Abstract
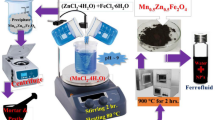
Herein, novel ferrofluid nanocomposites xFe2 O 3/(1 −x)Fe 3 O 4 with different ratios of x (0.0 ≤x≤ 1.0) from magnetite and hematite nanoparticles (NPs) were prepared via a sonochemical method, for hyperthermia purposes. Various analytical and characterization techniques have been used to analyze and characterize the prepared ferrofluid nanocomposites. XRD confirms the formation of two separate phases of nanocomposite components with average crystallite size ranging from 12 to 30 nm. The crystallite size was tuned via the hematite weight fraction of x (wt %) showing the lowest size at x= 0.2. FTIR shows that the band at 627 cm −1 could be referred to the Fe–O stretching vibrations and the band at 535 cm −1 could be assigned to Fe–O in Fe 2 O 3. HRTEM and FESEM show the spherical and rod-like shape of magnetite and hematite, respectively, with an average particle size of 12 nm for Fe 3 O 4 NPs and 11 nm for Fe 2 O 3 NPs. XRF confirms that the nominal and chemical compositions are close. VSM shows that the prepared ferrofluid nanocomposites exhibit almost superparamagnetic behavior at which the magnetic parameters vary with the weight fraction of x (wt %), in addition to superior magnetic responsively with the saturation magnetization value arising from 0.74 to 67.86 emu/g. Analytical thermal analysis techniques exhibit that the ferrofluid nanocomposites show a high degree of thermal stability. It is observed that the composition 0.2 shows different behavior and superior properties rather than others. Therefore, this composition is considered as the optimum ratio for different applications particularly for hyperthermia purposes. The hyperthermia behavior of 0.2Fe 2 O 3/0.8Fe 3 O 4 nanocomposite was checked primary by using a home-made induction coil at a tested frequency of 50 Hz. It was found that, 50 Hz frequency induced hyperthermia temperature of about 43 ∘C at very low magnetic field within 20 min. Finally, we recommend this nanocomposite due to its high magnetization, thermal stability, and acceptable biocompatibility for cancer treatment by localized hyperthermia technique.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Roca, A.G., Morales, M.P., O’Grady, K., Serna, C.J.: Structural and magnetic properties of uniform magnetite nanoparticles prepared by high temperature decomposition of organic precursors. Nanotechnology 17, 2783–2788 (2006)
Bhattacharya, S., Roychowdhury, A., Tiwari, V., Prasad, A., Ningthoujam, R.S., Patel, A.B., Das, D., Nayar, S.: Effect of biomimetic templates on the magnetostructural properties of Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5, 13777 (2015)
Blaney, L.: Magnetite (Fe3O4): Properties, synthesis, and applications. Volume 15 - (2007). Paper 5. (2007)
Chapa Gonzalez, C., Martínez Pérez, C.A., Martínez Martínez, A., Olivas Armendáriz, I., Zavala Tapia, O., Martel-Estrada, A., García-Casillas, P.E.: Development of antibody-coated magnetite nanoparticles for biomarker immobilization. J. Nanomater. 2014, 1–7 (2014)
Lee, J.B., Kim, H.J., Lužnik, J., Jelen, A., Pajić, D., Wencka, M., Jagličić, Z., Meden, A., Dolinšek, J.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of hematite particles in a “nanomedusa” morphology. J. Nanomater. 2014, 1–9 (2014)
Wang, D., Jiang, L., Wei, X., Song, C.: Construction of Fe3O4/Fe2O3 composite hollow spheres and their properties. Mater. Lett. 138, 164–166 (2015)
Mohammadi, A., Barikani, M.: Synthesis and characterization of superparamagnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles coated with thiodiglycol. Mater. Charact. 90, 88–93 (2014)
Hyeon, T.: Chemical synthesis of magnetic nanoparticles. Chem. Commun. 8, 927 (2003)
Garaio, E., Collantes, J.M., Garcia, J.A., Plazaola, F., Mornet, S., Couillaud, F., Sandre, O.: A wide-frequency range AC magnetometer to measure the specific absorption rate in nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 368, 432–437 (2014)
Jiang, Q.L., Zheng, S.W., Hong, R.Y., Deng, S.M., Guo, L., Hu, R.L., Gao, B., Huang, M., Cheng, L.F., Liu, G.H., Wang, Y.Q.: Folic acid-conjugated Fe3O4 magnetic nanoparticles for hyperthermia and MRI in vitro and in vivo. Appl. Surf. Sci. 307, 224–233 (2014)
Shah, R.R., Davis, T.P., Glover, A.L., Nikles, D.E., Brazel, C.S.: Impact of magnetic field parameters and iron oxide nanoparticle properties on heat generation for use in magnetic hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 387, 96–106 (2015)
Mahdavi, M., Ahmad, M.B., Haron, M.J., Namvar, F., Nadi, B., Rahman, M.Z., Amin, J.: Synthesis, surface modification and characterisation of biocompatible magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Molecules 18, 7533– 7548 (2013)
Ocana, M.R., Rodriquez-Clemente, R., Serna, C.J.: Uniform colloidal particles in solution: formation mechanisms. Adv. Mater., 212–216 (1995)
Ahmed, M.A., Imam, N.G., Abdelmaksoud, M.K., Saeid, Y.A.: Magnetic transitions and butterfly-shaped hysteresis of Sm–Fe-Al-based perovskite-type orthoferrite. J. Rare Dearth 33(9), 965 (2015)
Ahmed, M.A., Okasha, N., Imam, N.G.: Modification of composite ceramics properties via different preparation techniques. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 4136–4142 (2012)
Ahmed, M.A., Okasha, N., Imam, N.G.: Advanced imaging techniques for characterization of 0.5BaTiO 3/0.5Ni 0.5Zn 0.5Fe 2 O 4 multiferroic nanocomposite. J. Alloys Compd. 557, 130 (2013)
Elzinga, E.J., Sparks, D.L.: Phosphate adsorption onto hematite: an in situ ATR-FTIR investigation of the effects of pH and loading level on the mode of Dphosphate surface complexation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 308, 53–70 (2007)
Mostafa, N.Y., Mohamed, M.B., Imam, N.G., Alhamyani, M., Heiba, Z.K.: Electrical and optical properties of hydrogen titanate nanotube/PANI Dhybrid nanocomposites. Colloid and Polymer Science - Springer (2015). doi:10.1007/s00396-015-3769-3
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge all supports given by both Chemistry and Physics Departments in Cairo University and Nuclear Research Centre, Atomic Energy Authority. Further, N.G. Imam acknowledges the Italian Sincrotrone Trieste- (Elettra), and the head of XAFS Beamline (G. Aquilanti) for providing the nice atmosphere to write and review the paper carefully. Also, many thanks to S.I. El-Dek for her kind help. Finally, many thanks to IAEA, SESAME, and ICTP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zayed, M.A., Ahmed, M.A., Imam, N.G. et al. Analytical Characterization of Hematite / Magnetite Ferrofluid Nanocomposites for Hyperthermia Purposes. J Supercond Nov Magn 29, 2899–2916 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3587-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-016-3587-y