Abstract
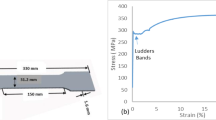
The sensitivity of magnetic Barkhausen noise to many factors has limited its potential application for basic material characterization and detection of residual stress in carbon steel, a common structural material. The present work investigates Barkhausen noise response in plain carbon steel under conditions of varying carbon content, applied elastic stress and different magnetization level. The surface Barkhausen noise measurement system uses a feedback for controlling the flux waveform, which facilitates reproducibility of measurements and also permits extraction of additional parameters from the B–H loop of magnetic circuit. Barkhausen noise parameters correlate with known material parameters, such as coercivity, which vary with carbon content and stress. These results demonstrate the potential for in-situ characterization of carbon steel.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jiles, D.C.: Dynamics of domain magnetization and the Barkhausen effect. Czechoslov. J. Phys. 50(8), 893–924 (2000)
Blaow, M., Evans, J., Shaw, B.: Magnetic Barkhausen noise: the influence of microstructure and deformation in bending. Acta Mater. 53(2), 279–287 (2005)
Yelbay, H.I., Cam, I., Gür, C.H.: Non-destructive determination of residual stress state in steel weldments by magnetic Barkhausen noise technique. NDT&E Int. 43(1), 29–33 (2010)
Xin, Q., Shu, D., Hui, L., Wei, W., Chen, J.: Magnetic Barkhausen noise, metal magnetic memory testing and estimation of the ship plate welded structure stress. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 31(1), 80–89 (2012)
Santa-Aho, S., Vippola, M., Sorsa, A., Latokartano, J., Lindgren, M., Leiviskä, K., Lepistö, T.: Development of Barkhausen noise calibration blocks for reliable grinding burn detection. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212(2), 408–416 (2012)
Mandal, K., Dufour, D., Atherton, D.: Use of magnetic Barkhausen noise and magnetic flux leakage signals for analysis of defects in pipeline steel. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 35(3), 2007–2017 (1999)
Vourna, P., Ktena, A., Hristoforou, E.: Residual stress analysis in nonoriented electrical steel sheets by Barkhausen noise measurements. IEEE Trans. Magn. 50(4), 1–4 (2014)
Pérez-Benítez, J., Espina-Hernández, J., Martínez-Ortiz, P.: Unwrapping the influence of multiple parameters on the magnetic Barkhausen noise signal using self-organizing maps. NDT&E Int. 54, 166–170 (2013)
Pérez-Benítez, J., Padovese, L.: Study of the influence of simultaneous variation of magnetic material microstructural features on domain wall dynamics. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322(20), 3101–3105 (2010)
Samimi, A.A., Krause, T.W., Clapham, L.: Stress-response of magnetic Barkhausen noise in submarine hull steel: a comparative study. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 35(2), 1–6 (2016)
Sakamoto, H., Okada, M., Homma, M.: Theoretical analysis of Barkhausen noise in carbon steels. IEEE Trans. Magn. 23(5), 2236–2238 (1987)
Clapham, L., Jagadish, C., Atherton, D.: The influence of pearlite on Barkhausen noise generation in plain carbon steels. Acta Metall. Mater. 39(7), 1555–1562 (1991)
Dhar, A., Atherton, D.: Influence of magnetizing parameters on the magnetic Barkhausen noise. IEEE Trans. Magn. 28(6), 3363–3366 (1992)
Stefanita, C.-G., Atherton, D., Clapham, L.: Plastic versus elastic deformation effects on magnetic Barkhausen noise in steel. Acta Mater. 48(13), 3545–3551 (2000)
Anglada-Rivera, J., Padovese, L., Capo-Sanchez, J.: Magnetic Barkhausen noise and hysteresis loop in commercial carbon steel: influence of applied tensile stress and grain size. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 231(2), 299–306 (2001)
Ranjan, R., Jiles, D.C., Rastogi, P.: Magnetic properties of decarburized steels: an investigation of the effects of grain size and carbon content. IEEE Trans. Magn. 23(3), 1869–1876 (1987)
Garstka, T., Krajowej, A.A.: The influence of product thickness on the measurements by Barkhausen noise method. J. Achiev. Mater. Manuf. Eng. 27(1), 47–50 (2008)
Chukwuchekwa, N., Moses, A., Anderson, P.: Effects of strip thickness and silicon content on magnetic Barkhausen noise of non-oriented electrical steel at 50 Hz. Int. J. Appl. Electromagn. Mech. 39(1), 541–545 (2012)
White, S., Krause, T.W., Clapham, L.: A multichannel magnetic flux controller for periodic magnetizing conditions. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 61(7), 1896–1907 (2012)
White, S.A.: A Barkhausen Noise Testing System for CANDU Feeder Pipes. PhD thesis, Queen’s University, Kingston (2009)
Koo, K., Yau, M., Ng, D.H., Lo, C.: Characterization of pearlite grains in plain carbon steel by Barkhausen emission. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 351(1), 310–315 (2003)
Pérez-Benítez, J., Capo-Sanchez, J., Padovese, L.: Modeling of the Barkhausen jump in low carbon steel. J. Appl. Phys. 103(4), 04391–04396 (2008)
Lo, C., Lee, S., Kerdus, L., Jiles, D.: Examination of the relationship between the parameters of Barkhausen effect model and microstructure of magnetic materials. J. Appl. Phys. 91(10), 7651–7653 (2002)
Thompson, S., Tanner, B.: The magnetic properties of pearlitic steels as a function of carbon content. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 123(3), 283–298 (1993)
Saquet, O., Chicois, J., Vincent, A.: Barkhausen noise from plain carbon steels: analysis of the influence of microstructure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 269(1), 73–82 (1999)
Cullity, B.D., Graham, C.D.: Introduction to Magnetic Materials. Wiley, Hoboken (2011)
Stupakov, O., Perevertov, O., Tomáš, I., Skrbek, B.: Evaluation of surface decarburization depth by magnetic Barkhausen noise technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 323(12), 1692–1697 (2011)
Stupakov, O., Uchimoto, T., Takagi, T.: Magnetic anisotropy of plastically deformed low-carbon steel. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 43(19), 195003 (2010)
Stupakov, O., Perevertov, O., Stoyka, V., Wood, R.: Correlation between hysteresis and Barkhausen noise parameters of electrical steels. IEEE Trans. Magn. 46(2), 517–520 (2010)
Stupakov, O., Takagi, T., Uchimoto, T.: Alternative magnetic parameters for characterization of plastic tension. NDT&E Int. 43(8), 671–676 (2010)
Tanner, B., Szpunar, J., Willcock, S., Morgan, L., Mundell, P.: Magnetic and metallurgical properties of high-tensile steels. J. Mater. Sci. 23(12), 4534–4540 (1988)
Sablik, M., Burkhardt, G., Kwun, H., Jiles, D.: A model for the effect of stress on the low-frequency harmonic content of the magnetic induction in ferromagnetic materials. J. Appl. Phys. 63(8), 3930–3932 (1988)
Krause, T.W., Clapham, L., Pattantyus, A., Atherton, D.L.: Investigation of the stress-dependent magnetic easy axis in steel using magnetic barkhausen noise. J. Appl. Phys. 79(8), 4242–4252 (1996)
Stefanita, C., Clapham, L., Atherton, D.: Subtle changes in magnetic Barkhausen noise before the macroscopic elastic limit. J. Mater. Sci. 35(11), 2675–2681 (2000)
Pérez-Benítez, J., Padovese, L., Capó-Sánchez, J., Anglada-Rivera, J.: Investigation of the magnetic Barkhausen noise using elementary signals parameters in 1000 commercial steel. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 263(1), 72–77 (2003)
Inaguma, T., Sakamoto, H., Hasegawa, M.: Stress dependence of Barkhausen noise in spheroidized cementite carbon steel. IEEE Trans. Magn. 49(4), 1310–1317 (2013)
Kasai, N., Koshino, H., Sekine, K., Kihira, H., Takahashi, M.: Study on the effect of elastic stress and microstructure of low carbon steels on Barkhausen noise. J. Nondestruct. Eval. 32(3), 277–285 (2013)
Langman, R.: Magnetic properties of mild steel under conditions of biaxial stress. IEEE Trans. Magn. 26(4), 1246–1251 (1990)
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Steven White for his help on system troubleshooting, and Philip Weetman for useful discussions. This work was supported by Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samimi, A.A., Krause, T.W. & Clapham, L. Multi-parameter Evaluation of Magnetic Barkhausen Noise in Carbon Steel. J Nondestruct Eval 35, 40 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-016-0358-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10921-016-0358-4