Abstract
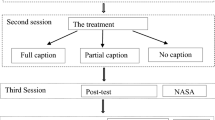
The present study examines the impact of implementing video captioning and subtitles on listening comprehension with special reference to the speaker’s speed. A total of 64 undergraduate Saudi EFL learners were assigned into six groups: fast speaker with full captioning, fast speaker with subtitles, fast speaker with no captioning nor subtitles, slow speaker with full captioning, and slow speaker with subtitles, slow speaker with no captioning nor subtitles. Each group was instructed to watch a video in English under its assigned condition and then answered a listening test. Participants also answered a questionnaire to determine the impact of these conditions on their cognitive load. The results revealed that the group that viewed the video of slow speakers with a caption obtained the highest score on the listening comprehension test, followed by the group that viewed the video of fast speakers with a caption. The group that viewed no caption video of fast speakers obtained the lowest scores. The questionnaire analysis indicated that the students in the subtitle slow group reported using low mental effort, whereas the students in the caption fast group reported using very high mental effort followed by the students in the caption slow group who also reported using high mental effort.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Aldera, A. S., & Mohsen, M. A. (2013). Annotations in captioned animation: Effects on vocabulary learning and listening skills. Computers & Education, 68, 60–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2013.04.018.
Almeida, P., & Costa, P. (2014). Foreign language acquisition: The role of subtitling. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 141(25), 1234–1238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.05.212.
Avello, D., & Muñoz, C. (2023). The development of receptive language skills from captioned video viewing in primary school EFL learners. Education Sciences, 13(5), 479.
Başaran, H., & Köse, G. (2013). The effects of captioning on EFL learners’ listening comprehension. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 70, 702–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.01.112.
Bird, S. A., & Williams, J. N. (2002). The effect of bimodal input on implicit and explicit memory: An investigation into the benefits of within-language subtitling. Applied Psycholinguistics, 23(4), 509–533. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0142716402004022.
Black, S. (2022). Subtitles as a tool to boost language learning and intercultural awareness? Children’s views and experiences of watching films and television programmes in other languages with interlingual subtitles. Journal of Audiovisual Translation, 5(1), 73–93. https://doi.org/10.47476/jat.v5i1.2022.157.
Blau, E. K. (1990). The effect of syntax, speed, and pauses on listening comprehension. TESOL Quarterly, 24(4), 746–753. https://doi.org/10.2307/3587129.
Brown, G., & Yule, G. (1983). Teaching the spoken language. Cambridge University Press.
Buck, G. (2001). Assessing listening. Cambridge University Press.
Chang, A. C. S. (2018). Speech rate in second language listening. In J. I. Liontas, & T. E. S. O. L. International Association (Eds.), The TESOL Encyclopedia of English Language Teaching (pp. 1–6). Wiley. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118784235.eelt0576.
Chiu, C. W., & Chen, T. P. (2023). Speech rate and young EFL learners’ listening comprehension. English Language Teaching, 16(7), 74–80. https://doi.org/10.5539/elt.v16n7p74.
Cooper, G. (1990). Cognitive load theory as an aid for instructional design. Australasian Journal of Educational Technology, 6(2), 108–113. https://doi.org/10.14742/AJET.2322.
Council of Europe. (2001). Common European framework of reference for languages: Learning, teaching, assessment. Cambridge University Press.
Dizon, G., & Thanyawatpokin, B. (2021). Language learning with Netflix: Exploring the effects of dual subtitles on vocabulary learning and listening comprehension. Computer Assisted Language Learning Electronic Journal, 22(3), 52–65.
d’Ydewalle, G., & Pavakanum, U. (1992). Watching foreign television programs and language learning. In F. Engels, D. Bouwhuis, T. Bösser, & G. d’Ydewalle (Eds.), Cognitive modelling and interactive environments in language learning (pp. 193–198). Springer-.
d’Ydewalle, G., & Van de Poel, M. (1999). Incidental foreign-language acquisition by children watching subtitled television programs. Journal of Psycholinguistic Research, 28(3), 227–244. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023202130625.
East, M., & King, C. (2012). L2 learners’ engagement with high stakes listening tests: Does technology have a beneficial role to play? CALICO Journal, 29(2), 208–223.
Flaherty, S. E. (1979). Rate-controlled speech in foreign language education. Foreign Language Annals, 12, 275–280. https://www.jstor.org/stable/calicojournal.29.2.208.
Goh, C. C. (2000). A cognitive perspective on language learners’ listening comprehension problems. System, 28(1), 55–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0346-251X(99)00060-3.
Griffiths, R. (1990). Speech rate and nonnative speaker comprehension: A preliminary study in the time-benefit analysis. Language Learning, 40, 311–336. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-1770.1990.tb00666.x.
Guillory, H. G. (1998). The effects of key word captions to authentic French video in foreign language instruction. CALICO Journal, 15(1–3), 89–108. https://doi.org/10.1558/cj.v15i1-3.89-108.
Hamouda, A. (2013). An investigation of listening comprehension problems encountered by Saudi students in the EL listening classroom. International Journal of Academic Research in Progressive Education and Development, 2(2), 113–155.
Hao, T., Sheng, H., Ardasheva, Y., & Wang, Z. (2021). Effects of dual subtitles on Chinese students’ English listening comprehension and vocabulary learning. The Asia-Pacific Education Researcher, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40299-021-00601-w.
Harmer, J. (2001). The practice of English language teaching. Pearson Education Limited.
Hayati, A. (2010). The effect of speech rate on listening comprehension of EFL learners. Creative Education, 1(2), 107–114. https://doi.org/10.4236/ce.2010.12016.
Hayati, A., & Mohmedi, F. (2011). The effect of films with and without subtitles on listening comprehension of EFL learners. British Journal of Educational Technology, 42(1), 181–192. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8535.2009.01004.x.
Hermida, R. (2021). Listening comprehension difficulties faced by EFL students. Accentia: Journal of English Language and Education, 1(2), 78–86.
Hsieh, Y. (2019). Effects of video captioning on EFL vocabulary learning and listening comprehension. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 33(5–6), 567–589. https://doi.org/10.1080/09588221.2019.1577898.
Jones, L. C., & Plass, J. L. (2002). Supporting listening comprehension and vocabulary acquisition in French with multimedia annotations. The Modern Language Journal, 86(4), 546–561. https://doi.org/10.1111/1540-4781.00160.
Koolstra, C. M., & Beentjes, J. W. (1999). Children’s vocabulary acquisition in a foreign language through watching subtitled television programs at home. Educational Technology Research and Development, 47, 51–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02299476.
Korucu-kiş, S. (2021). On the effectiveness and limitations of captioning in L2 listening. International Journal of Modern Education Studies, 5(2), 516–536. https://doi.org/10.51383/ijonmes.2021.153.
Lee, P. J., Liu, Y. T., & Tseng, W. T. (2021). One size fits all? In search of the desirable caption display for second language learners with different caption reliance in listening comprehension. Language Teaching Research, 25(3), 400–430. https://doi.org/10.1177/1362168819856451.
Leppink, J., Paas, F., Van der Vleuten, C. P., Van Gog, T., & Van Merriënboer, J. J. (2013). Development of an instrument for measuring different types of cognitive load. Behavior Research Methods, 45(4), 1058–1072. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13428-013-0334-1.
Lin, C. C., & Yu, Y. C. (2017). Effects of presentation modes on mobile-assisted vocabulary learning and cognitive load. Interactive Learning Environments, 25(4), 528–542. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2016.1155160.
Linebarger, D., Piotrowski, J. T., & Greenwood, C. R. (2010). On-screen print: The role of captions as a supplemental literacy tool. Journal of Research in Reading, 33(2), 148–167. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9817.2009.01407.x.
Lin, J. J. H., Lee, Y. H., Wang, D. Y., & Lin, S. S. J. (2016). Reading subtitles and taking enotes while learning scientific materials in a multimedia environment: Cognitive load perspectives on EFL students. Educational Technology & Society, 19(4), 47–58.
Lin, P. (2022). Developing an intelligent tool for computer-assisted formulaic language learning from YouTube videos. ReCALL, 34(2), 185–200. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0958344021000252.
Markham, P., & Peter, L. (2003). The influence of English language and Spanish language captions on foreign language listening/reading comprehension. Journal of Educational Technology Systems, 31(3), 331–341. https://doi.org/10.2190/BHUH-420B-FE23-ALA0.
McBride, K. (2011). The effect of rate of speech and distributed practice on the development of listening comprehension. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 24(2), 131–154.
Metruk, R. (2018). The effects of watching authentic English videos with and without subtitles on listening and reading skills of EFL learners. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics Science and Technology Education, 14(6), 2545–2553. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/90088.
Mirzaei, M. S., Akita, Y., & Kawahara, T. (2014). Partial and synchronized captioning: A new tool for second language listening development. In S. Jager, L. Bradley, E. J. Meima, & S. Thouësny (Eds.), CALL Design: Principles and Practice; Proceedings of the 2014 EUROCALL Conference, Groningen, The Netherlands (pp. 230–236). Research-publishing.net.
Mohsen, M. A., & Mahdi, H. S. (2021). Partial versus full captioning mode to improve L2 vocabulary acquisition in a mobile-assisted language learning setting: Words pronunciation domain. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 33(2), 524–543.
Montero Perez, M. M., Noortgate, W. V., & Desmet, P. (2013). Captioned video for L2 listening and vocabulary learning: A meta-analysis. System, 41, 720–739. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.system.2013.07.013.
Montero Perez, M. M., Peters, E., & Desmet, P. (2014). Is less more? Effectiveness and perceived usefulness of keyword and full captioned video for L2 listening comprehension. ReCALL, 26(1), 21–43. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0958344013000256.
Plass, J., & Jones, L. (2005). Multimedia learning in second language acquisition. In R. Mayer (Ed.), The Cambridge handbook of multimedia learning (pp. 467–488). Cambridge University Press.
Pujadas, G., & Munoz, C. (2020). Examining adolescent EFL learners’ TV viewing comprehension through captions and subtitles. Studies in Second Language Acquisition, 42(3), 551–575. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0272263120000042.
Rost, M. (2002). Teaching and researching listening. Longman.
Sefer, A., & Benzer, A. (2020). Listening skill with a holistic approach in teaching Turkish as a foreign language. IJLA, 8(3), 123–142. https://doi.org/10.29228/ijla.42254.
Sohn, J. (2023). Recognition of the usefulness of drama subtitles: Focusing on listening learning. Korean Education Research, 18, 21–44. https://doi.org/10.25022/jkler.2023.18.021.
Sweller, J. (2010). Cognitive Load Theory: Cognitive Load Theory: Recent Theoretical Advances. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511844744.004.
Sweller, J., Ayres, P., & Kalyuga, S. (2011). Intrinsic and extraneous cognitive load. In J. Sweller, P. Ayres, & S. Kalyuga (Eds.), Cognitive load theory (pp. 57–69). Springer.
Sweller, J., van Merriënboer, J. J., & Paas, F. (2019). Cognitive architecture and instructional design: 20 years later. Educational Psychology Review, 31(2), 261–292. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10648-019-09465-5.
Taylor, G. (2005). Perceived processing strategies of students watching captioned video. Foreign Language Annals, 38(3), 422–427. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1944-9720.2005.tb02228.x.
Teng, F. (2019). Maximizing the potential of captions for primary school ESL students’ comprehension of English-language videos. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 32(7), 665–691. https://doi.org/10.1080/09588221.2018.1532912.
Vanderplank, R. (1988). The value of teletext subtitles in language learning. ELT Journal, 42(4), 272–281. https://doi.org/10.1093/elt/42.4.272.
Vanderplank, R. (2016). The state of the art I: Selected research on listening comprehension and vocabulary acquisition. In R. Vanderplank(Ed.), Captioned Media in Foreign Language Learning and Teaching (pp. 75–104). Palgrave Macmillan.
Winke, P., Gass, S., & Sydorenko, T. (2010). The effects of captioning videos used for foreign language listening activities. Language Learning & Technology, 14(1), 65–86.
Winke, P., Gass, S., & Sydorenko, T. (2013). Factors influencing the use of captions by foreign language learners: An eye-tracking study. The Modern Language Journal, 97(1), 254–275. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2016.1155160.
Yang, J. C., & Chang, P. (2014). Captions and reduced forms instruction: The impact on EFL students’ listening comprehension. ReCALL, 26(1), 44–61. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0958344013000219.
Yuksel, D., & Tanriverdi, B. (2009). Effects of watching captioned movie clip on vocabulary development of EFL learners. The Turkish Online Journal of Educational Technology, 8(2), 48–54.
Zhao, Y. (1997). The effects of listeners’ control of speech rate on second language comprehension. Applied Linguistics, 18, 49–68. https://doi.org/10.1093/applin/18.1.49.
Zheng, Y., Ye, X., & Hsiao, J. H. (2022). Does adding video and subtitles to an audio lesson facilitate its comprehension? Learning and Instruction, 77, 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2021.101542.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University for supporting and funding this project.
Funding
This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU-RG23007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
Based on Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) institutional review board rules and regulations, the instruments used in this research were reviewed and approved. The IRB approval number (638360259258732698) was granted.
Clinical Trial Registration
Not applicable.
Permission to Reproduce Material from Other Sources
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The author has no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix A
All of the following questions refer to the activity (watching the video) that you have just finished. Please respond to each of the questions on the following scale (1 = strongly disagree, 2 = disagree, 3 = neutral, 4 = agree, 5 = strongly agree).
-
1.
The topic covered in the video was/were very complex.
-
2.
The activity covered ideas that I perceived as very complex.
-
3.
The activity covered concepts and definitions that I perceived as very complex.
-
4.
The explanations during the activity were very unclear.
-
5.
The explanations were, in terms of learning, very ineffective.
-
6.
The explanations were full of unclear language.
-
7.
The activity really enhanced my understanding of the topic covered.
-
8.
The activity really enhanced my knowledge of the ideas covered.
-
9.
The activity really enhanced my understanding of the ideas covered.
-
10.
The activity really enhanced my understanding of concepts and definitions.
Please choose the category (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9) that applies to you:
A In the video that I have just listened to, I invested.
-
1.
Very, very low mental effort.
-
2.
Very low mental effort.
-
3.
Low mental effort.
-
4.
Rather low mental effort.
-
5.
Neither low nor high mental effort.
-
6.
Rather high mental effort.
-
7.
High mental effort.
-
8.
Very high mental effort.
-
9.
Very, very high mental effort.
B The video that just finished was:
-
1.
Very, very easy.
-
2.
Very easy.
-
3.
Easy.
-
4.
Rather easy.
-
5.
Neither easy nor difficult.
-
6.
Rather difficult.
-
7.
Difficult.
-
8.
Very difficult.
-
9.
Very, very difficult.
C How much did you concentrate while listening to the video?
-
1.
Very, very little.
-
2.
Very little.
-
3.
Little.
-
4.
Rather little.
-
5.
Neither little nor much.
-
6.
Rather much.
-
7.
Much.
-
8.
Very much.
-
9.
Very, very much.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Almusharraf, A., Mahdi, H.S., Al-Nofaie, H. et al. Video Captioning and Subtitles in Second Language Listening Comprehension: Fast-Paced Versus Slow-Paced Speakers. J Psycholinguist Res 53, 29 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-024-10070-z
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10936-024-10070-z