Abstract
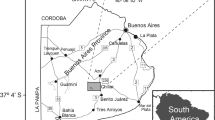
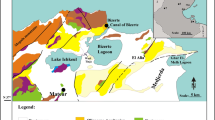
A multi-proxy analysis, including pollen, non-pollen palynomorphs and plant macrofossil remains was performed to reconstruct the paleoenvironmental history of the Cabeza de Buey shallow lake (36°17′S, 61°10′W) over the last 600 years. We identified the main forcing factors behind changes in the structure and dynamics of the lake communities. Given the relatively low intensity of human activity during the early period of the lake history (prior to 1880 AD), changes in dominant communities were mainly controlled by climate. Afterwards, changes probably resulted from a combination of climate and human impacts that generated an accelerated eutrophication. Four periods in the lake’s evolution were recognized based on changes in macrophyte and algae communities’ structure. Between ca. 1320 and ca. 1630 AD a shift was evidenced from an oligotrophic brackish with low nutrient content (dominated by Botryococcus braunii) to a mesotrophic fresh water body (dominated by Pediastrum and Scenedesmus), due to an increase in the water level associated with an increase in precipitation. At ca. 1840 AD a transition towards a phase dominated by Myriophyllum spicatum was noted, induced by a low water level as a consequence of low precipitation. Later, at ca. 1880 AD, the current lake conditions were established, and the increase in nutrient and organic matter supply influenced plant community structure towards organic tolerant species of submerged macrophytes (Potamogeton pectinatus). Towards the beginning of the twenty-first century, the lake turned to a more eutrophic state, which is evidenced by the dominance of the phytoplankton community. The last hundred years of the lake history were characterized by the eutrophication process related to the impact of agriculture and cattle breeding implemented in the landscape as well as to the urban settlement. This study made it possible to infer changes in the structure and dynamics of Cabeza de Buey lake and to elucidate the forcing factors that induced these changes on a high-resolution scale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agosta EA, Compagnucci RH (2008) The 1976/77 austral summer climate transition effects on the atmospheric circulation and climate in southern South America. J Clim 21:4365–4383
Allende L, Tell G, Zagarese H, Torremorell A, Perez G, Bustingorry J, Escaray R, Izaguirre I (2009) Phytoplankton and primary production in clear-vegetated, inorganic-turbid, and algal-turbid shallow lakes from the pampa plain (Argentina). Hydrobiologia 624:45–60
Batten DJ, Grenfell HR (1996) Chapter 7D. Botryococcus. In: Jansonius J, McGregor DC (eds) Palynology: principles and applications. Texas, American Association of Stratigraphic Palynologist Fundation, Dallas, pp 205–214
Bennett KD, Willis KJ (2001) Pollen. In: Smol JP, Birks HJB, Last WM (eds) Tracking environmental change using lake sediments: Terrestrial, Algal and Siliceous Indicators, 3. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 5–32
Bennion H, Davidson TA, Sayer CD, Simpson GL, Rose NL, Sadler JP (2015) Harnessing the potential of the multi-indicator palaeoecological approach: an assessment of the nature and causes of ecological change in a eutrophic shallow lake. Freshwater Biol 60:1423–1442
Bennion H, Sayer CD, Clarke SJ, Davidson TA, Rose NL, Goldsmith B, Rawcliffe R, Burgess A, Clarke G, Turner S, Wiik E (2017) Sedimentary macrofossil records reveal ecological change in English lakes: implications for conservation. J Paleolimnol 60(2):329–348
Blaauw M (2010) Methods and code for ‘classical’ age-modelling of radiocarbon sequences. Quat Geochronol 5:512–518
Blindow I (1992) Decline of charophytes during eutrophication: comparison with angiosperms. Freshwater Biol 28:9–14
Borel CM, Guerstein GR, Prieto AR (2003) Palinomorfos acuáticos (algas y acritarcos) del Holoceno de la laguna Hinojales (Buenos Aires, Argentina): interpretación paleoecológica. Ameghiniana 40:531–544
Cano MG, Casco MA, Solari LC, Mac Donagh ME, Gabellone NA, Claps MC (2008) Implications of rapid changes in chlorophyll-a of plankton, epipelon, and epiphyton in a Pampean shallow lake: an interpretation in terms of a conceptual model. Hydrobiologia 614:33–45
Cano MG, Casco MA, Claps MC (2016) Epipelon dynamics in a shallow lake through a turbid-and a clear-water regime. J Limnol. https://doi.org/10.4081/jlimnol.2016.1340
Cony NL, Ferrer NC, Cáceres EJ (2014) Evolución del estado trófico y estructura del fitoplancton de un lago somero de la Región Pampeana: laguna Sauce Grande (provincia de Buenos Aires, Argentina). Biología Acuática 30:70–91
Córdoba F, Guerra L, Cuña Rodríguez C, Sylvestre F, Piovano EL (2014) Una visión paleolimnológica de la variabilidad hidroclimática reciente en el centro de Argentina: desde la Pequeña Edad de Hielo al siglo XXI. Lat Am J Sedimentol Basin Anal 21:139–163
Egertson CJ, Kopaska JA, Downing JA (2004) A century of change in macrophyte abundance and composition in response to agricultural eutrophication. Hydrobiologia 524:145–156
Fontana SL (2005) Holocene vegetation history and palaeoenvironmental conditions of the temperate Atlantic coast of Argentina, as inferred from multiple proxy lacustrine records. J Paleolimnol 34:445–469
Fontijn K, Rawson H, Van Daele M, Moernaut J, Abarzúa AM, Heirman K, Bertrand S, Pyle DM, Mather TA, De Batist M, Naranjo JA, Moreno H (2016) Synchronisation of sedimentary records using tephra: a postglacial tephrochronological model for the Chilean Lake District. Quaternary Sci Rev 137:234–254
Garavaglia JC (1999) Pastores y labradores de Buenos Aires. Una historia agraria de la campaña bonaerense 1700–1840. Buenos Aires, Ediciones de la Flor, p 408
García P, Fernández R, Cirujano S (2009) Habitantes del agua Macrófitos. Editorial Monto Cultura, 278 pp
Geraldi AM, Piccolo MC, Perillo GME (2011) El rol de lagunas bonaerenses en el paisaje pampeano. Ciencia Hoy 21:8–14
Ghersa CM, Martinez Ghersa MA (1991) Cambios Ecológicos en los Agroecosistemas de la Pampa Ondulada. Efectos de la Introducción de la Soja. Cienc Invest 5:182–188
Grimm E (2015) Tilia Software. Springfield, Illinois State Museum
Guerra L, Piovano EL, Córdoba FE, Sylvestre F, Damatto S (2015) The hydrological and environmental evolution of shallow Lake Melincué, central Argentinean Pampas, during the last millennium. J Hydrol 529:570–583
Heiri O, Lotter AF, Lemcke G (2001) Loss on ignition as a method for estimating organic and carbonate content in sediments: reproducibility and comparability of results. J Paleolimnol 25:101–110
Hogg AG, Hua Q, Blackwell PG, Niu M, Buck CE, Guilderson TP, Heaton TJ, Palmer JG, Reimer PJ, Reimer RW, Turney CS, Zimmerman SRH (2013) SHCal13 Southern Hemisphere calibration, 0–50,000 years cal BP. Radiocarbon 55:1889–1903
Izaguirre I, Allende L, Escaray R, Bustingorry J, Pérez G, Tell G (2012) Comparison of morpho-functional phytoplankton classifications in human-impacted shallow lakes with different stable states. Hydrobiologia 698:203–216
Kowalewski GA, Kornijów R, McGowan S, Kaczorowska A, Bałaga K, Namiotko T, Gąsiorowski M, Wasiłowska A (2016) Disentangling natural and anthropogenic drivers of changes in a shallow lake using palaeolimnology and historical archives. Hydrobiologia 767:301–320
Labraga JC, Scian B, Frumento O (2002) Anomalies in the atmospheric circulation associated with the rainfall excess or deficit in the Pampa Region in Argentina. J Geophys Res Atmos. https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002113
Laprida C, Valero-Garcés B (2009) Cambios ambientales de épocas históricas en la pampa bonaerense en base a ostrácodos: historia hidrológica de la laguna de Chascomús. Ameghiniana 46:95–111
Laprida C, Orgeira MJ, García Chapori N (2009) El registro de la Pequeña Edad de Hielo en lagunas pampeanas. Revista de la Asociación Geológica Argentina 65:603–611
Laprida C, Massaferro J, Mercau R, Josefina M, Cusminsky G (2014) Paleobioindicadores del fin del mundo: ostrácodos y quironómidos del extremo sur de Sudamérica en ambientes lacustres cuaternarios. Lat Am J Sedimentol Basin Anal 21:97–117
Leon RJC (1991) Vegetacion. In: Coupland RT (ed) Ecosystems of the World 8A. Natural Grasslands. Introduction and Western Hemisphere, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, Elsevier, pp 380–387
Mancini M, Salinas V, Biolé F, Morra G, Montenegro H (2013) Nuevo registro para la provincia de Córdoba (Argentina) y aportes a la ecología de Parapimelodus valenciennis (Pisces, Pimelodidae). Bioscriba 6:1–8
Martinez AM (1967) San Carlos de Bolivar. Impresiones Schmidel, Buenos Aires, p 506
Medeanic S (2006) Freshwater algal palynomorph records from Holocene deposits in the coastal plain of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Rev Palaeobot Palyno 141:83–101
Messineo PG, Tonello MS, Stutz S, Tripaldi A, Scheifler N, Pal N, Sanchez Vuihard G, Navarro D (2019) Human occupation strategies and related environmental-climate during the middle and late Holocene in central Pampas of Argentina. Holocene 29:244–261
O’Farrell I, Izaguirre I, Chaparro G, Unrein F, Sinistro R, Pizarro H, Rodríguez P, Tezanos Pinto P, Lombardo R, Tell G (2011) Water level as the main driver of the alternation between a free-floating plant and a phytoplankton dominated state: a long-term study in a floodplain lake. Aquat Sci 73:275–287
Piovano EL, Ariztegui D, Moreira SD (2002) Recent environmental changes in Laguna Mar Chiquita (central Argentina): a sedimentary model for a highly variable saline lake. Sedimentology 49:1371–1384
Piovano EL, Ariztegui D, Cordoba F, Cioccale M, Sylvestre F (2009) Hydrological variability in South America below the Tropic of Capricorn (Pampas and Patagonia, Argentina) during the last 13.0. In: Vimeux F (ed) Past Climate Variability in South America and Surrounding Regions: from the Last Glacial Maximum to the Holocene. Dev Paleoenviron Res, Springer, New York, pp 323–351
Plastani MS, Laprida C, Montes de Oca F, Massaferro J, Panarello HO, Ramón Mercau J, Lami A (2019) Recent environmental changes inferred from sediments in a shallow lake of the Argentinean pampas. J Paleolimnol 61:37–52
Plastani (2016) Ostrácodos y paleolimnología del sur de la pampa bonaerense: reconstrucción de parámetros ambientales y climáticos para el Holoceno Tardío. Ph. D. Thesis. University of Buenos Aires, Argentina
Poggio SL, Perelman SB, Mollard FPO, Leon RJC (2015) Guests and gatecrashers in a New World’s banquet: Old World plant species introduced from the Mediterranean Basin enriched the flora of grasslands and croplands in the Pampas of Argentina. Flora Mediterránea 25:39–54
Prieto AR (1996) Late quaternary vegetational and climatic changes in the Pampa grassland of Argentina. Quaternary Res 45:73–88
Prieto AR (2000) Vegetational history of the Late glacial-Holocene transition in the grassland of eastern Argentina. Palaeogeogr Palaeocl 157:167–188
Quirós R, Boveri MB, Renella AM, Rosso J, Sosnovsky A, von Bernard HT (2006) Los efectos de la agriculturización del humedal pampeano sobre la eutrofización de sus lagunas. Causas, conseqüências e tecnologias de gerenciamentoe controle. Eutrofização na América do Sul: 1–16
Quirós R, Rennella AM, Boveri MB, Rosso JJ, Sosnovsky A (2002) Factores que afectan la estructura y el funcionamiento de las lagunas pampeanas. Ecología austral 12:175–185
Reynolds CS (2006) Ecology of phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, p 535
Rull V, Lara A, Rubio-Inglés MJ, Giralt S, Gonçalves V, Raposeiro P, Hernandez A, Sanchez-Lopez G, Vazquez-Loureiro D, Bao R, Masque P, Masqué P (2017) Vegetation and landscape dynamics under natural and anthropogenic forcing on the Azores Islands: a 700-year pollen record from the São Miguel Island. Quaternary Sci Rev 159:155–168
Sánchez ML, Lagomarsino L, Allende L, Izaguirre I (2015) Changes in the phytoplankton structure in a Pampean shallow lake in the transition from a clear to a turbid regime. Hydrobiologia 752:65–76
Sanchez Vuichard G (2019) Historia reciente (últimos 500 años) de los lagos someros de la llanura Pampeana a partir del análisis de múltiples indicadores. Ph. D. Thesis. National University of Mar del Plata, Argentina
Sanzano P, Grosman F, Colasurdo V (2014) Estudio limnologico de laguna Blanca Chica (Olavarria, Provincia de Buenos Aires) durante un periodo de sequía. Biol Acuat 30:189–202
Sayer CD, Burgess A, Kari K, Davidson TA, Peglar S, Yang H, Rose N (2010) Long-term dynamics of submerged macrophytes and algae in a small and shallow, eutrophic lake: implications for the stability of the macrophyte dominance. Freshwater Biol 55:565–583
Scheffer M (1998) Ecology of shallow lakes. Ed. Chapman & Hall. Londres, 357 pp.
Stutz S, Borel CM, Fontana SL, del Puerto L, Inda H, García-Rodriguez F, Tonello MS (2010) Late Holocene environmental evolution of Nahuel Rucá freshwater shallow lake, SE Pampa grasslands, Argentina. J Paleolimnol 44:761–775
Stutz S, Borel CM, Fontana SL, Tonello MS (2012) Holocene evolution of three shallow lakes in the SE Pampa plain (Argentina) as evidenced by analyses of pollen, non-pollen palynomorphs and plant macrofossils. Holocene 22:1215–1222
Stutz S, Tonello MS, González Sagrario MS, Navarro D, Fontana SL (2014) Historia ambiental de los lagos someros de la llanura Pampeana (Argentina) desde el Holoceno medio: inferencias paleoclimáticas. Lat Am J Sedimentol Basin Anal 21:119–138
Tietze E, De Francesco CG (2010) Environmental significance of freshwater mollusks in the Southern Pampas, Argentina: to what detail can local environments be inferred from mollusk composition? Hydrobiologia 641:133–143
Tonello MS, Prieto AR (2008) Modern vegetation-pollen-climate relationship for the Pampa grasslands of Argentina. J Biogeogr 35:926–938
Tripaldi A, Zárate MA (2016) A review of Late Quaternary inland dune systems of South America east of the Andes. Quatern Int 410:96–110
Van den Berg MS, Coops H, Meijer ML, Scheffer M, Simons J (1998) Clear water associated with a dense Chara vegetation in the shallow and turbid Lake Veluwemeer, The Netherlands. In: Jeppesen E, Sondergaard M, Sondergaard M, Christoffersen K (eds) The structuring role of submerged macrophytes in lakes. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 339–352
Van Geel B (2001) Non-pollen palynomorphs. In: Smol JP, Birks HJB, Last WM (eds) Tracking Environmental Change using Lake Sediments: Terrestrial, Algal and Siliceous Indicators, 3. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 99–119
Vervoorst F (1967) La vegetación de la República Argentina. VII Las comunidades vegetales de la depresión del Salado (Provincia de Buenos Aires). INTA Serie Fitogeográfica 7 Buenos Aires, 262 pp
Vilanova I, Schittek K, Geilenkirchen M, Schäbitz F, Schulz W (2015) Last millennial environmental reconstruction based on a multi-proxy record from Laguna Nassau, Western Pampas, Argentina. Neues Jahrb Geol P-A 277:209–224
Zárate MA, Tripaldi A (2012) The aeolian system of central Argentina. Aeolian Res 3:401–417
Acknowledgements
We thank Pablo Messineo, Nahuel Scheifler and Gonzalo Sottile for their support during coring activities. Alfonsina Tripaldi provided useful comments on the manuscript. Financial support was provided by PIP CONICET 582 (2015-2017), PIP CONICET 0088 (2014-2016), National Geographic Society Grants 9773-15, EXA 913/18 (UNMdP).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sánchez Vuichard, G., Stutz, S., Tonello, M.S. et al. Structure and dynamics of a Pampa plain, (Argentina) shallow lake over the last 600 years. J Paleolimnol 66, 141–155 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-021-00194-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10933-021-00194-w