Abstract
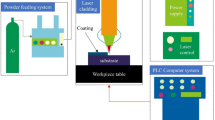
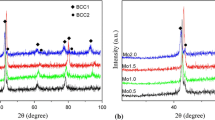
The energy distribution characteristics of fast axial flow CO2 lasers demonstrate that they are often used for cutting and welding metal materials, and it is generally believed that they are not suitable for material heat treatment. In order to expand the application range of these lasers, we prepare graphene (Gr) reinforced high entropy alloy (HEA) coatings, employing this type of laser under loworder mode conditions by adjusting processing parameters and cladding powder composition through orthogonal experiments. Then we study the effect of laser processing parameters on Gr/AlxCoCrNiTi composite coatings. The research results indicate that the optimum process parameters are as follows: the laser power P = 3200 W, the scanning speed V = 14 mm/s, the cladding powder thickness d = 1.2 mm, and the spot diameter D = 4.0 mm. We find that, under the optimum process parameters, the Gr/AlxCoCrNiTi laser cladding coatings exhibit typical dendrites and equiaxed grains. The microstructure refines with increase in the Al content. The Gr/AlxCoCrNiTi laser cladding coating mainly consists of the face centered cubic (FCC), body centered cubic (BCC), and M23C6. Increase in the Al content promotes the formation of the BCC structure. The microhardness of Gr/AlxCoCrNiTi composite coatings range from 550 to 725 HV. The hardness is related to the solid solution strengthening caused by Gr and Al. With increase in the Al content, the microhardness of the coating shows a trend to increase, the wear resistance first increases and then decreases. The wear resistance is related to the BCC content and cracks in the coating. Orthogonal experiments and coating performance indicate that, by adjusting laser processing parameters and alloy composition, it is possible for fast axial flow CO2 lasers to prepare Gr/AlxCoCrNiTi composite coatings under low-order mode conditions, which can expand the applicability of these lasers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Chen, Y.-J. Guan, G. Jin, et al., Surf. Coat. Tech., 461, 129447 (2023).
C.-G. Liu, X.-W. Qiu, J. Peng, et al., Opt. Laser. Eng., 163, 107458 (2023).
Q. Zhang, Q. Wang, B. Han, et al., J. Alloy. Compd., 947, 169517 (2023).
F.-K. Shi, Q.-K. Zhang, C. Xu, et al., Opt. Laser. Technol., 151, 108020 (2022).
Q. Zhu, Y. Liu, and C.-Y. Zhang, Mater. Lett., 318, 132133 (2022).
Z.-F. Sun, J.-H. Kang, Z. Zhang, et al., Opt. Commun., 527, 128946 (2023).
J.-H. Kang, B. Wu, Z. Zhang, et al., Opt. Laser. Eng., 142, 106591 (2021).
W.-C. Lai, P.-F. Ma, W. Liu, et al., Opt. Laser. Eng., 149, 106826 (2022).
C. O. Saeed, A. A. Qader, S. B. Aziz, et al., Opt. Mater., 132, 112815 (2022).
H. Christian, S. Peter, W. Rudolf, et al., Opt. Laser. Eng., 100, 131 (2018).
X.-M. Qin, Y. Xu, Y.-F. Sun, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 782, 139277 (2020).
O. N. Senkov and D. B. Miracle, J. Alloy. Compd., 658, 603 (2016).
S. Park, H. Nam, J. Park, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 788, 139547 (2020).
D.-C. Zhao, T. Yamaguchi, D. Tusbasa, et al., Mater. Des., 193, 108872 (2020).
X. Yang and Y. Zhang, Mater. Chem. Phys., 132, 233 (2012).
L. Yuan, J.-T. Xiong, Y. J. Du, et al., J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 61, 176 (2021).
X.-W. Qiu, J. Alloy. Compd., 887, 161422 (2021).
X.-W. Qiu, J. Mater. Res. Technol., 9, 5127 (2020).
W. M. Choi, Y. H. Jo, S. S. Sohn, et al., NPJ Comput. Mater., 3, 39 (2019).
Y.-Z. Wang and Y.-J. Wang, Acta Mater., 224, 117527 (2022).
Z.-J. Wang, C.-T. Liu, and P. Dou, Phy. Rev. Mat., 1, 043601 (2017).
B. Gludovatz, A. Hohenwarter, D. Catoor, et al., Science, 345, 1153 (2014).
W. Li, D. Xie, D. Li, et al., Prog. Mater. Sci., 118, 100777 (2021).
J.-C. Li, X.-C. Meng, L. Wan, et al., J. Manuf. Process, 68, 293 (2021).
B. Cantor, I. Chang, P. Knight, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 375, 213 (2004).
O. N. Senkov, G. Wilks, D. Miracle, et al., Intermetallics, 18, 1758 (2010).
O. N. Senkov, G. Wilks, and J. Scott, Intermetallics, 19, 698 (2011).
X. Nie, M. Cai, and S. Cai, Int. J. Refract Met. Hard Mater., 98, 105568 (2021).
S. Huang, W. Li, O. Eriksson et al., Acta Mater., 199, 53 (2020).
K.-D. Yu, W. Zhao, Z. Li, et al., Surf. Coat. Tech., 458, 129352 (2023).
X.-F. Li, Y.-B. Feng, X. Wang, et al., J. Alloy. Compd., 926, 166778 (2022).
T. Wang, C. Wang, J.-J. Li, et al., Mater. Charact., 193, 112314 (2022).
X. Wen, X.-F. Cui, G. Jin, et al., Intermetallics, 156, 107851 (2023).
K.-D. Yu, W. Zhao, Z. Li, et al., Ceram. Int., 49, 10151 (2023).
Z.-Q. Cui, Z. Qin, P. Dong, et al., Mater. Lett., 259, 126769 (2020).
C.-Y. Liu, X.-S. Jiang, H.-L. Sun, et al., Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 859, 144198 (2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, X. Effect of Fast Axial Flow CO2 Laser Processing Parameters on Graphene/AlxCoCrNiTi High Entropy Alloy. J Russ Laser Res 44, 470–479 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-023-10154-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-023-10154-6