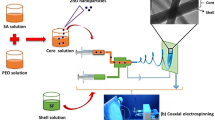
Abstract
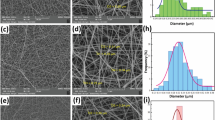
In the field of biomedical engineering, nanofiber scaffolds have excellent biomaterial properties, making them highly suitable for superior wound dressing applications. This work presents the fabrication of a novel bimetal blend comprising palladium and platinum nanoparticles integrated with silk fibroin and collagen composite nanofibers through the electrospinning method. The fabricated composite nanofibrous scaffolds were investigated to analyze their chemical composition, surface morphology, thermal stability, porosity, hemocompatibility, mechanical strength, swelling, and degradation properties. The average diameter length of the SF/CL/Pd–Pt composite nanofiber scaffolds is 141.62 ± 33.03 nm, with Pd and Pt nanoparticle diameters measured at 8.64 and 7.36 nm, respectively. In vitro assessments of SF/CL and SF/CL/Pd–Pt composite nanofiber scaffolds demonstrated outstanding antibacterial efficacy against both gram-positive (S. aureus) and gram-negative (E. coli) bacteria. The antioxidant activity of SF/CL/Pd–Pt composite nanofibers exhibited a free radical scavenging percentage of 94.34%. Additionally, cell proliferation studies conducted on the fibroblast (NIH3T3) cell line, along with in vivo investigations on male Sprague–Dawley rats, underscored the remarkable wound-healing ability of the SF/CL/Pd–Pt composite nanofiber scaffolds. Furthermore, histopathological examination of wounded tissue samples using H&E and Masson trichrome staining revealed faster reepithelialization, granulation, angiogenesis, and reduced inflammatory response. These findings demonstrate that SF/CL/Pd–Pt composite nanofibrous scaffolds are excellent wound dressing materials for all biomedical applications.
Graphical Abstract















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Zhang Z, Wang J, Luo Y, Li C, Sun Y, Wang K, Deng G, Zhao L, Yuan C, Lu J, Chen Y (2023) A pH-responsive ZC-QPP hydrogel for synergistic antibacterial and antioxidant treatment to enhance wound healing. J Mater Chem B 11(38):9300–9310. https://doi.org/10.1039/D3TB01567J
Zahra D, Shokat Z, Ahmad A, Javaid A, Khurshid M, Ashfaq UA, Nashwan AJ (2023) Exploring the recent developments of alginate silk fibroin material for hydrogel wound dressing: a review. Int J Biol Macromol 25:125989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.125989
Abd Elkodous M, Samuel Oluwaseun O, Sumanta S, Rajesh K (2023) Recent advances in modification of novel carbon-based composites: synthesis, properties, and biotechnological/ biomedical applications. Chem Biol Interact 379:110517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110517
Patil PP, Reagan MR, Bohara RA (2020) Silk fibroin and silk-based biomaterial derivatives for ideal wound dressings. Int J Biol Macromol 164:4613–4627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.041
Ghaeli I, De Moraes MA, Beppu MM, Lewandowska K, Sionkowska A, Ferreira-Da-Silva F, Ferraz MP, Monteiro FJ (2017) Phase behaviour and miscibility studies of collagen/silk fibroin macromolecular system in dilute solutions and solid state. Molecules. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22081368
Zhao G, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Ye ZG, Ren W, Xu F, Wang S, Liu M, Zhang X (2017) 3D conformal modification of electrospun silk nanofibers with nanoscaled ZnO deposition for enhanced photocatalytic activity. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3:2900–2906. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.6b00548
Martin P, Nunan R (2015) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of repair in acute and chronic wound healing. Br J Dermatol 173:370–378. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.13954
Heydari P, Zargar Kharazi A, Asgary S, Parham S (2022) Comparing the wound healing effect of a controlled release wound dressing containing curcumin/ciprofloxacin and simvastatin/ciprofloxacin in a rat model: a preclinical study. J Biomed Mater Res A 110:341–352. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.37292
Murugesan B, Arumugam M, Pandiyan N, Veerasingam M, Sonamuthu J, Samayanan S, Mahalingam S (2019) Ornamental morphology of ionic liquid functionalized ternary doped N, P, F and N, B, F-reduced graphene oxide and their prevention activities of bacterial biofilm-associated with orthopedic implantation. Mater Sci Eng C 98:1122–1132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.052
Amgarten B, Rajan R, Martínez-Sáez N, Oliveira BL, Albuquerque IS, Brooks RA, Reid DG, Duer MJ, Bernardes GJL (2015) Collagen labelling with an azide-proline chemical reporter in live cells. Chem Commun 51:5250–5252. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc07974d
Kandhasamy S, Perumal S, Madhan B, Umamaheswari N, Banday JA, Perumal PT, Santhanakrishnan VP (2017) Synthesis and fabrication of collagen-coated ostholamide electrospun nanofiber scaffold for wound healing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:8556–8568. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b16488
Yaqoob SB, Adnan R, Rameez Khan RM, Rashid M (2020) Gold, silver, and palladium nanoparticles: a chemical tool for biomedical applications. Front Chem 8:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00376
Reizabal A, Brito-Pereira R, Fernandes MM, Castro N, Correia V, Ribeiro C, Costa CM, Perez L, Vilas JL, Lanceros-Méndez S (2020) Silk fibroin magnetoactive nanocomposite films and membranes for dynamic bone tissue engineering strategies. Materialia. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtla.2020.100709
Siddiqi KS, Husen A (2016) Green synthesis, characterization and uses of palladium/platinum nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res Lett. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-016-1695-z
Dadras Chomachayi M, Solouk A, Akbari S, Sadeghi D, Mirahmadi F, Mirzadeh H (2018) Electrospun nanofibers comprising of silk fibroin/gelatin for drug delivery applications: thyme essential oil and doxycycline monohydrate release study. J Biomed Mater Res A 106:1092–1103. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.36303
Ghalei S, Nourmohammadi J, Solouk A, Mirzadeh H (2018) Enhanced cellular response elicited by addition of amniotic fluid to alginate hydrogel-electrospun silk fibroin fibers for potential wound dressing application. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 172:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.08.028
Ramadass SK, Nazir LS, Thangam R, Perumal RK, Manjubala I, Madhan B, Seetharaman S (2019) Type i collagen peptides and nitric oxide releasing electrospun silk fibroin scaffold: a multifunctional approach for the treatment of ischemic chronic wounds. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 175:636–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2018.12.025
Ribeiro N, Sousa A, Cunha-Reis C, Oliveira AL, Granja PL, Monteiro FJ, Sousa SR (2021) New prospects in skin regeneration and repair using nanophased hydroxyapatite embedded in collagen nanofibers, nanomedicine nanotechnology. Biol Med 33:102353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2020.102353
Sun W, Gregory DA, Tomeh MA, Zhao X (2021) Silk fibroin as a functional biomaterial for tissue engineering. Int J Mol Sci 22:1–28. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031499
Du C, Li Y, Xia X, Du E, Lin Y, Lian J, Ren C, Li S, Wei W, Qin Y (2021) Identification of a novel collagen-like peptide by high-throughput screening for effective wound-healing therapy. Int J Biol Macromol 173:541–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.104
Aioub M, Panikkanvalappil SR, El-Sayed MA (2017) Platinum-coated gold nanorods: efficient reactive oxygen scavengers that prevent oxidative damage toward healthy, untreated cells during plasmonic photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 11:579–586. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.6b06651
Shibuya S, Ozawa Y, Watanabe K, Izuo N, Toda T, Yokote K, Shimizu T (2014) Palladium and platinum nanoparticles attenuate aging-like skin atrophy via antioxidant activity in mice. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0109288
Czarnomysy R, Radomska D, Szewczyk OK, Roszczenko P, Bielawski K (2021) Platinum and palladium complexes as promising sources for antitumor treatments. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158271
He SB, Yang L, Lin MT (2021) Platinum group element-based nanozymes for biomedical applications: an overview. Biomed Mater. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-605X/abc90416:32001
Yang S, Li X, Liu P, Zhang M, Wang C, Zhang B (2020) Multifunctional chitosan/polycaprolactone nanofiber scaffolds with varied dual-drug release for wound-healing applications. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 6:4666–4676. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c00674
Arumugam M, Murugesan B, Malliappan P (2023) Electrospun silk fibroin and gelatin blended nanofibers functionalized with noble metal nanoparticles for enhanced biomedical applications. Process Biochem 124:221–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2022.11.019
Polini A, Pagliara S, Stabile R, Netti GS, Roca L, Prattichizzo C, Gesualdo L, Cingolani R, Pisignano D (2010) Collagen-functionalised electrospun polymer fibers for bioengineering applications. Soft Matter 6:1668–1674. https://doi.org/10.1039/b921932c
Wang J, Yang Q, Cheng N, Tao X, Zhang Z, Sun X, Zhang Q (2016) Collagen/silk fibroin composite scaffold incorporated with PLGA microsphere for cartilage repair. Mater Sci Eng C 61:705–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.12.097
Rho KS, Jeong L, Lee G, Seo BM, Park YJ, Hong SD, Roh S, Cho JJ, Park WH, Min BM (2006) Electrospinning of collagen nanofibers: effects on the behavior of normal human keratinocytes and early-stage wound healing. Biomaterials 27:1452–1461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.08.004
Felicitas P, Sascha B, Nadja S, Goran M, Sabine D, Daniel Dietrich R (2022) Physiological oxygen and co-culture with human fibroblasts facilitate in vivo-like properties in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells. Chem Biol Interact. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109959
Balakrishnan SB, Kuppu S, Thambusamy S (2021) Biologically important alumina nanoparticles modified polyvinylpyrrolidone scaffolds in vitro characterizations and it is in vivo wound healing efficacy. J Mol Struct 1246:131195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131195
Balakrishnan SB, Alam M, Ahmad N, Govindasamy M, Kuppu S, Thambusamy S (2021) Electrospinning nanofibrous graft preparation and wound healing studies using ZnO nanoparticles and glucosamine loaded with poly(methyl methacrylate)/polyethylene glycol. New J Chem 45:7987–7998. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj05409g
Qi P, Zeng J, Tong X, Shi J, Wang Y, Sui K (2021) Bioinspired synthesis of fiber-shaped silk fibroin-ferric oxide nanohybrid for superior elimination of antimonite. J Hazard Mater 403:123909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123909
Arumugam M, Murugesan B, Pandiyan N, Chinnalagu DK, Rangasamy G, Mahalingam S (2021) Electrospinning cellulose acetate/silk fibroin/Au-Ag hybrid composite nanofiber for enhanced biocidal activity against MCF-7 breast cancer cell. Mater Sci Eng C. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2021.112019
Murugesan B, Pandiyan N, Arumugam M, Sonamuthu J, Samayanan S, Yurong C, JumingS. Y (2020) Mahalingam, fabrication of palladium nanoparticles anchored polypyrrole functionalized reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for antibiofilm associated orthopedic tissue engineering. Appl Surf Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.145403
Kasinathan K, Marimuthu K, Murugesan B, Samayanan S, Panchu SJ, Swart HC, Savariroyan SRI (2021) Synthesis of biocompatible chitosan functionalized Ag decorated biocomposite for effective antibacterial and anticancer activity. Int J Biol Macromol 178:270–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.127
Wang LJ, Zhang J, Zhao X, Xu LL, Lyu ZY, Lai M (2015) Palladium nanoparticles functionalized graphene nanosheets for Li-O 2 batteries : enhanced performance by tailoring the morphology of the discharge product. RCS Adv 5:73451–73456. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b10882
Chen J, Niu Q, Chen G, Nie J, Ma G (2017) Electrooxidation of methanol on Pt @Ni bimetallic catalyst supported on porous carbon nanofibers. J Phys Chem C 121:1463–1471. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b10882
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Jiang Z, Wang J, Xu Z, Meng K, Zhao H (2021) Poly(glyceryl sebacate)/silk fibroin small-diameter artificial blood vessels with good elasticity and compliance. Smart Mater Med 2:74–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smaim.2021.01.001
Chen ZJ, Shi HH, Zheng L, Zhang H, Cha YY, Ruan HX, Zhang Y, Zhang XC (2021) A new cancellous bone material of silk fibroin/cellulose dual network composite aerogel reinforced by nano-hydroxyapatite filler. Int J Biol Macromol 182:286–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.204
Zhang D, Li L, Shan Y, Xiong J, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Gao J (2019) In vivo study of silk fibroin/gelatin electrospun nanofiber dressing loaded with astragaloside IV on the effect of promoting wound healing and relieving scar. J Drug Deliv Sci Technol 52:272–281. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jddst.2019.04.021
Wu J, Wang S, Zheng Z, Li J (2022) Fabrication of biologically inspired electrospun collagen/silk fibroin/bioactive glass composited nanofibrous scaffold to accelerate the treatment efficiency of bone repair. Regen Ther 21:122–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reth.2022.05.006
Wang Q, Zhou S, Wang L, You R, Yan S, Zhang Q, Li M (2021) Bioactive silk fibroin scaffold with nanoarchitecture for wound healing. Compos Part B Eng 224:109165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109165
Xiao L, Wu M, Yan F, Xie Y, Liu Z, Huang H, Yang Z, Yao S, Cai L (2021) A radial 3D polycaprolactone nanofiber scaffold modified by biomineralization and silk fibroin coating promote bone regeneration in vivo. Int J Biol Macromol 172:19–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.036
Wang Y, Zhang M, Yan Z et al (2024) Metal nanoparticle hybrid hydrogels: the state-of-the-art of combining hard and soft materials to promote wound healing. Theranostics 14:1534
Desai MP, Patil RV, Pawar KD (2020) Green biogenic approach to optimized biosynthesis of noble metal nanoparticles with potential catalytic, antioxidant and antihaemolytic activities. Process Biochem 98:172–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2020.08.005
Anila PA, Keerthiga B, Ramesh M, Muralisankar T (2021) Synthesis and characterization of palladium nanoparticles by chemical and green methods: a comparative study on hepatic toxicity using zebrafish as an animal model. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol 244:108979. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpc.2021.108979
Huang K, Jinzhong Z, Zhu T, Morsi Y, Aldalbahi A, El-Newehy M, Yan X, Mo X (2020) PLCL/Silk fibroin based antibacterial nano wound dressing encapsulating oregano essential oil: fabrication, characterization and biological evaluation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 196:111352. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2020.111352
You C, Li Q, Wang X, Wu P, Ho JK, Jin R, Zhang L, Shao H, Han C (2017) Silver nanoparticle loaded collagen/chitosan scaffolds promote wound healing via regulating fibroblast migration and macrophage activation. Sci Rep 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10481-0
Murugesan B, Pandiyan N, Kasinathan K, Rajaiah A, Arumuga M, Subramanian P, Sonamuthu J, Samayanan S, Arumugam VR, Marimuthu K, Yurong C, Mahalingam S (2020) Fabrication of heteroatom doped NFP-MWCNT and NFB-MWCNT nanocomposite from imidazolium ionic liquid functionalized MWCNT for antibiofilm and wound healing in Wistar rats: synthesis, characterization, in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Mater Sci Eng C 111:110791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2020.110791
Peng Y, Ma Y, Bao Y, Liu Z, Chen L, Dai F, Li Z (2021) Electrospun PLGA/SF/artemisinin composite nanofibrous membranes for wound dressing. Int J Biol Macromol 183:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.04.021
Chouhan D, Chakraborty B, Nandi SK, Mandal BB (2017) Role of non-mulberry silk fibroin in deposition and regulation of extracellular matrix towards accelerated wound healing. Acta Biomater 48:157–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.019
Sylvester MA, Amini F, Keat TC (2019) Electrospun nanofibers in wound healing. Mater Today Proc 29:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.05.686
White ES, Mantovani AR (2013) Inflammation, wound repair, and fibrosis: reassessing the spectrum of tissue injury and resolution. J Pathol 229:141–144. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4126
Bloch K, Pardesi K, Satriano C, Ghosh S (2021) Bacteriogenic platinum nanoparticles for application in nanomedicine. Front Chem 9:1–11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2021.624344
Xu X, Zhang J, Wang X (2024) Multifunctional Pd single-atom nanozyme for enhanced cascade chemodynamic therapy of chronic wounds. ACS Appl Nano Mater. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.3c06198
Chlumsky O, Purkrtova S, Michova H, Sykorova H, Slepicka P, Fajstavr D, Ulbrich P, Viktorova J, Demnerova K (2021) Antimicrobial properties of palladium and platinum nanoparticles: a new tool for combating food-borne pathogens. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22157892
Agarwal Y, Rajinikanth PS, Ranjan S, Tiwari U, Balasubramnaiam J, Pandey P, Arya DK, Anand S, Deepak P (2021) Curcumin loaded polycaprolactone-/polyvinyl alcohol-silk fibroin based electrospun nanofibrous mat for rapid healing of diabetic wound: an in-vitro and in-vivo studies. Int J Biol Macromol 176:376–386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.02.025
Dhanavel S, Manivannan N, Mathivanan N, Gupta VK, Narayanan V, Stephen A (2018) Preparation and characterization of cross-linked chitosan/palladium nanocomposites for catalytic and antibacterial activity. J Mol Liq 257:32–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.076
Acknowledgements
The financial support provided to the Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA-Phase 2.0) Ref. Lr. No. F. 24-51/2014-U, Policy (TNMulti-Gen), Dept. of Education, Government of India
Funding
The financial support provided to the Rashtriya Uchchatar Shiksha Abhiyan (RUSA-Phase 2.0) Ref. Lr. No. F. 24-51/2014-U, Policy (TNMulti-Gen), Dept. of Education, Government of India
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
In this manuscript, all persons who meet authorship criteria are listed as authors, and all authors certify that they have participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for the content, including participation in the concept, design, analysis, writing, or revision of the manuscript. Furthermore, each author certifies that this material or similar material has not been and will not be submitted to or published in any other publication before its appearance in the Journal of Polymers and the Environment. Mayakrishnan Arumugam: Conceptualization, Methodology, Investigation; Writing-Original Draft and Formal analysis, Balaji Murugesan: Validation, Resources, Formal analysis, Reviewing and Editing, Dhilipkumar Chinnalagu: Methodology, Formal analysis, Premkumar Balasekar: Resources, Formal analysis and Editing, Yurong Cai: Formal analysis, Reviewing and Editing, Ponnurengam Malliappan Sivakumar: Resources, Formal analysis, Gowri Rengasamy: Methodology, Formal analysis, Krithikapriya Chinniah: Methodology, Formal analysis, Sundrarajan Mahalingam: Validation, Visualization, Supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Arumugam, M., Murugesan, B., Chinnalagu, D. et al. Electrospun Silk Fibroin and Collagen Composite Nanofiber Incorporated with Palladium and Platinum Nanoparticles for Wound Dressing Applications. J Polym Environ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-024-03261-1
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-024-03261-1