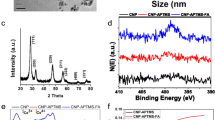
Abstract
The aim of this study is to determine the cytotoxic and apoptotic effects of newly synthesized folic acid (FA) and luteolin (carboxylated luteolin (CL)) conjugated superparamagnetic nanoparticle (SPION@FA-PEG@CL) on folate receptor positive (FAR (+)) and negative (FAR (−)) cell lines in vitro. Cytotoxicity analysis by real-time cell analyzer system (RTCA) and apoptosis by TUNEL and Annexin assay, Caspase 3/7 activities, and Caspase 3/7 expression level were determined. According to RTCA results, SPION@FA-PEG@CL nanodrug showed higher cytotoxicity against U87, MCF-7, HeLa cell lines in comparison with L929 and A549 cell lines. TUNEL and Annexin assays indicated that SPION@FA-PEG@CL increased the apoptotic and necrotic cell ratio in FAR (+) cell. In L929 and A549 cells, are FAR (−) cell lines apoptotic and necrotic cell ratio was lower than FAR (+) cell lines (U87, MCF-7 and HeLa). Caspase 3 and 7 analyses also showed that SPION@FA-PEG@CL nanodrug have apoptotic and necrotic impact on cell lines, they were higher in FAR (+) cells than FAR (−) cells. According to results, synthesized SPION@FA-PEG@CL can be a novel nanodrug delivery system for in cancer chemotherapy.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akal, Z.Ü., Alpsoy, L., Baykal, A.: Superparamagnetic iron oxide conjugated with folic acid and carboxylated quercetin for chemotherapy applications. Ceram. Int. 9065–9072 (2016)
Alpsoy, L., Baykal, A., Ulker, Z.: Synthesis and characterization of carboxylated luteolin (CL)—functionalized SPION. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. doi:10.1007/s10948-017-4056
Amin, A.R., Kucuk, O., Khuri, F.R., Shin, D.M.: Perspectives for cancer prevention with natural compounds. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 27, 2712–2725 (2009)
Chakrabarti, M., Ray, S.K.: Anti-tumor activities of luteolin and silibinin in glioblastoma cells: overexpression of miR-7-1-3p augmented luteolin and silibinin to inhibit autophagy and induce apoptosis in glioblastoma in vivo. Apoptosis 21, 312–328 (2016)
Chen, Q., Liu, S., Chen, J., Zhang, Q., Lin, S., Chen, Z., Jiang, J.: Luteolin induces mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell. Nat. Prod. Commun. 7, 29–32 (2012)
Cheng, W.Y., Chiao, M.T., Liang, Y.J., Yang, Y.C., Shen, C.C., Yang, C.Y.: Luteolin inhibits migration of human glioblastoma U-87 MG and T98G cells through downregulation of Cdc42 expression and PI3K/AKT activity. Mol. Biol. Rep. 40, 5315–5326 (2013)
Chertok, B., David, A.E., Yang, V.C.: Polyethyleneimine-modified iron oxide nanoparticles for brain tumor drug delivery using magnetic targeting and intracarotid administration. Biomaterials 31(24), 6317–6324 (2010)
Dorai, T., Aggarwal, B.B.: Role of chemopreventive agents in cancer therapy. Cancer Lett. 215, 129–140 (2004)
Elkhodiry, M.A., Husseini, G.A., Velluto, D.: Targeting the folate receptor: effects of conjugating folic acid to DOX loaded polymeric micelles. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. (2016)
Ferrari, M.: Cancer nanotechnology: opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Cancer 5, 161–171 (2005)
Gref, R., Minamitake, Y., Peracchia, M.T., Trubetskoy, V., Torchilin, V., Langer, R.: Biodegradable long-circulating polymeric nanospheres. Science 263, 1600–1603 (1994)
Jeon, Y.W., Suh, Y.J.: Synergistic apoptotic effect of celecoxib and luteolin on breast cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 29, 819–825 (2013)
Kandasamy, G., Maity, D.: Recent advances in superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) for in vitro and in vivo cancer nanotheranostics. Int. J. Pharm. 496(2), 191–218 (2015)
Kandaswami, C., Lee, L.T., Lee, P.P., Hwang, J.J., Ke, F.C., Huang, Y.T., Lee, M.T.: The antitumor activities of flavonoids. In Vivo 19, 895–909 (2005)
Khosroshahi, M.E., Rezvani, H.A., Keshvari, H., Bonakdar, S., Tajabadi, M.: Evaluation of cell viability and T2 relaxivity of fluorescein conjugated SPION-PAMAM third generation nanodendrimers for bioimaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 62, 544–552 (2016)
Lee, E.J., Oh, S.Y., Sung, M.K.: Luteolin exerts anti-tumor activity through the suppression of epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated pathway in MDA-MB-231 ER-negative breast cancer cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 50, 4136–4143 (2012)
Lin, C.H., Chang, C.Y., Lee, K.R., Lin, H.J., Chen, T.H., Wan, L.: Flavones inhibit breast cancer proliferation through the Akt/ FOXO3a signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 15, 958–970 (2015)
Lin, Y., Shi, R., Wang, X., Shen, H.M.: Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 8, 634–646 (2008)
Liu, Y., Wang, L., Zhao, Y., He, M., Zhang, X., Niu, M., Feng, N.: Nanostructured lipid carriers versus microemulsions for delivery of the poorly water-soluble drug luteolin. Int. J. Pharm. 476, 169–177 (2014)
Mahmoudi, M., Sant, S., Wang, B., Laurent, S., Sen, T.: Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63, 24–46 (2011)
Majumdar, D., Jung, K.H., Zhang, H., Nannapaneni, S., Wang, X., Amin, A. R., Chen, Z., Chen, Z.G., Shin, D.M.: Luteolin nanoparticle in chemoprevention: in vitro and in vivo anticancer activity. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila) 7, 65–73 (2014)
Nabavi, S.F., Braidy, N., Gortzi, O., Sobarzo-Sanchez, E., Daglia, M., Skalicka-Wozniak, K., Nabavi, S.M.: Luteolin as an anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective agent: a brief review. Brain Res. Bull. 119, 1–11 (2015)
Nie, S., Xing, Y., Kim, G.J., Simons, J.W.: Nanotechnology applications in cancer. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 9, 257–288 (2007)
Nishiyama, N.: Nanomedicine: nanocarriers shape up for long life. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2, 203–204 (2007)
Park, S.H., Ham, S., Kwon, T.H., Kim, M.S., Lee, D.H., Kang, J.W., Oh, S.R., Yoon, D.Y.: Luteolin induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through extrinsic and intrinsic signaling pathways in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol.: Official Organ of the International Society for Environmental Toxicology and Cancer 33, 219–231 (2014)
Qiu, J.F., Gao, X., Wang, B.L., Wei, X.W., Gou, M.L., Men, K., Liu, X.Y., Guo, G., Qian, Z.Y., Huang, M.J.: Preparation and characterization of monomethoxy poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) micelles for the solubilization and in vivo delivery of luteolin. Int. J. Nanomed. 8, 3061–3069 (2013)
Rao, P.S., Satelli, A., Moridani, M., Jenkins, M., Rao, U.S.: Luteolin induces apoptosis in multidrug resistant cancer cells without affecting the drug transporter function: involvement of cell line-specific apoptotic mechanisms. Int. J. Cancer 130, 2703–2714 (2012)
Scialabba, C., Licciardi, M., Mauro, N., Rocco, F., Ceruti, M., Giammona, G.: Inulin-based polymer coated SPIONs as potential drug delivery systems for targeted cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 695–705 (2014)
Siddiqui, I.A., Adhami, V.M., Bharali, D.J., Hafeez, B.B., Asim, M., Khwaja, S.I., Ahmad, N., Cui, H.D., Mousa, S.A., Mukhtar, H.: Introducing nanochemoprevention as a novel approach for cancer control: proof of principle with green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Res. 69, 1712–1716 (2009)
Siddiqui, I.A., Afaq, F., Adhami, V.M., Mukhtar, H.: Prevention of prostate cancer through custom tailoring of chemopreventive regimen. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 171, 122–132 (2008)
Sui, J.Q., Xie, K.P., Xie, M.J.: Inhibitory effect of luteolin on the proliferation of human breast cancer cell lines induced by epidermal growth factor. Sheng Li Xue Bao 68, 27–34 (2016)
Thangapazham, R.L., Puri, A., Tele, S., Blumenthal, R., Maheshwari, R.K.: Evaluation of a nanotechnology-based carrier for delivery of curcumin in prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 32, 1119–1123 (2008)
Tsai, Y.D., Chen, H.J., Hsu, H.F., Lu, K., Liang, C.L., Liliang, P.C., Wang, K.W., Wang, H.K., Wang, C.P., Houng, J.Y.: Luteolin inhibits proliferation of human glioblastoma cells via induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 44(6), 837–845 (2013)
Wang, F., Gao, F., Pan, S., Zhao, S., Xue, Y.: Luteolin induces apoptosis, G0/G1 cell cycle growth arrest and mitochondrial membrane potential loss in neuroblastoma brain tumor cells. Drug Res. 65, 91–95 (2015)
Zhang, H., Li, J.C., Hu, Y., Shen, M.W., Shi, X.Y., Zhang, G.F.: Folic acid-targeted iron oxide nanoparticles as contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging of human ovarian cancer. J. Ovarian Res. 9, 9–19 (2016)
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the TÜBİTAK, Research Project Foundation (Contract no: 114Z581 for financial support of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alpsoy, L., Baykal, A. & Akal, Z.Ü. Luteolin-Loaded Spion as a Drug Carrier for Cancer Cell In Vitro. J Supercond Nov Magn 31, 467–474 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4199-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-017-4199-x