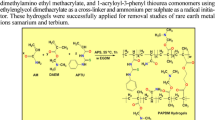
Abstract
Synthesis and identification of some thermo-responsive hydrogel metal absorbents based on Schiff base modified PNIPAM is described. PNIPAM hydrogel is produced through conventional free-radical polymerization method. The hydrogel is amino modified with different amines and then treated with various aldehydes to make polymeric Schiff-bases supposing to utilize as an absorbent for Cu salt. Characterization of the as-prepared hydrogels was performed properly and confirmed the corresponding structures. Kinetic and equilibrium function of the absorbents and the effect of distinct variables like pH, adsorbent amount and contact time in the absorption process are investigated in detail. Kinetic and adsorption isotherm data agreed with pseudo-second order model and Langmuir isotherm, respectively. The maximum value of adsorption capacity of the prepared adsorbent was around 8550 mg g−1. In addition, the corresponding switchable catalytic activity using one of the thermo-responsive hydrogel metal absorbents in the reduction of 4-nitro phenol to 4-amino phenol in the role of model reaction is examined.


















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zarrintaj P, Jouyandeh M, Ganjali MR, Hadavand BS, Mozafari M, Sheiko SS, Vatankhah-Varnoosfaderani M, Gutiérrez TJ, Saeb MR (2019) Thermo-sensitive polymers in medicine: a review. Eur Polym J 117:402–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2019.05.024
Ofridam F, Tarhini M, Lebaz N, Gagniere E, Mangin D, Elaïssari A (2021) pH-sensitive polymers: classification and some fine potential applications. Polym Adv Technol 32(4):1455–1484. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5230
Manouras T, Vamvakaki M (2017) Field responsive materials: photo-, electro-, magnetic-and ultrasound-sensitive polymers. Polym Chem 8(1):74–96. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6PY01455K
Lam KY, Lee CS, Pichika MR, Cheng SF, Tan RYH (2022) Light-responsive polyurethanes: classification of light-responsive moieties, light-responsive reactions, and their applications. RSC Adv 12(24):15261–15283. https://doi.org/10.1039/D2RA01506D
Zhang J, Jiang X, Wen X, Xu Q, Zeng H, Zhao Y, Liu M, Wang Z, Hu X, Wang Y (2019) Bio-responsive smart polymers and biomedical applications. JPhys Mater 2(3):032004. https://doi.org/10.1088/2515-7639/ab1af5
Rudko M, Urbaniak T, Musiał W (2021) Recent developments in ion-sensitive systems for pharmaceutical applications. Polym 13(10):1641. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13101641
Vassalini I, Alessandri I (2018) Switchable stimuli-responsive heterogeneous catalysis. Catalysts 8(12):569. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal8120569
Choudhury J (2018) Recent developments on artificial switchable catalysis. Tetrahedron Lett 59(6):487–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2017.12.070
Brighenti R, Cosma MP (2020) Swelling mechanism in smart polymers responsive to mechano-chemical stimuli. J Mech Phys Solids 143:104011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmps.2020.104011
Ghasemi S, Owrang M, Javaheri F, Farjadian F (2022) Spermine modified PNIPAAm nano-hydrogel serving as thermo-responsive system for delivery of cisplatin. Macromol Res 30(5):314–324. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13233-022-0035-7
Herrmann A, Haag R, Schedler U (2021) Hydrogels and their role in biosensing applications. Adv Healthc Mater 10(11):2100062. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.202100062
Wang L, Zhou M, Xu T, Zhang X (2022) Multifunctional hydrogel as wound dressing for intelligent wound monitoring. J Chem Eng 433:134625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134625
El-Husseiny HM, Mady EA, Hamabe L, Abugomaa A, Shimada K, Yoshida T, Tanaka T, Yokoi A, Elbadawy M, Tanaka R (2022) Smart/stimuli-responsive hydrogels: cutting-edge platforms for tissue engineering and other biomedical applications. Mater Today Bio 13:100186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtbio.2021.100186
Mantha S, Pillai S, Khayambashi P, Upadhyay A, Zhang Y, Tao O, Pham HM, Tran SD (2019) Smart hydrogels in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Materials 12(20):3323. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12203323
Nazarzadeh Zare E, Mudhoo A, Ali Khan M, Otero M, Bundhoo ZMA, Patel M, Srivastava A, Navarathna C, Mlsna T, Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2021) Smart adsorbents for aquatic environmental remediation. Small 17(34):2007840. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202007840
Sobczak M (2022) Enzyme-responsive hydrogels as potential drug delivery systems—state of knowledge and future prospects. Int J Mol Sci 23(8):4421. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23084421
Güngör A, Demir D, Bölgen N, Özdemir T, Genç R (2021) Dual stimuli-responsive chitosan grafted poly (NIPAM-co-AAc)/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogels for drug delivery applications. Int J Polym Mater Polym Biomater 70(11):810–819. https://doi.org/10.1080/00914037.2020.1765355
Shakya AK, Nandakumar KS (2018) An update on smart biocatalysts for industrial and biomedical applications. J R Soc Interface 15(139):20180062. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2018.0062
Ho DK, Nguyen DT, Thambi T, Lee DS, Huynh DP (2019) Polyamide-based pH and temperature-responsive hydrogels: synthesis and physicochemical characterization. J Polym Res 26(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-018-1666-4
Ilyas N, Ilyas S, Sajjad-ur-Rahman SUR, Yousaf S, Zia A, Sattar S (2018) Removal of copper from an electroplating industrial effluent using the native and modified spirogyra. Water Sci Technol 78(1):147–155. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.226
Al-Saydeh SA, El-Naas MH, Zaidi SJ (2017) Copper removal from industrial wastewater: a comprehensive review. J Ind Eng Chem 56:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2017.07.026
Panigrahi T, Santhoskumar AU (2020) Adsorption process for reducing heavy metals in Textile Industrial Effluent with low cost adsorbents. Prog Chem Biochem Res 3(2):135–139. https://doi.org/10.33945/SAMI/PCBR.2020.2.7
Virolainen S, Wesselborg T, Kaukinen A, Sainio T (2021) Removal of iron, aluminium, manganese and copper from leach solutions of lithium-ion battery waste using ion exchange. Hydrometallurgy 202:105602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2021.105602
Arbabi M, Golshani N (2016) Removal of copper ions Cu (II) from industrial wastewater: a review of removal methods. Int J Epidemiol 3(3):283–293
Maiti S, Prasad B, Minocha AK (2020) Optimization of copper removal from wastewater by fly ash using central composite design of response surface methodology. SN Appl Sci 2(12):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03892-8
Zhang K, Xue K, Loh XJ (2021) Thermo-responsive hydrogels: from recent progress to biomedical applications. Gels 7(3):77. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels7030077
Tzounis L, Doña M, Lopez-Romero JM, Fery A, Contreras-Caceres R (2019) Temperature-controlled catalysis by core–shell–satellite AuAg@ pNIPAM@ Ag hybrid microgels: a highly efficient catalytic thermoresponsive nanoreactor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(32):29360–29372. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b10773
Kakar MU, Khan K, Akram M, Sami R, Khojah E, Iqbal I, Helal M, Hakeem A, Deng Y, Dai R (2021) Synthesis of bimetallic nanoparticles loaded on to PNIPAM hybrid microgel and their catalytic activity. Sci Rep 11(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-94177-6
Chen J, Luo Q, Ma XZ (2019) Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide)@ graphene oxide-Ag responsive hydrogels. Characterization and smart tunable catalytic activity. J Macromol Sci Part A Pure Appl Chem 56:943–951. https://doi.org/10.1080/10601325.2019.1618192
Li L, Wang R, Xing X, Qu W, Chen S, Zhang Y (2019) Preparation of porous semi-IPN temperature-sensitive hydrogel-supported nZVI and its application in the reduction of nitrophenol. Res J Environ Sci 82:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.02.024
Elella M, Aamer N, Mohamed Y, Nazer H, Mohamed RR (2023) High-potential removal of copper (II) ions from aqueous solution using Antimicrobial Crosslinked grafted gelatin hydrogels. J Polym Environ 31(3):1071–1089
Nie L, Chang P, Liang S, Hu K, Hua D, Liu S, Shavandi A (2021) Polyphenol rich green tea waste hydrogel for removal of copper and chromium ions from aqueous solution. Clean Eng Technol 4:100167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2021.100167
Zhang H, Li GW, Feng W, Yao ZY (2022) Cu (II) adsorption from aqueous solution onto poly (acrylic acid/chestnut shell pigment) hydrogel. Water 14(21):3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/w14213500
Liu M, Wen Y, Song X, Zhu JL, Li J (2019) A smart thermoresponsive adsorption system for efficient copper ion removal based on alginate-g-poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) graft copolymer. Carbohydr Polym 219:280–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.018
Tang J, Huang J, Tun T, Liu S, Hu J, Zhou G (2021) Cu (II) and cd (II) capture using novel thermosensitive hydrogel microspheres: adsorption behavior study and mechanism investigation. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 96(8):2382–2389. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.6767
Chen JJ, Ahmad AL, Ooi BS (2013) Poly (N-isopropylacrylamide-co-acrylic acid) hydrogels for copper ion adsorption: equilibrium isotherms, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. J Environ Chem Eng 1(3):339–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.05.012
Yuan S, Ning K, He Y (2020) Removal of copper ions using poly (acrylic acid-co-acrylamide) hydrogel microspheres with controllable size prepared by W/O Pickering emulsions. Colloid Polym Sci 298:1465–1472. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04715-3
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Shiraz University Research Council.
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SG contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by MO. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SG and SG and FJ wrote the main manuscript text. All authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemi, S., Owrang, M. & Javaheri, F. Kinetic and Equilibrium Function and Switchable Catalytic Activity of Some Thermo-Responsive Hydrogel Metal Absorbents Based on Modified PNIPAM. J Polym Environ 31, 4972–4989 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-02915-w
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-023-02915-w