Abstract
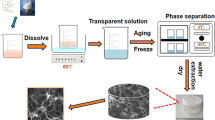
This work reports the design and fabrication of scaffolds made of aggregated microparticles of either polycaprolactone (PCL) or PCL loaded with hydroxyapatite (HA) nanoparticles for tissue engineering purposes. The scaffolds are obtained by the thermally induced phase separation (TIPS) technique, employing ethyl lactate (EL) as a green solvent for PCL processing, which avoided the use of potentially toxic chemicals. The TIPS process was further improved by using NaCl particles as a leachable porogen to obtain highly porous scaffolds with an interconnected network of large pores. The scaffolds were characterized to assess the effect of the processing conditions on their thermal properties, crystallinity, morphology and porous structure. The results of this study demonstrate that porous PCL and PCL-HA scaffolds, with architecture of aggregated microparticles, can be achieved by dissolving the polymer in an EL/water mixture and optimizing the freezing temperature. Besides, the incorporation of HA nanoparticles into the polymer resulted in scaffolds with a more heterogeneous morphology and structure. Concomitantly, the NaCl particles enabled to enhance the scaffolds porosity up to a value of 92 %, while they induced the formation of a highly interconnected network of large pores inside the aggregated microparticles structure.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
F.J. O’Brien, Materialstoday 14, 88 (2011)
T. Tateishi, G. Chen, T. Ushida, J. Art. Org. 5, 77 (2002)
A. Salerno, D. Guarnieri, M. Iannone, S. Zeppetelli, P.A. Netti, Tissue Eng. Part A 16, 2661 (2010)
H. Zhang, L. Zhou, W. Zhang, Tissue Eng. Part B (in press). doi:10.1089/ten.teb.2013.0452
L.S. Nair, C.T. Laurencin, Prog. Polym. Sci. 32, 762 (2007)
P.A. Gunatillake, R. Adhikari, Eur. Cells Mater. 5, 1 (2003)
A. Salerno, M. Oliviero, E. Di Maio, S. Iannace, P.A. Netti, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 21, 2569 (2010)
J.R. Jones, Acta Biomater. 9, 4457 (2013)
J.L. Simon, S. Michna, J.A. Lewis, E.D. Rekow, V.P. Thompson, J.E. Smay, A. Yampolsky, J.R. Parsons, J.L. Ricci, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 83A, 747 (2007)
R. Murugan, S. Ramakrishna, Compos. Sci. Technol. 65, 2385 (2005)
A. Salerno, S. Zeppetelli, E. Di Maio, S. Iannace, P.A. Netti, Compos. Sci. Technol. 70, 1838 (2010)
S. Heo, S. Kim, J. Wei, Y. Hyun, H. Yun, D. Kim, J.W. Shin, J. Shin, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 89A, 108 (2009)
V. Karangeorgiou, D. Kaplan, Biomaterials 26, 5474 (2005)
S. Yang, K. Leong, Z. Du, C. Chua, Tissue Eng. 7, 679 (2001)
X. Liu, P.X. Ma, Biomaterials 30, 4094 (2009)
M. Singh, B. Sandhu, A. Scurto, C. Berkland, M.S: Detamore. Acta Biomater. 6, 137 (2010)
X. Shi, L. Ren, M. Tian, J. Yu, W. Huang, C. Du, D. Wang, Y. Wang, J. Mater. Chem. 20, 9140 (2010)
A. Salerno, R. Levato, M.A. Mateos-Timoneda, E. Engel, P.A. Netti, J.A. Planell, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 101A, 720 (2013)
M. Wang, L. Ma, D. Li, P. Jiang, C. Gao, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 101A, 3219 (2013)
A. Salerno, C. Domingo, Mater. Sci. Eng. C 42, 102 (2014)
S. Aparicio, R. Alcalde, Green Chem. 11, 65 (2009)
A. Salerno, M.A. Fanovich, C. Domingo, J. Super, Fluids 95, 394 (2014)
J. Shen, X. Chen, W. Huang, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 88, 1864 (2003)
A. Salerno, S. Zeppetelli, E. Di Maio, S. Iannace, P.A. Netti, Biotechnol. Bioeng. 108, 963 (2011)
X. Xiao, R. Liu, Q. Huang, X. Ding, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 20, 2375 (2009)
L. Liu, Y. Wang, S. Guo, Z. Wang, W. Wang, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B: Appl. Biomater. 100B, 956 (2012)
D.R. Lloyd, S.S. Kim, K.E. Kinzer, J. Membr. Sci. 64, 1 (1991)
S.S. Kim, D.R. Lloyd, J. Membr. Sci. 64, 13 (1991)
K.S. McGuire, D.R. Lloyd, G.B.A. Lim, J. Membr. Sci. 79, 27 (1993)
W.L. Murphy, R.G. Dennis, J.L. Kileny, D.J. Mooney, Tissue Eng. 8, 43 (2002)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad through the research project BIOREG (MAT2012-35161) and the CSIC Intramural Project 201460E113. Additional support has been provided by the Generalitat of Catalonia under project 2014SGR-377.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salerno, A., Domingo, C. Pore structure properties of scaffolds constituted by aggregated microparticles of PCL and PCL-HA processed by phase separation. J Porous Mater 22, 425–435 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-9911-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-015-9911-2