Abstract
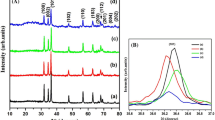
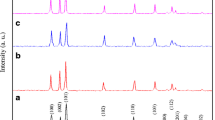
We have prepared Zn1−xCoxS nanoparticles (NPs) and studied their local-geometric, electronic, and magnetic properties. X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated that NPs with average crystallite sizes of 2.2 ∼ 2.9 nm are single phase and crystallize in the zincblende-type structure. Cobalt ions with oxidation state + 2 (Co2+) replaced for Zn2+ and almost unchanged the zincblende-type structure of the ZnS host lattice. Interestingly, all samples show room-temperature ferromagnetism and ferromagnetic order increases with increasing Co content (x) in Zn1−xCoxS NPs. With the results obtained from analyzing the local-geometric structures at Zn and Co K-edges and photoluminescence spectra, we believe that ferromagnetism in Zn1−xCoxS NPs is related to intrinsic defects and exchange interactions between Co2+ ions. We have also reviewed the recent studies on ZnS-based dilute-magnetic materials.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilbert, B., Frazer, B.H., Zhang, H., Huang, F., Banfield, J.F., Haskel, D., Lang, J.C., Srajer, G., Stasio, G.: De: X-ray absorption spectroscopy of the cubic and hexagonal polytypes of zinc sulfide. Phys. Rev. B. 66, 245205 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.66.245205
Schröer, P., Krüger, P., Pollmann, J.: First-principles calculation of the electronic structure of the wurtzite semiconductors ZnO and ZnS. Phys. Rev. B. 47, 6971–6980 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.47.6971
Yuan, G.D., Zhang, W.J., Zhang, W.F., Fan, X., Bello, I., Lee, C.S., Lee, S.T.: p-type conduction in nitrogen-doped ZnS nanoribbons. Appl. Phys. Lett. 93, 213102 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3025846
Murugadoss, G.: Synthesis and characterization of transition metals doped ZnO nanorods. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 28, 587–593 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1005-0302(12)60102-9
Ren, G., Lin, Z., Wang, C., Liu, W., Zhang, J., Huang, F., Liang, J.: Relationship between the coprecipitation mechanism, doping structure and physical properties of Zn1−xCoxS nanocrystallites. Nanotechnology. 18, 035705 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/3/035705
Peng, Y.-P., Zou, X., Bai, Z., Leng, Y., Jiang, B., Jiang, X., Zhang, L.: Mid-infrared laser emission from Cr:ZnS channel waveguide fabricated by femtosecond laser helical writing. Sci. Rep. 5, 18365 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18365
Li, H., Shih, W.Y., Shih, W.-H.: Non-heavy-metal ZnS quantum dots with bright blue photoluminescence by a one-step aqueous synthesis. Nanotechnology. 18, 205604 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/18/20/205604
Zhu, Y.-C., Bando, Y., Xue, D.-F., Golberg, D.: Nanocable-aligned ZnS tetrapod nanocrystals. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 125, 16196–16197 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja037965d
Jiang, Y., Zhang, W.J., Jie, J.S., Meng, X.M., Zapien, J.A., Lee, S.-T.: Homoepitaxial growth and lasing properties of ZnS nanowire and nanoribbon arrays. Adv. Mater. 18, 1527–1532 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.200501913
Fang, X., Bando, Y., Liao, M., Zhai, T., Gautam, U.K., Li, L., Koide, Y., Golberg, D.: An efficient way to assemble ZnS nanobelts as ultraviolet-light sensors with enhanced photocurrent and stability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 500–508 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.200901878
Farhangfar, S., Yang, R.B., Pelletier, M., Nielsch, K.: Atomic layer deposition of ZnS nanotubes. Nanotechnology. 20, 325602 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/20/32/325602
Ni, W.-S., Lin, Y.-J.: Defect-induced magnetic properties of Cu-doped ZnS films with different copper contents. J. Alloys Compd. 649, 968–972 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.07.190
Ichino, K., Kato, H., Sakai, Y., Ohmi, K., Honma, T., Itoh, J., Sasakura, A.: Optical properties and X-ray absorption fine structure analysis of ZnS:Cu,Cl thin-film phosphors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49, 082602 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1143/JJAP.49.082602
Kumar, S., Chen, C.L., Dong, C.L., Ho, Y.K., Lee, J.F., Chan, T.S., Thangavel, R., Chen, T.K., Mok, B.H., Rao, S.M., Wu, M.K.: Room temperature ferromagnetism in Ni doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 554, 357–362 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.12.001
Patel, S.P., Pivin, J.C., Chawla, A.K., Chandra, R., Kanjilal, D., Kumar, L.: Room temperature ferromagnetism in Zn1−xCoxS thin films with wurtzite structure. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323, 2734–2740 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.05.057
Chen, H., Shi, D., Qi, J.: Comparative studies on the magnetic properties of ZnS nanowires doped with transition metal atoms. J. Appl. Phys. 109, 084338 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3573388
Kaur, N., Singh, K.L., Sharma, H.: First principle investigation of the magnetic properties of transition metal doped (ZnS)n (n = 1–16) clusters. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 388, 160–166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.04.035
Zhao, W., Wei, Z., Zhang, L., Wu, X., Wang, X., Jiang, J.: Optical and magnetic properties of Co and Ni co-doped ZnS nanorods prepared by hydrothermal method. J. Alloys Compd. 698, 754–760 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.12.127
Wei, M., Yang, J., Yan, Y., Yang, L., Cao, J., Fu, H., Wang, B., Fan, L.: Influence of Mn ions concentration on optical and magnetic properties of Mn-doped ZnS nanowires. Phys. E Low-dimensional Syst. Nanostructures. 52, 144–149 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2013.04.007
Chandra Patel, P., Ghosh, S., Srivastava, P.C.: Effect of impurity concentration on optical and magnetic properties in ZnS:Cu nanoparticles. Phys. E Low-dimensional Syst. Nanostructures. 93, 148–152 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physe.2017.06.009
Kunapalli, C.K., Shaik, K.: Room-temperature ferromagnetic Zn1−xNixS nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. A. 124, 384 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1811-2
Sreenivasulu, B., Venkatramana Reddy, S., Venkateswara Reddy, P.: Structural, optical and magnetic properties of (Cu, Ni) co-doped ZnS nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 251–259 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-7911-5
Kumar, S., Verma, N.K.: Room temperature investigations on optical and magnetic studies of CoxZn1−xS nanorods. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 374, 548–552 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.08.100
Goktas, A.: Sol–gel derived Zn1−xFexS diluted magnetic semiconductor thin films: compositional dependent room or above room temperature ferromagnetism. Appl. Surf. Sci. 340, 151–159 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.02.115
Peng, W.Q., Qu, S.C., Cong, G.W., Zhang, X.Q., Wang, Z.G.: Optical and magnetic properties of ZnS nanoparticles doped with Mn2 + . J. Cryst. Growth. 282, 179–185 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2005.05.005
Zeng, X., Zhang, J., Huang, F.: Optical and magnetic properties of Cr-doped ZnS nanocrystallites. J. Appl. Phys. 111, 123525 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4729877
Zhu, G., Zhang, S., Xu, Z., Ma, J., Shen, X.: Ultrathin ZnS single crystal nanowires: controlled synthesis and room-temperature ferromagnetism properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 15605–15612 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/ja2049258
Ławniczak-Jabońska, K., Goacki, Z.: Extended X-ray absorption fine structure studies of Co doped ZnS and ZnSe alloys. Acta Phys. Pol. A. 86, 727–735 (1994). https://www.infona.pl/resource/bwmeta1.element.bwnjournal-article-appv86z508kz
Pong, W.F., Mayanovic, R.A., Kao, J.K., Hsieh, H.H., Pieh, J.Y., Chang, Y.K., Kuo, K.C., Tseng, P.K., Lee, J.F.: Degree of p-d hybridization in Zn1−xMnxY (Y = S, Se) and Zn1−xCoxS alloys as studied by X-ray-absorption spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B. 55, 7633–7640 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.55.7633
Curcio, A.L., Bernardi, M.I.B., Mesquita, A.: Local structure and photoluminescence properties of nanostructured Zn1−xMnxS material. Phys. status solidi. 12, 1367–1371 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssc.201510135
Teo, B.K.: EXAFS: Basic Principles and Data Analysis. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Chen, X.B., Yang, N., Liu, X.F., Yu, R.H.: Structure dependent photoluminescence and magnetic properties of Co:ZnS nanostructures. Phys. Scr. 88, 035703 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-8949/88/03/035703
Patel, P.C., Ghosh, S., Srivastava, P.C.: Antiferromagnetic coupling in Co-doped ZnS. J. Mater. Sci. 50, 7919–7929 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-015-9356-7
Yang, J., Niu, H., Cao, J., Han, D., Yang, S., Liu, Q., Wang, T.: Room temperature ferromagnetism and optical property of Zn1−xCoxS nanorods. Superlattices Microstruct. 82, 75–81 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2015.02.016
Lewicki, A., Schindler, A.I., Furdyna, J.K., Giriat, W.: Magnetic susceptibility of Zn1-x CoxS and Zn1−xCoxSe alloys. Phys. Rev. B. 40, 2379–2382 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.40.2379
L/awniczak-Jabl/onska, K., Iwanowski, R.J., Gol/acki, Z., Traverse, A., Pizzini, S., Fontaine, A., Winter, I., Hormes, J.: Local electronic structure of ZnS and ZnSe doped by Mn, Fe, Co, and Ni from X-ray-absorption near-edge structure studies. Phys. Rev. B. 53, 1119–1128 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.53.1119
Valério, L.R., Mamani, N.C., de Zevallos, A.O., Mesquita, A., Bernardi, M.I.B., Doriguetto, A.C., de Carvalho, H.B.: Preparation and structural-optical characterization of dip-coated nanostructured Co-doped ZnO dilute magnetic oxide thin films. RSC Adv. 7, 20611–20619 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA01200D
Cho, D.-Y., Xi, L., Boothroyd, C., Kardynal, B., Lam, Y.M.: The role of ion exchange in the passivation of In(Zn)P nanocrystals with ZnS. Sci. Rep. 6, 22818 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22818
Shannon, R.D.: Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 32, 751–767 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001551
Sreekantha Reddy, D., Kang, B., Yu, S.C., Gunasekhar, K.R., Sreedhara Reddy, P.: Synthesis and characterization of Zn1−xMnxS nanocrystalline films prepared on glass substrates. Appl. Phys. A. 91, 627–630 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-008-4488-0
Hassan, M., Younas, S., Sher, F., Husain, S.S., Riaz, S., Naseem, S.: Room temperature ferromagnetism in single-phase Zn1−xMnxS diluted magnetic semiconductors fabricated by co-precipitation technique. Appl. Phys. A. 123, 352 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-017-0975-5
Chu, X.-Y., Wang, X.-N., Li, J.-H., Yao, D., Fang, X., Fang, F., Wei, Z.-P., Wang, X.-H.: Influence factors and mechanism of emission of ZnS:Cu nanocrystals. Chinese Phys. B. 24, 067805 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1088/1674-1056/24/6/067805
Saikia, D., Borah, J.P.: Carrier-induced ferromagnetism in half-metallic Co-doped ZnS-diluted magnetic semiconductor: a DFT study. Appl. Phys. A. 124, 240 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-018-1623-4
de Queiroz, A.A.A., Martins, M., Soares, D.A.W., França, E.́J.: Modeling of ZnS quantum dots synthesis by DFT techniques. J. Mol. Struct. 873, 121–129 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2007.03.013
Ma, L., Chen, W.: Zns:cu,co water-soluble afterglow nanoparticles: synthesis, luminescence and potential applications. Nanotechnology 21, 385604 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/21/38/385604
Dong, J., Zeng, X., Xia, W., Zhang, X., Zhou, M., Wang, C.: Ferromagnetic behavior of non-stoichiometric ZnS microspheres with a nanoplate-netted surface. RSC Adv. 7, 20874–20881 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1039/C7RA02521A
Sambasivam, S., Joseph, D.P., Reddy, D.R., Reddy, B.K., Jayasankar, C.K.: Synthesis and characterization of thiophenol passivated Fe-doped ZnS nanoparticles. Mater. Sci. Eng. B. 150, 125–129 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2008.03.009
Coey, J.M.D.: Ferromagnetism. Solid State Sci. 7, 660–667 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2004.11.012
Phan, T.-L., Yu, S.C.: Optical and magnetic properties of Zn1−xMnxO nanorods grown by chemical vapor deposition. J. Phys. Chem. C. 117, 6443–6453 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp312080v
Phan, T.-L., Zhang, Y.D., Yang, D.S., Nghia, N.X., Thanh, T.D., Yu, S.C.: Defect-induced ferromagnetism in ZnO nanoparticles prepared by mechanical milling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 072408 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4793428
Straumal, B., Mazilkin, A., Protasova, S., Myatiev, A., Straumal, P., Goering, E., Baretzky, B.: Influence of texture on the ferromagnetic properties of nanograined ZnO films. Phys. status solidi. 248, 1581–1586 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1002/pssb.201001182
Funding
This work is supported by Thai Nguyen University of Technology (Grant No. T2018-B01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pham, M.T., Ca, N.X., Loan, P.N. et al. Electronic Structure and Ferromagnetism in Zincblende Zn1−xCoxS Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 1761–1768 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4874-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4874-6