Abstract
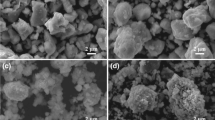
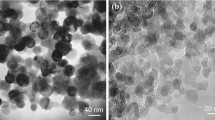
We have studied the flux-pinning mechanisms of YBa 2Cu 3 O y (Y-123) and YBa 2Cu 3 O y embedded by Y-deficient Y-123 nanoparticles induced by planetary ball-milling technique. Samples were synthesized in air using a standard solid-state reaction technique by considering a thermal cycle with two stages of sintering at 950 °C separated by intermediate crushing; a traditional crushing (in a mortar) and another energetic (in a planetary crusher). Phase analysis by X-ray diffraction (XRD), granular structure examination by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), microstructure investigation by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and the global critical current density dependence on temperature (J ct(T)) at several applied magnetic fields were carried out. The temperature dependence of J ct(T) was analyzed within the collective pinning model. For both samples and at self-magnetic field, the temperature dependence of the critical current density is in agreement with the δ T c pinning mechanism which is due to the spatial fluctuation of the Ginsburg-Landau coefficient associated with the transition temperature T c. Under an applied magnetic field of 100 mT there is evidence of δ ε and δ l pinning mechanisms in the unmilled sample; however, the δ ε pinning is strongly dominant in the milled one These results agree with TEM observations showing the appearance of defects and contrast deformation due to the nanophases generated by ball milling and embedded inside the superconducting matrix.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang, J., Shi, Z.X., Lv, H., Tamegai, T.: Physica C 445–448, 462 (2006)
Xu, M., Kitazawa, H., Takano, Y., Ye, J., Nishida, K., Abe, H., Matsushita, A., Kido, G.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 2779 (2001)
Kim, K.H.P., Choi, J.H., Jung, C.U., Chowdhury, P., Hyun-Sook Lee, Park, M.S., Kim, H.J., Kim, J.Y., Du, Z., Choi, E.M., Kim, M.S., Kang, W.N., Lee, S.I., Sung, G.Y., Lee, J.Y.: Phys. Rev. B 65, 100510(R) (2002)
Pradhan, A.K., Shi, Z.X., Tokunaga, M., Tamegai, T., Takano, Y., Togano, K., Kito, H., Ihara, H.: Phys. Rev. B 64, 212509 (2001)
Kim, H.-J., Kang, W.N., Choi, E.-Mi., Kim, M.-S., Kim, K. H. P., Lee, S.-I.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 087002 (2001)
Kim, M.-S., Jung, C.U., Park, M.-S., Lee, S.Y., Kim, K.H.P., Kang, W.N., Lee, S.-I.: Phys. Rev. B 64, 012511 (2001)
Pallecchi, I., Tarantini, C., Aebersold, H.U., Braccini, V., Fanciulli, C., Ferdeghini, C., Gatti, F., Lehmann, E., Manfrinetti, P., Marré, D., Palenzona, A., Siri, A.S., Vignolo, M., Putti, M.: Phys. Rev. B 71, 212507 (2005)
Wen, H.H., Zhao, Z.X., Xiao, Y.G., Yin, B., Li, J.W.: Physica C 251, 371 (1995)
Blatter, G., Feigelman, M.V., Geshkenbein, V.B., Larkin, A.I., Vinokur, V.M.: Rev. Mod. Phys. 66, 1125 (1994)
Wen, H.H., Zhao, Z.X., Wang, R.L., Li, H.C., Yin, B.: Physica C 262, 81 (1996)
Ben Salem, M.K., Hamrita, A., Hannachi, E., Slimani, Y., Ben Salem, M., Ben Azzouz, F.: Physica C 498, 38–44 (2014)
Jha, A.K., Khare, N., Pinto, R.: J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 25, 377–380 (2012)
Xiang, F.X., Wang, X.L., Xun, X., De Silva, K.S.B., Wang, Y.X., Dou, S.X.: Appl. Phys. Lett. 102, 152601 (2013)
Ghorbani, S.R., Wang, X.L., Dou, S.X., Lee, S.-I., Hossain, M.S.A.: Phys. Rev. B 78, 184502 (2008)
Zeng, R., Dou, S.X., Lu, L., Li, W.X., Kim, J.H., Munroe, P., Zheng, R.K., Ringer, S.P.: Vol. 94, p 042510 (2009)
Griessen, R., Wen, Hai-hu, van Dalen, A.J.J., Dam, B., Rector, J., Schnack, H.G., Libbrecht, S., Osquiguil, E., Bruynseraede, Y.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 72, 1910 (1994)
Pan, H.Y., Xu, X.L., Guo, J.D.: Mats. Lett. 57, 3869 (2003)
Alikhanzadeh-Arania, S., Salavati-Niasari, M.: JNS 1, 62 (2012)
Hamrita, A., Slimani, Y., Ben Salem, M.K., Hannachi, E., Bessais, L., Ben Azzouz, F., Ben Salem, M.: Ceram. Int. 40, 1461 (2014)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hannachi, E., Hamrita, A., Slimani, Y. et al. Effect of the Ball-Milling Technique on the Transport Current Density of Polycrystalline Superconductor YBa 2 Cu 3 O y -Pinning Mechanism. J Supercond Nov Magn 28, 493–498 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2746-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-014-2746-2