Abstract
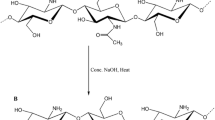
In the present study, an adsorbent with a synergistic effect was developed from chitosan (CS) and Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fe3O4 Nps) to remove Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions. The Fe3O4 Nps were synthesized by co-precipitation and were characterized by TEM. The CS/NPs composites were prepared by electrospinning technique and analyzed by SEM, FT-IR, DSC, and TGA. In the batch system, the influence of Fe3O4 Nps content, pH, contact time, Cr(VI) initial concentration, adsorbent dosage, and the temperature was investigated; the Cr(VI) concentration was determined using a colorimetric method by UV–Vis spectroscopy. The Fe3O4 Nps presented a quasi-spherical shape and an average size of 18 nm, with a low particle distribution. The SEM analysis reveals the presence of highly porous, interconnected micrometric structures. The optimal adsorption conditions were 1% load of Fe3O4 Nps by weight of CS, pH 3, 25 °C, and equilibrium was reached at just 9 min. Besides, the adsorption is favored by increasing Cr(VI) initial concentration and adsorbent dosage. The studies of reaction kinetics and adsorption equilibrium showed that the experimental data were better fitted to the Pseudo-second-order and Langmuir isotherm models, establishing monolayer formation and chemisorption. The maximum adsorption capacity of CS/Fe3O4 Nps was 440.75 mg/g, which indicates a high affinity of the adsorbent for Cr(VI). Finally, a kinetic diffusion study established that intraparticle diffusion, and in particular surface diffusion, are important resistances in the transport of Cr(VI) from the liquid phase to the active site.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed in this study are available by the corresponding author on reasonable request (eulalia.vanegas@ucuenca.edu.ec).
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Swaroop A, Bagchi M, Preuss HG et al (2019) Benefits of chromium(III) complexes in animal and human health. The Nutritional Biochemistry of Chromium (III). Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 251–278
Debnath S, Ghosh UC (2008) Kinetics, isotherm and thermodynamics for Cr(III) and Cr(VI) adsorption from aqueous solutions by crystalline hydrous titanium oxide. J Chem Thermodyn 40:67–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCT.2007.05.014
Goswami S, Bhat SC, Ghosh UC (2006) Crystalline hydrous ferric oxide: an adsorbent for chromium(VI)-contaminated industrial wastewater treatment. Water Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.2175/106143005X73604
Fang Y, Wen J, Zhang H et al (2020) Enhancing Cr(VI) reduction and immobilization by magnetic core-shell structured NZVI@MOF derivative hybrids. Environ Pollut 260:114021. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2020.114021
Fellenz N, Perez-Alonso FJ, Martin PP et al (2017) Chromium (VI) removal from water by means of adsorption-reduction at the surface of amino-functionalized MCM-41 sorbents. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 239:138–146. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROMESO.2016.10.012
Carrington NA, Thomas GH, Rodman DL et al (2007) Optical determination of Cr(VI) using regenerable, functionalized sol–gel monoliths. Anal Chim Acta 581:232–240. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ACA.2006.08.032
DesMarias TL, Costa M (2019) Mechanisms of chromium-induced toxicity. Current Opinion in Toxicology 14:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cotox.2019.05.003
Ertani A, Mietto A, Borin M, Nardi S (2017) Chromium in agricultural soils and crops: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 228:190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-017-3356-y
Stambulska UY, Bayliak MM, Lushchak VI (2018) Chromium(VI) toxicity in legume plants: modulation effects of rhizobial symbiosis. BioMed Res Int 2018:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8031213
Chen Z, Pan K (2021) Enhanced removal of Cr(VI) via in-situ synergistic reduction and fixation by polypyrrole/sugarcane bagasse composites. Chemosphere 272:129606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.129606
Liu M, Yin W, Qian F-J et al (2020) A novel synthesis of porous TiO2 nanotubes and sequential application to dye contaminant removal and Cr(VI) visible light catalytic reduction. J Environ Chem Eng 8:104061. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2020.104061
Long B, Ye J, Ye Z et al (2020) Cr(VI) removal by Penicillium oxalicum SL2: reduction with acidic metabolites and form transformation in the mycelium. Chemosphere 253:126731. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126731
Zhang Y, Xu X, Yue C et al (2021) Insight into the efficient co-removal of Cr(VI) and Cr(III) by positively charged UiO-66-NH2 decorated ultrafiltration membrane. Chem Eng J 404:126546. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2020.126546
Tian X, Wang W, Tian N et al (2016) Cr(VI) reduction and immobilization by novel carbonaceous modified magnetic Fe3O4/halloysite nanohybrid. J Hazard Mater 309:151–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2016.01.081
Valle JP, Gonzalez B, Schulz J et al (2017) Sorption of Cr(III) and Cr(VI) to K2Mn4O9 nanomaterial a study of the effect of pH, time, temperature and interferences. Microchem J 133:614–621. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.MICROC.2017.04.021
Rajput S, Pittman CU, Mohan D (2016) Magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticle synthesis and applications for lead (Pb2+) and chromium (Cr6+) removal from water. J Colloid Interface Sci 468:334–346. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2015.12.008
Zhang Y, Jiao X, Liu N et al (2020) Enhanced removal of aqueous Cr(VI) by a green synthesized nanoscale zero-valent iron supported on oak wood biochar. Chemosphere 245:125542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125542
Upadhyay U, Sreedhar I, Singh SA et al (2021) Recent advances in heavy metal removal by chitosan based adsorbents. Carbohyd Polym 251:117000. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117000
Weska RF, Moura JM, Batista LM et al (2007) Optimization of deacetylation in the production of chitosan from shrimp wastes: Use of response surface methodology. J Food Eng 80:749–753. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JFOODENG.2006.02.006
Oberlintner A, Bajić M, Kalčíková G et al (2021) Biodegradability study of active chitosan biopolymer films enriched with Quercus polyphenol extract in different soil types. Environ Technol Innov 21:101318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101318
Begum S, Yuhana NY, Md Saleh N et al (2021) Review of chitosan composite as a heavy metal adsorbent: Material preparation and properties. Carbohyd Polym 259:117613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117613
Xu H, Yuan H, Yu J, Lin S (2019) Study on the competitive adsorption and correlational mechanism for heavy metal ions using the carboxylated magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (MNPs-COOH) as efficient adsorbents. Appl Surf Sci 473:960–966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.006
Chen T, Wang Q, Lyu J et al (2020) Boron removal and reclamation by magnetic magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticle: An adsorption and isotopic separation study. Sep Purif Technol 231:115930. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115930
Liu X, Guan J, Lai G et al (2020) Stimuli-responsive adsorption behavior toward heavy metal ions based on comb polymer functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. J Clean Prod 253:119915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119915
Mokadem Z, Saidi-Besbes S, Lebaz N, Elaissari A (2020) Magnetic monolithic polymers prepared from high internal phase emulsions and Fe3O4 triazole-functionalized nanoparticles for Pb2+, Cu2+ and Zn2+ removal. React Funct Polym 155:104693. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2020.104693
Kim DK, Zhang Y, Voit W et al (2001) Synthesis and characterization of surfactant-coated superparamagnetic monodispersed iron oxide nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 225:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-8853(00)01224-5
Chabaane L, Tahiri S, Albizane A et al (2011) Immobilization of vegetable tannins on tannery chrome shavings and their use for the removal of hexavalent chromium from contaminated water. Chem Eng J 174:310–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2011.09.037
Sanchayanukun P, Muncharoen S (2019) Elimination of Cr(VI) in laboratory wastewater using chitosan coated magnetite nanoparticles (chitosan@Fe3O4). EnvironmentAsia 12:32–48. https://doi.org/10.14456/ea.2019.25
Li Q, Kartikowati CW, Horie S et al (2017) Correlation between particle size/domain structure and magnetic properties of highly crystalline Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Sci Rep 7:9894. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-09897-5
Zuo P-P, Feng H-F, Xu Z-Z et al (2013) Fabrication of biocompatible and mechanically reinforced graphene oxide-chitosan nanocomposite films. Chem Cent J 7:39. https://doi.org/10.1186/1752-153X-7-39
Neto CGT, Giacometti JA, Job AE et al (2005) Thermal analysis of chitosan based networks. Carbohyd Polym 62:97–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2005.02.022
Pendekal MS, Tegginamat PK (2012) Development and characterization of chitosan-polycarbophil interpolyelectrolyte complex-based 5-fluorouracil formulations for buccal, vaginal and rectal application. DARU J Pharm Sci 20:67. https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-20-67
Cruzat Contreras C, Peña O, Meléndrez MF et al (2011) Synthesis, characterization and properties of magnetic colloids supported on chitosan. Colloid Polym Sci 289:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-010-2302-y
Cárdenas-Triviño G, Cruzat-Contreras C (2018) Study of Aggregation of Gold Nanoparticles in Chitosan. J Clust Sci 29:1081–1088. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-1419-x
Liao S-K, Hung C-C, Lin M-F (2004) A kinetic study of thermal degradations of chitosan/polycaprolactam blends. Macromol Res 12:466–473. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03218428
Etemadi M, Samadi S, Yazd SS et al (2017) Selective adsorption of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions using Cr6+-imprinted Pebax/chitosan/GO/APTES nanofibrous adsorbent. Int J Biol Macromol 95:725–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.IJBIOMAC.2016.11.117
Wen Y, Tang Z, Chen Y, Gu Y (2011) Adsorption of Cr(VI) from aqueous solutions using chitosan-coated fly ash composite as biosorbent. Chem Eng J 175:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.09.066
Yuan P, Fan M, Yang D et al (2009) Montmorillonite-supported magnetite nanoparticles for the removal of hexavalent chromium [Cr(VI)] from aqueous solutions. J Hazard Mater 166:821–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2008.11.083
Li L, Li Y, Cao L, Yang C (2015) Enhanced chromium (VI) adsorption using nanosized chitosan fibers tailored by electrospinning. Carbohyd Polym 125:206–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CARBPOL.2015.02.037
Pholosi A, Naidoo EB, Ofomaja AE (2020) Intraparticle diffusion of Cr(VI) through biomass and magnetite coated biomass: A comparative kinetic and diffusion study. S Afr J Chem Eng 32:39–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sajce.2020.01.005
Hu J, Lo IMC, Chen G (2004) Removal of Cr(VI) by magnetite. Water Sci Technol 50:139–146
Jung C, Heo J, Han J et al (2013) Hexavalent chromium removal by various adsorbents: powdered activated carbon, chitosan, and single/multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Sep Purif Technol 106:63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SEPPUR.2012.12.028
Nakano Y, Takeshita K, Tsutsumi T (2001) Adsorption mechanism of hexavalent chromium by redox within condensed-tannin gel. Water Res 35:496–500. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(00)00279-7
Park D, Lim S-R, Yun Y-S, Park JM (2007) Reliable evidences that the removal mechanism of hexavalent chromium by natural biomaterials is adsorption-coupled reduction. Chemosphere 70:298–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CHEMOSPHERE.2007.06.007
Sarin V, Pant KK (2006) Removal of chromium from industrial waste by using eucalyptus bark. Biores Technol 97:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.BIORTECH.2005.02.010
Bozorgpour F, Ramandi HF, Jafari P et al (2016) Removal of nitrate and phosphate using chitosan/Al2O3/Fe3O4 composite nanofibrous adsorbent: Comparison with chitosan/Al2O3/Fe3O4 beads. Int J Biol Macromol 93:557–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.09.015
Razzaz A, Ghorban S, Hosayni L et al (2016) Chitosan nanofibers functionalized by TiO2 nanoparticles for the removal of heavy metal ions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 58:333–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JTICE.2015.06.003
Wang L, Shi C, Wang L et al (2020) Rational design, synthesis, adsorption principles and applications of metal oxide adsorbents: a review. Nanoscale 12:4790–4815. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR09274A
Edet UA, Ifelebuegu AO (2020) Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic modeling of the adsorption of phosphates from model wastewater using recycled brick waste. Processes 8:665. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr8060665
Pauletto PS, Dotto GL, Salau NPG (2020) Diffusion mechanisms and effect of adsorbent geometry on heavy metal adsorption. Chem Eng Res Des 157:182–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2020.02.031
Popovic AL, Rusmirovic JD, Velickovic Z et al (2021) Kinetics and column adsorption study of diclofenac and heavy-metal ions removal by amino-functionalized lignin microspheres. J Ind Eng Chem 93:302–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.10.006
Lunge S, Singh S, Sinha A (2014) Magnetic iron oxide (Fe3O4) nanoparticles from tea waste for arsenic removal. J Magn Magn Mater 356:21–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.12.008
Beheshti H, Irani M, Hosseini L et al (2016) Removal of Cr (VI) from aqueous solutions using chitosan/MWCNT/Fe3O4 composite nanofibers-batch and column studies. Chem Eng J 284:557–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2015.08.158
Burks T, Avila M, Akhtar F et al (2014) Studies on the adsorption of chromium(VI) onto 3-Mercaptopropionic acid coated superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Colloid Interface Sci 425:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2014.03.025
Silva M, Baltrusaitis J (2020) A review of phosphate adsorption on Mg-containing materials: kinetics, equilibrium, and mechanistic insights. Environ Sci Water Res Technol 6:3178–3194. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EW00679C
Valderrama C, Gamisans X, Heras X et al (2008) Sorption kinetics of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons removal using granular activated carbon: Intraparticle diffusion coefficients. J Hazard Mater 157:386–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.12.119
Doke KM, Khan EM (2017) Equilibrium, kinetic and diffusion mechanism of Cr(VI) adsorption onto activated carbon derived from wood apple shell. Arab J Chem 10:S252–S260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2012.07.031
Inglezakis VJ, Balsamo M, Montagnaro F (2020) Liquid-solid mass transfer in adsorption systems—an overlooked resistance? Ind Eng Chem Res 59:22007–22016. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.0c05032
Hu X, Wang J, Liu Y et al (2011) Adsorption of chromium (VI) by ethylenediamine-modified cross-linked magnetic chitosan resin: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamics. J Hazard Mater 185:306–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JHAZMAT.2010.09.034
Kera NH, Bhaumik M, Pillay K et al (2017) Selective removal of toxic Cr(VI) from aqueous solution by adsorption combined with reduction at a magnetic nanocomposite surface. J Colloid Interface Sci 503:214–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JCIS.2017.05.018
Zhao Y-G, Shen H-Y, Pan S-D et al (2010) Preparation and characterization of amino-functionalized nano-Fe3O4 magnetic polymer adsorbents for removal of chromium(VI) ions. J Mater Sci 45:5291–5301. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4574-5
Anush SM, Chandan HR, Gayathri BH et al (2020) Graphene oxide functionalized chitosan-magnetite nanocomposite for removal of Cu(II) and Cr(VI) from waste water. Int J Biol Macromol 164:4391–4402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.059
Yan E, Cao M, Ren X et al (2018) Synthesis of Fe3O4 nanoparticles functionalized polyvinyl alcohol/chitosan magnetic composite hydrogel as an efficient adsorbent for chromium (VI) removal. J Phys Chem Solids 121:102–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2018.05.028
Wang X, Liu X, Xiao C et al (2020) Triethylenetetramine-modified hollow Fe3O4/SiO2/chitosan magnetic nanocomposites for removal of Cr(VI) ions with high adsorption capacity and rapid rate. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 297:110041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110041
Subedi N, Lähde A, Abu-Danso E et al (2019) A comparative study of magnetic chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4) and graphene oxide modified magnetic chitosan (Chi@Fe3O4GO) nanocomposites for efficient removal of Cr(VI) from water. Int J Biol Macromol 137:948–959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.06.151
Thinh NN, Hanh PTB, Ha LTT et al (2013) Magnetic chitosan nanoparticles for removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution. Mater Sci Eng, C 33:1214–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2012.12.013
Yang W, Tang Q, Dong S et al (2016) Single-step synthesis of magnetic chitosan composites and application for chromate (Cr(VI)) removal. J Cent South Univ 23:317–323. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11771-016-3076-2
Koushkbaghi S, Jafari P, Rabiei J et al (2016) Fabrication of PET/PAN/GO/Fe3O4 nanofibrous membrane for the removal of Pb(II) and Cr(VI) ions. Chem Eng J 301:42–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.CEJ.2016.04.076
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Dirección de Investigación de la Universidad de Cuenca (DIUC) through the project DIUC_XV_2017_006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study's conception and design. Investigation, Formal analysis, Writing = original draft, Writing = review & editing were performed by EV; Methodology, Writing = original draft, Formal analysis, and Investigation PC; Investigation was performed by NN; Investigation and Formal analysis were performed by RA; Visualization, Data curation, Writing = review & editing were performed by DJ; Conceptualization, Writing = original draft; Editing, Supervision, Validation, Resources, Funding acquisition, and Project administration were performed by CC. The first draft of the manuscript was written by EV, CC and PC and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanegas, E., Castro, P., Novoa, N. et al. Potential Biopolymer Adsorbent Functionalized with Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for the Removal of Cr(VI) From Aqueous Solution. J Polym Environ 30, 2022–2036 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02323-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02323-y