Abstract
The ecological theory of social perception suggests that people’s first impressions should be especially accurate for judgments relevant to their goals. Here, we tested whether people could accurately judge others’ levels of antigay prejudice and whether gay men’s accuracy would exceed straight men’s accuracy in making these judgments. We found that people judged men’s (but not women’s) levels of antigay prejudice accurately from photos of their faces and that impressions of facial power supported their judgments. Gay men and straight men did not significantly differ in their sensitivity to antigay prejudice, however. People may therefore judge others’ levels of prejudice accurately regardless of their personal stake in its consequences.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
We did not collect the ages of 97 of these participants due to a programming error.
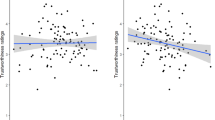
Confidence intervals obtained by bootstrapping the analysis 5000 times.
As in Study 1, the Facial Power composite again mediated the accuracy of these judgments (ab = .13, 95% CI [.02, .25]).
References
Alaei, R., & Rule, N. O. (2016). Accuracy of perceiving social attributes. In J. A. Hall, M. Schmid Mast, & T. V. West (Eds.), The social psychology of perceiving others accurately (pp. 125–142). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Anderson, C. R. (1977). Locus of control, coping behaviors, and performance in a stress setting: A longitudinal study. Journal of Applied Psychology, 62, 446–451.
Andrzejewski, S. A., Hall, J. A., & Salib, E. R. (2009). Anti-semitism and identification of Jewish group membership from photographs. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 33, 47–58.
Biernat, M., & Manis, M. (1994). Shifting standards and stereotype-based judgments. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 66, 5–20.
Bjornsdottir, R. T., Alaei, R., & Rule, N. O. (2017). The perceptive proletarian: Subjective social class predicts interpersonal accuracy. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 41, 185–201.
Bond, C. F., Jr., & DePaulo, B. M. (2008). Individual differences in judging deception: Accuracy and bias. Psychological Bulletin, 134, 477–492.
Carney, D. R., & Harrigan, J. A. (2003). It takes one to know one: Interpersonal sensitivity is related to accurate assessments of others’ interpersonal sensitivity. Emotion, 3, 194–200.
Dardenne, B., Dumont, M., & Bollier, T. (2007). Insidious dangers of benevolent sexism: Consequences for women’s performance. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93, 764–779.
DeYoung, C. G., Quilty, L. C., & Peterson, J. B. (2007). Between facets and domains: 10 aspects of the Big Five. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 93, 880–896.
Ding, J. Y. C., & Rule, N. O. (2012). Gay, straight, or somewhere in between: Accuracy and bias in the perception of bisexual faces. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 36, 165–176.
Ekman, P., Sorensen, E. R., & Friesen, W. V. (1969). Pan-cultural elements in facial displays of emotion. Science, 164, 86–88.
Funder, D. C. (1995). On the accuracy of personality judgment: A realistic approach. Psychological Review, 102, 652–670.
Goh, J. X., Rad, A., & Hall, J. A. (2017). Bias and accuracy in judging sexism in mixed-gender social interactions. Group Processes & Intergroup Relations, 20, 820–856.
Griskevicius, V., Goldstein, N. J., Mortensen, C. R., Cialdini, R. B., & Kenrick, D. T. (2006). Going along versus going alone: When fundamental motives facilitate strategic (non)conformity. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 91, 281–294.
Haddock, G., Zanna, M., & Esses, V. (1993). Assessing the structure of prejudicial attitudes: The case of attitudes toward homosexuals. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 65, 1105–1118.
Hall, J. A., Andrzejewski, S. A., & Yopchick, J. E. (2009a). Psychosocial correlates of interpersonal sensitivity: A meta-analysis. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 33, 149–180.
Hall, J. A., Blanch, D. C., Horgan, T. G., Murphy, N. A., Rosip, J. C., & Mast, M. S. (2009b). Motivation and interpersonal sensitivity: Does it matter how hard you try? Motivation and Emotion, 33, 291–302.
Haselhuhn, M. P., Ormiston, M. E., & Wong, E. M. (2015). Men’s facial width-to-height ratio predicts aggression: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE, 10, e0122637.
Hehman, E., Leitner, J. B., Deegan, M. P., & Gaertner, S. L. (2013). Facial structure is indicative of explicit support for prejudicial beliefs. Psychological Science, 24, 289–296.
Herek, G. M. (2004). Beyond ‘homophobia’: Thinking about sexual stigma and prejudice in the twenty-first century. Sexuality Research and Social Policy, 1, 6–24.
Heslin, P. A., Bell, M. P., & Fletcher, P. O. (2012). The devil without and within: A conceptual model of social cognitive processes whereby discrimination leads stigmatized minorities to become discouraged workers. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 33, 840–862.
Katz-Wise, S. L., & Hyde, J. S. (2012). Victimization experiences of lesbian, gay, and bisexual individuals: A meta-analysis. Journal of Sex Research, 49, 142–167.
Keltner, D., Gruenfeld, D. H., & Anderson, C. (2003). Power, approach, and inhibition. Psychological Review, 110, 265–284.
Kraus, M. W., Côté, S., & Keltner, D. (2010). Social class, contextualism, and empathic accuracy. Psychological Science, 21, 1716–1723.
Lakens, D. (2017). Equivalence tests: A practical primer for t tests, correlations, and meta-analyses. Social Psychological and Personality Science, 8, 355–362.
Larson, A., Gillies, M., Howard, P. J., & Coffin, J. (2007). It’s enough to make you sick: The impact of racism on the health of Aboriginal Australians. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Public Health, 3, 322–329.
McArthur, L. Z., & Baron, R. M. (1983). Toward an ecological theory of social perception. Psychological Review, 90, 215–238.
Mehta, P. H., & Beer, J. (2009). Neural mechanisms of the testosterone-aggression relation: The role of the orbitofrontal cortex. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 22, 2357–2368.
Morrison, M. A., & Morrison, T. G. (2003). Development and validation of a scale measuring modern prejudice toward gay men and lesbian women. Journal of Homosexuality, 43, 15–37.
Murphy, N. A., & Hall, J. A. (2011). Intelligence and interpersonal sensitivity: A meta-analysis. Intelligence, 39, 54–63.
Oosterhof, N. N., & Todorov, A. (2008). The functional basis of face evaluation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 105, 11087–11092.
Penton-Voak, I. S., Pound, N., Little, A. C., & Perrett, D. I. (2006). Personality judgments from natural and composite facial images: More evidence for a “kernel of truth” in social perception. Social Cognition, 24, 607–640.
Ragins, B. R., Singh, R., & Cornwell, J. M. (2007). Making the invisible visible: Fear and disclosure of sexual orientation at work. Journal of Applied Psychology, 92, 1103–1118.
Richeson, J. A., & Shelton, J. N. (2005). Brief report: Thin slices of racial bias. Journal of Nonverbal Behavior, 29, 75–86.
Rotter, J. B. (1966). Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychological Monographs: General and Applied, 80, 1–28.
Rule, N. O. (2017). Perceptions of sexual orientation from minimal cues. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 46, 129–139.
Rule, N. O., Adams, R. B., Jr., Ambady, N., & Freeman, J. B. (2012). Perceptions of dominance following glimpses of faces and bodies. Perception, 41, 687–706.
Rule, N. O., & Alaei, R. (2016). Gaydar: The perception of sexual orientation from subtle cues. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 25, 444–448.
Rule, N. O., Ambady, N., & Hallett, K. C. (2009). Female sexual orientation is perceived accurately, rapidly, and automatically from the face and its features. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 45, 1245–1251.
Rule, N. O., Krendl, A. C., Ivcevic, Z., & Ambady, N. (2013). Accuracy and consensus in judgments of trustworthiness from faces: Behavioral and neural correlates. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 104, 409–426.
Rule, N. O., Rosen, K. S., Slepian, M. L., & Ambady, N. (2011). Mating interest improves women’s accuracy in judging male sexual orientation. Psychological Science, 22, 881–886.
Sandler, I. N., & Lakey, B. (1982). Locus of control as a stress moderator: The role of control perceptions and social support. American Journal of Community Psychology, 10, 65–80.
Tskhay, K. O., Krendl, A. C., & Rule, N. O. (2016). Age-related physical changes interfere with judgments of male sexual orientation from faces. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 42, 1217–1226.
Tskhay, K. O., & Rule, N. O. (2013). Accuracy in categorizing perceptually ambiguous groups: A review and meta-analysis. Personality and Social Psychology Review, 17, 72–86.
Tskhay, K. O., & Rule, N. O. (2017). Internalized homophobia influences perceptions of men’s sexual orientation from photos of their faces. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 46, 755–761.
Zebrowitz, L. A. (1997). Reading faces: Window to the soul?. Boulder, CO: Westview Press.
Zebrowitz, L. A., & Montepare, J. M. (2006). The ecological approach to person perception: Evolutionary roots and contemporary offshoots. In M. Schaller, J. A. Simpson, & D. T. Kenrick (Eds.), Evolution and social psychology (pp. 81–113). New York, NY: Psychology Press.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council of Canada to RA and NOR. We thank Garrett Arathoon, Joseph Choi, Emerson Daniele, and Chuyun Shen for their assistance in experimental set-up.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Experimental design: RA and NOR; Data collection: RA and NOR; Data analysis: RA; Writing: RA and NOR.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Standards
All procedures performed in this study followed the ethical standards of the University of Toronto Research Ethics Board and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
We obtained informed consent from all participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alaei, R., Rule, N.O. People Can Accurately (But Not Adaptively) Judge Strangers’ Antigay Prejudice from Faces. J Nonverbal Behav 43, 397–409 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10919-019-00305-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10919-019-00305-2