. Lett. 24, 1756–1758 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0256-307X/24/6/089
Zhu, H.T., Luo, J., Liang, J.K., Rao, G.H., Li, J.B., Zhang, J.Y., Du, Z.M.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of antiferromagnetic Co3O4 nanoparticles. Phys. B Condens. Matter. 403, 3141–3145 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2008.03.024
Gopinath, S., Sivakumar, K., Karthikeyen, B., Ragupathi, C., Sundaram, R.: Structural, morphological, optical and magnetic properties of Co3O4 nanoparticles prepared by conventional method. Physica E. 81, 66–70 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2016.02.006
Sinkó, K., Szabó, G., Zrínyi, M.: Liquid-phase synthesis of cobalt oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 11, 4127–4135 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1166/jnn.2011.3875
Sahoo, S.C., Venkataramani, N., Prasad, S., Bohra, M., Krishnan, R.: Stability of nonthermodynamic equilibrium cation distribution frozen during pulsed laser deposition of Co-ferrite thin films. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 98, 889–894 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-009-5471-0
Chikazumi, S., Jr, C.D.G.: Physics of Ferromagnetism. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1997)
Al-Qirby, L.M., Radiman, S., Siong, C.W., Ali, A.M.: Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of Co3O4 nanocrystals in the presence of the ionic liquid [EMIM][BF 4 ]. Ultrason. Sonochem. 38, 640–651 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.08.016
Han, D.H., Wang, J.P., Luo, H.L.: Crystallite size effect on saturation magnetization of fine ferrimagnetic particles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 136, 176–182 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-8853(94)90462-6
Ahmad, M.M.: Enhanced lithium ionic conductivity and study of the relaxation and giant dielectric properties of spark plasma sintered Li5La3Nb2O12 nanomaterials. Ceram. Int. 5(PA), 6398–6408 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.01.077
Mansour, S.F., Abdo, M.A.: Electrical modulus and dielectric behavior of Cr3+ substituted Mg–Zn nanoferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 428, 300–305 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.12.039
Gokul, B., Matheswaran, P., Abhirami, K.M., Sathyamoorthy, R.: Structural and dielectric properties of NiO nanoparticles. J. Non-Cryst. Solids. 363, 161–166 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2012.12.007
Dakhel, A.A.: Dielectric relaxation behaviour of Li and La co-doped NiO ceramics. Ceram. Int. 39(4), 4263–4268 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2012.10.278
Nandan, K.R., Kumar, A.R.: Structural and electrical properties of Ca0.9Dy0.1MnO3 prepared by sol-gel technique. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 8, 2996–3003 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2017.05.020
Acknowledgments
This research was accomplished in the Specialized Materials Science Lab and Advanced Nanomaterials Research Lab, Physics Department, Faculty of Science, Beirut Arab University, Lebanon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdallah, A.M., Awad, R. Study of the Structural and Physical Properties of Co3O4 Nanoparticles Synthesized by Co-Precipitation Method. J Supercond Nov Magn 33, 1395–1404 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05296-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-019-05296-1