Abstract
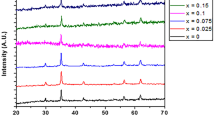
Dysprosium doped magnetite (Fe3−xDyxO4 with x = 0.0–0.1) nanoparticles have been synthesized using the co-precipitation method. Magnetic characterization using vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) has revealed an enhancement in the saturation magnetization with Dy3+ doping. The occupancy of the dopant ions in magnetite lattice has been probed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The shifting of ν2 (Fe–O) band at 452 cm− 1 for undoped samples to 443 cm− 1 for dysprosium-doped samples is indicative of occupancy of dysprosium at the octahedral site. X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns have been used to calculate the strain and lattice constant. The strain is found to increase with doping level and attained a maximum value for the x = 0.03. This increase in the strain can be attributed to occupancy of large diameter Dy3+ ions at the octahedral site of spinel structure of the magnetite lattice.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bird, S.M., Galloway, J.M., Rawlings, A.E., Bramblea, J.P., Staniland, S.S.: Taking a hard line with biotemplating: cobalt doped magnetite magnetic nanoparticle arrays. Nanoscale 7, 7340–7351 (2015)
Xia, Y., Yang, P., Sun, Y., Wu, Y., Mayers, B., Gates, B., Yin, Y., Kim, F., Yan, Y.: One-dimensional nanostructure: synthesis, characterization and application. Adv. Mater. 15, 353–389 (2003)
Alcantara, D., Lopez, S., García-Martin, M.L., Pozo, D.: Iron oxide nanoparticles as magnetic relaxation switching (MRSw) sensors: current applications in nanomedicine. Nanomed.: Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 12, 1253–1262 (2016)
Jamshaid, T., Taveira Tenório Neto, E., Eissa, M.M., Zine, N., Hiroiuqui Kunita, M., El-Salhi, A.E., Elaissari, A.: Magnetic particles: from preparation to lab-on-a-chip, biosensors, microsystems and microfluidics applications. Trends Anal. Chem. 79, 344–362 (2016)
Zhao, Z., Chi, X., Yang, L., Yang, R., Ren, B.W., Zhu, X., Zhang, P., Gao, J.: Cation exchange of anisotropic-shaped magnetite nanoparticles generates highrelaxivity contrast agents for liver tumor imaging. Chem. Mater. 28, 3497–3506 (2016)
Chowdhuri, A.R., Bhattacharya, D., Sahu, S.K.: Magnetic nanoscale metal organic frameworks for potential targeted anticancer drug delivery, imaging and MRI contrast agent. Dalton Trans. 45, 2963–2973 (2016)
Zhang, H., Malik, V., Mallapragada, S., Akinc, M.: Synthesis and characterization of Gd-doped magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 423, 386–394 (2017)
Rice, K.P., Russek, S.E., Geiss, R.H., Shaw, J.M., Usselman, R.J., Evarts, E.R., Silva, T.J., Nembach, H.T., Arenholz, E., Idzerda, Y.U.: Temperature dependent structure of Tb-doped magnetite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 106, 0624091-4 (2015)
Kittel, C.: Introduction to Solid State Physics, 7th edn. Wiley, New Delhi (1995)
Kulkarni, S.K.: Nanotechnology: Principles and Practices, 2nd edn. Capital Publishing Company, New Delhi (2011)
Aghazadeh, M., Ganjali, M.R.: Evaluation of supercapacitive and magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nano-particles electrochemically doped with dysprosium cations: development of a novel iron-based electrode. Ceram. Int. 44, 520–529 (2018)
Shi, J., Tong, L., Ren, X., Li, Q., Yang, H.: Multifuctional Fe3O4@C/YVO4:Dy3+ nanopowers: preparation, luminescence and magnetic properties. Ceram. Int. 39, 6391–6397 (2013)
Huan, W., Ji, G., Cheng, C., An, J., Yang, Y., Liu, X.: Preparation, characterization of high-luminescent and magnetic Eu3+, Dy3+ doped superparamagnetic nano-Fe3O4. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14, 1–9 (2014)
Jain, R., Luthra, V., Gokhale, S.: Dysprosium doping induced shape and magnetic anisotropy of Fe3−xDyxO4 (x = 0.01–0.1) nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 414, 111–115 (2016)
Chandra, S., Das, R., Kalappattil, V., Eggers, T., Harnagea, C., Nechache, R., Phan, M.-H., Rosei, F., Srikanth, H.: Epitaxial magnetite nanorods with enhanced room temperature magnetic anisotropy. Nanoscale 9, 7858–7867 (2017)
Sharma, R., Singhal, S.: Structural, magnetic and electrical properties of zinc doped nickel ferrite and their application in photo catalytic degradation of methylene blue. Physica B 414, 83–90 (2013)
Caruntu, D., Caruntu, G., O’Connor, C.J.: Magnetic properties of variable-sized Fe3O4 nanoparticles synthesized from non-aqueous homogeneous solutions of polyol. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40, 5801–5809 (2007)
Gadkari, A., Shinde, T., Vasambekar, P.: Influence of rare-earth ions on structural and magnetic properties of CdFe2O4. Rare Met. 29, 168–173 (2010)
Rana, S., Philip, J., Raj, B.: Micelle based synthesis of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles and its characterization using Fourier transform infrared transmission spectrometry and thermogravimetry. Mater. Chem. Phys. 124, 264–269 (2010)
Karamipour, S., Sadjadi, M.S., Farhadyar, N.: Fabrication and spectroscopic studies of folic acid conjugated Fe3O4@Au core–shell for targeted drug delivery application. Spectrochim. Acta Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 148, 146–155 (2015)
Gasparov, L.V., Tanner, D.B., Romero, D.B., Margaritondo, H. Berger G., Forro, L.: Infrared and Raman studies of the Verwey transition in magnetite. Phys. Rev. B 62, 7939–7944 (2000)
Wolska, E., Piszora, P., Nowicki, W., Darul, J.: Vibrational spectra of lithium ferrites: infrared spectroscopic studies of Mn-substituted LiFe5O8. Int. J. Inorg. Mater. 3, 503–507 (2001)
Giri, J., Bahadur, T., Sriharsha, D.: Optimization of parameters for the synthesis of nano-sized Co1−xZnxFe2O4, (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.8) by microwave refluxing. Mater. Chem. 14, 875–880 (2004)
Tan, X., Fang, M., Chen, C., Yu, S., Wang, X.: Counterion effects of nickel and sodium dodecylbenzene sulfonate adsorption to multiwalled carbon nanotubes in aqueous solution. Carbon 46, 1741–1750 (2008)
Zhao, F., Zhang, B., Feng, L.: Preparation and magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 68, 112–114 (2012)
Sudakar, C., Subbanna, G.N., Narayanan Kutty, T.R.: Synthesis of acicular hydrogoethite (α-FeOOH⋅ x H2O; 0.1 < x < 0.22) particles using morphology controlling cationic additives and magnetic properties of maghemite derived from hydrogoethite. J. Mater. Chem. 12, 107–116 (2002)
Pawar, R.A., Patange, S.M., Tamboli, Q.Y., Ramanathan, V., Shirsath, S.E.: Spectroscopic, elastic and dielectric properties of Ho3+ substituted Co-Zn ferrites synthesized by sol-gel method. Ceram. Int. 42, 16096–16102 (2016)
Shirsath, S.E., Mane, M.L., Yasukawa, Y., Liu, X., Morisako, A.: Self-ignited high temperature synthesis and enhanced super-exchange interactions of Ho3+-Mn2+-Fe3+-O2− ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 16, 2347–2357 (2014)
Amiri, S., Shokrollahi, H.: Magnetic and structural properties of RE doped Co-ferrite (RE=Nd, Eu, Gd) nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 345, 18–23 (2013)
Ma, M., Zhang, Y., Yu, W., Shen, H.-Y., Zhang, H.-Q., Gu, N.: Preparation and characterization of magnetite nanoparticles coated by amino silane. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 212, 219–226 (2003)
Iyengar, S.J., Joy, M., Ghosh, C.K., Dey, S., Kotnala, R.K., Ghosh, S.: Magnetic, X-ray and Mössbauer studies on magnetite/maghemite core–shell nanostructures fabricated through an aqueous route. RSC Adv. 4, 64919–64929 (2014)
Kambale, R.C., Song, K.M., Koo, Y.S., Hur, N.: Low temperature synthesis of nanocrystalline Dy3+ doped cobalt ferrite: structural and magnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 0539101-7 (2011)
Padalia, D., Johri, U.C., Zaidi, M.G.H.: Effect of cerium substitution on structural and magnetic properties of magnetite nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Phys. 169, 89–95 (2016)
Ibrahim Dar, M., Shivashankar, S.A.: Single crystalline magnetite, maghemite, and hematite nanoparticles with rich coercivity. RSC Adv. 4, 4105–4113 (2014)
Prathapani, S., Vinitha, M., Jayaraman, T.V., Das, D.: Effect of Er doping on the structural and magnetic properties of cobalt-ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 115, 17A502 (2014)
Zhao, X., Wang, W., Zhang, Y., Wu, S., Li, F., Liu, J.P.: Synthesis and characterization of gadolinium doped Cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with enhanced adsorption capability for Congo Red. Chem. Eng. J. 250, 164–174 (2014)
Anita, Luthra, V.: Tweaking electrical and magnetic properties of Al–Ni co-doped ZnO Nanopowders. Ceram. Int. 40, 14927–14932 (2014)
Anjum, S., Tufail, R., Saleem, H., Zia, R., Riaz, S.: Investigation of stability and magnetic properties of Ni- and Co-doped iron oxide nano-particles. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 2291–2301 (2017)
Anjum, S., Saleem, H., Rasheed, K., Zia, R., Riaz, S., Usman, A.: Role of Ni2+ ions in magnetite nano-particles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 30, 1177–1186 (2017)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank USIC, Delhi University for facilitating the FTIR measurements. The authors acknowledge the Indian Institute of Technology, New Delhi for XRD characterization. The authors thank Prof. Annapoorni, Delhi University, Delhi for facilitating the VSM measurements. The TEM characterization was carried out at the Advanced Instrumentation Research Facility, Jawaharlal Nehru University, New Delhi. Authors are thankful to Dr. Gajender Saini for the help rendered in SAED analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, R., Luthra, V., Arora, M. et al. Infrared Spectroscopic Study of Magnetic Behavior of Dysprosium Doped Magnetite Nanoparticles. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 325–333 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4717-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4717-5