Abstract
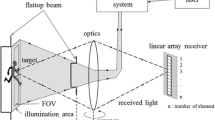
The beaconless acquisition pointing and tracking (APT) system uses signal light to act as beacon. But the signal light’s divergence angle is so small that it is difficult to capture. In this work, aiming at the different requirements of divergence angle for a free-space optical-communication (FSO) system in a different working phase, we use a stepper motor for automatic focusing control in the acquisition and pointing process to change the spot size. For this purpose, we derive a formula for the average acquisition time of continuous raster scanning. The relationship between the received power and the divergence angle under the influence of the atmospheric transmission and the pointing errors is analyzed to obtain the optimum range of the divergence angle. Also the relationship between defocusing and the divergence angle of collimated beam is given. Finally, we prove by experiments that the automatic focusing control method effectively solves the contradiction of the different divergence angles between communication phase and acquisition phase.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. T. Nielsen, Proc. SPIE, 2381, 194 (1995).
X. Ma, L. Liu, X. Zhang, and J. Tang, Appl. Opt., 49, 718 (2010).
B. Tu, L. Liu, Y. Liu, et al., Appl. Opt., 52, 3147 (2013).
K. J. Held, and J. D. Barry, Opt. Eng., 27, 325 (1988).
S. Bai, J. Qiang, L. Zhang, and J. Wang, Opt. Lett., 40, 3750 (2015).
J. Wang, J. M. Kahn, and K. Y. Lau, Appl. Opt., 41, 7592 (2002).
X. Li, S. Yu, J. Ma, and L. Tan, Opt. Express, 19, 2381 (2011).
D. He, Q. Wang, B. Qi, et al., Appl. Opt., 57, 1351 (2018).
T. T. Nguyen, K. M. Riesing, R. W. Kingsbury, and K. Cahoy, Proc. SPIE, 9354, 93540O (2015).
B. Smutny, R. Lange, H. K¨ampfner, and K. Cahoy, Proc. SPIE, 6877, 687702 (2008).
X. Li, S. Yu, J. Ma, et al., J. Russ. Laser Res., 33, 143 (2012).
T. Tolker-Nielsen and G. Oppenhauser, Proc. SPIE, 4635, 1 (2002).
J. W. Alexander, S. Lee, and C. Chen, Proc. SPIE, 3615, 230 (1999).
J. C. Ricklin and F. M. Davidson, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A, 19, 1794 (2002).
J. Wang, J. Lv, G. Zhang, and G. Wang, Opt. Express, 23, 20655 (2015).
V. V. Mai and H. Kim, IEEE Photon. J., 11, 1 (2019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ke, X., Zhang, P. Automatic Focusing Control in Beaconless APT System. J Russ Laser Res 41, 61–71 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-020-09848-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10946-020-09848-y