Abstract
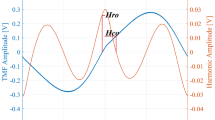
In this study, a novel method for predicting hardness of ferromagnetic alloy based on the magnetic Barkhausen noise (MBN) is proposed. A set of new frequency features of MBN and a new hardness prediction method are proposed. The new features are derived from the first and second derivative of the auto-regressive spectrum of MBN signal. The new automatic hardness prediction method include Bag-of-Words, principal component analysis and back propagate neural network optimized by ensemble learning. The experimental results of the hardness classification show that the new features are superior to the previous features—the misclassification rate using the new features is less than 0.67%, while the misclassification rate using the previous features is about 2%. The efficiency of the new method is also proved by hardness classification experiment. Compared with the traditional time-domain method and the previous frequency domain method, the misclassification rate of the new method decreased significantly from 25% to less than 1%. In addition, the new method is highly automatic, so it is more versatile than manual algorithms. The above characteristics make the proposed new method suitable for predicting the hardness of ferromagnetic alloys in practice.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perez-Benitez, J.A., Espina-Hernandez, J.H., Martinez-Ortiz, P.: Unwrapping the influence of multiple parameters on the Magnetic Barkhausen Noise signal using self-organizing maps. NDT E Int. 54, 166–170 (2013)
Perez-Benitez, J.A., Capo-Sanchez, J., Anglada-Rivera, J., Padovese, L.R.: A model for the influence of microstructural defects on magnetic Barkhausen noise in plain steels. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 288, 433–442 (2005)
Sorsa, A., Santa-aho, S., Vippola, M.: A case study of using radial basis function neural networks for predicting material properties from Barkhausen noise signal. In: Proceedings of 18th Nordic Process Control Workshop, Oulu, Finland, pp. 1–6 (2013)
Luo, X.Y., Wang, Y.L., Zhu, B., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y.S.: Super-resolution spectral analysis and signal reconstruction of magnetic Barkhausen noise. NDT E Int. 70, 16–21 (2015)
Luo, X.Y., Wang, Y.L., Wang, L., Xie, J., Zhang, Y.S.: Non-destructive hardness measurement of hot-stamped high strength steel sheets based on magnetic Barkhausen noise. Procedia Eng. 81, 1768–1773 (2014)
Sorsa, A., Leiviska, K., Santa-aho, S., Lepisto, T.: Quantitative prediction of residual stress and hardness in case-hardened steel based on the Barkhausen noise measurement. NDT E Int. 46, 100–106 (2012)
Franco, F.A., Gonzalez, M.F.R., de Campos, M.F., Padovese, L.R.: Relation between magnetic Barkhausen noise and hardness for Jominy quench tests in SAE 4140 and 6150 steels. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 32(1), 93–103 (2013)
Wang, P., Zhu, L., Zhu, Q.J., Ji, X.L., Wang, H.T., Tian, G.Y., Yao, E.T.: An application of back propagation neural network for the steel stress detection based on Barkhausen noise theory. NDT E Int. 55, 9–14 (2013)
Sorsa, A., Leiviska, K., Santa-aho, S., Vippola, M., Lepisto, T.: An efficient procedure for identifying the prediction model between residual stress and Barkhausen noise. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 32(4), 341–349 (2013)
Lindgren, M., Lepisto, T.: Effect of cyclic deformation on Barkhausen noise in a mild steel. NDT E Int. 36(6), 401–409 (2003)
Kim, D.W., Kwon, D.: Quantification of the Barkhausen noise method for the evaluation of time-dependent degradation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 257(2–3), 175–183 (2003)
O’Sullivan, D., Cotterell, M., Tanner, D.A., Mészáros, I.: Characterisation of ferritic stainless steel by Barkhausen techniques. NDT E Int. 37(6), 489–496 (2004)
Freyhardt, H.C.: Flux pinning in high-current-density superconductors. IEEE Trans. Magn. 19(3), 545–547 (1983)
Ramuhalli, P., Udpa, L., Udpa, S.S.: Electromagnetic NDE signal inversion by function-approximation neural networks. IEEE Trans. Magn. 38(6), 3633–3642 (2002)
Sipahi, L.B., Jiles, D.C., Chandler, D.: Comprehensive analysis of Barkhausen emission-spectra using pulse-height analysis, frequency-spectrum, and pulse-wave form analysis. J. Appl. Phys. 73(10), 5623–5625 (1993)
Kinser, E.R., Lo, C.C.H., Barsic, A.J., Jiles, D.C.: Modeling microstructural effects on Barkhausen emission in surface-modified magnetic materials. IEEE Trans. Magn. 41(10), 3292–3294 (2005)
Sorsa, A., Isokangas, A., Santa-aho, S., Vippola, M., Lepisto, T., Leiviska, K.: Prediction of residual stresses using partial least squares regression on Barkhausen noise signals. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 33(1), 43–50 (2014)
Eftekhari, M., Moallem, M., Ghadamyari, M.A.: Predicting mechanical properties of cold-rolled low carbon steel based on magnetic parameter measurement using ANFIS model (2011). http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/IAS.2011.6074385
Altpeter, I., Becker, R., Dobmann, G., Kern, R., Theiner, W., Yashan, A.: Robust solutions of inverse problems in electromagnetic non-destructive evaluation. Inverse Probl. 18(6), 1907–1921 (2002)
Ghanei, S., Vafaeenezhad, H., Kashefi, M., Eivani, A.R., Mazinani, M.: Design of an expert system based on neuro-fuzzy inference analyzer for on-line microstructural characterization using magnetic NDT method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 379, 131–136 (2015)
Feng, C., Wang, X.H.: Image retrieval system based on bag of view words model. In: 2016 IEEE/ACIS 15th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS), pp. 1185–1188 (2016)
Passalis, N., Tefas, A.: Entropy optimized feature-based bag-of-words representation for information retrieval. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 28(7), 1664–1677 (2016)
Lee, C.H., Lin, H.S., Chen, L.H.: Music classification using the bag of words model of modulation spectral features. In: 2015 15th International Symposium on Communications and Information Technologies (ISCIT), pp. 121–124 (2015)
Pokorny, F.B., Graf, F., Pernkopf, F., Schuller, B.W.: Detection of negative emotions in speech signals using bags-of-audio-words. In: 1st International Workshop on Automatic Sentiment Analysis in the Wild (WASA 2015) held in conjunction with the 6th Biannual Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction (ACII 2015), Xi’an, China, pp. 879–884 (2015)
Shahbaz Khan, F., et al.: Scale coding bag-of-words for action recognition. In: IEEE International Conference on Pattern Recognition, 2014, pp. 1514–1519
Shlens, J.: A tutorial on principal component analysis: derivation, discussion and singular value decomposition, 1–16. Online note (2003). http://www.Snl.Salk.Edushlenspubnotespca.Pdf2
Wong, T.T., Yang, N.Y.: Dependency analysis of accuracy estimates in k-fold cross validation. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 29(11), 2417–2427 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (11527801, 61305026 and 41706201).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, G., Liu, H., He, C. et al. A Novel Prediction Method for Hardness Using Auto-regressive Spectrum of Barkhausen Noise. J Nondestruct Eval 37, 85 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-018-0539-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-018-0539-4