Abstract
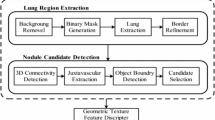
Lung cancer is still the most concerned disease around the world. Lung nodule generates in the pulmonary parenchyma which indicates the latent risk of lung cancer. Computer-aided pulmonary nodules detection system is necessary, which can reduce diagnosis time and decrease mortality of patients. In this study, we have proposed a new computer aided diagnosis (CAD) system for detection of early pulmonary nodule, which can help radiologists quickly locate suspected nodules and make judgments. This system consists of four main sections: pulmonary parenchyma segmentation, nodule candidate detection, features extraction (total 22 features) and nodule classification. The publicly available data set created by the Lung Image Database Consortium (LIDC) is used for training and testing. This study selects 6400 slices from 80 CT scans containing totally 978 nodules, which is labeled by four radiologists. Through a fast segmentation method proposed in this paper, pulmonary nodules including 888 true nodules and 11,379 false positive nodules are segmented. By means of an ensemble classifier, Random Forest (RF), this study acquires 93.2, 92.4, 94.8, 97.6% of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, area under the curve (AUC), respectively. Compared with support vector machine (SVM) classifier, RF can reduce more false positive nodules and acquire larger AUC. With the help of this CAD system, radiologist can be provided with a great reference for pulmonary nodule diagnosis timely.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Dikshit, R., et al., Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 136(5):E359–E386, 2015.
Della, P. C., Cigarette smoking: the most widespread and insidious weapon of mass destruction. Arch. Med. Vet. 1(1):5, 2015.
Pesch, B., Kendzia, B., Gustavsson, P., et al., Cigarette smoking and lung cancer—relative risk estimates for the major histological types from a pooled analysis of case–control studies. Int. J. Cancer 131(5):1210–1219, 2012.
World Health Organization International, Tobacco smoke and involuntary smoking. Lyon, France, 2002.
Chen, X., Shao, S., Tian, Z., et al., Impacts of air pollution and its spatial spillover effect on public health based on China’s big data sample. J. Clean. Prod. 2016. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2016.02.119.
Diederich, S., Lentschig, M., Overbeck, T., et al., Detection of pulmonary nodules at spiral CT: comparison of maximum intensity projection sliding slabs and single-image reporting. Eur. Radiol. 11(8):1345–1350, 2001.
Valente, I. R. S., Cortez, P. C., Neto, E. C., et al., Automatic 3D pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: a survey. Comput. Meth. Programs Biomed. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.10.006.
Swensen, S. J., Viggiano, R. W., Midthun, D. E., et al., Lung nodule enhancement at CT: multicenter study 1. Radiology 214(1):73–80, 2000.
Xu, D. M., van der Zaag-Loonen, H. J., Oudkerk, M., et al., Smooth or attached solid indeterminate nodules detected at baseline CT screening in the NELSON study: cancer risk during 1 year of follow-up. Radiology 250(1):264–272, 2009.
Li, Q., Sone, S., and Doi, K., Selective enhancement filters for nodules, vessels, and airway walls in two-and three-dimensional CT scans. Med. Phys. 30(8):2040–2051, 2003.
Ozekes, S., and Osman, O., Computerized lung nodule detection using 3D feature extraction and learning based algorithms. J. Med. Syst. 34(2):185–194, 2010.
Noor, N. M., Than, J. C. M., Rijal, O. M., et al., Automatic lung segmentation using control feedback system: morphology and texture paradigm. J. Med. Syst. 39(3):1–18, 2015.
Ma, Q., Ji, B., Jia, B., et al., Differential diagnosis of solitary pulmonary nodules using 99mTc-3P4-RGD2 scintigraphy. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 38(12):2145–2152, 2011.
Firmino, M., Morais, A. H., and Mendoça, R. M., Computer-aided detection system for lung cancer in computed tomography scans: review and future prospects. Biomed. Eng. Online 13:1–16, 2014.
Taşcı, E., and Uğur, A., Shape and texture based novel features for automated juxtapleural nodule detection in lung CTs. J. Med. Syst. 39(5):1–13, 2015.
Peña, D. M., Luo, S., and Abdelgader, A., Auto diagnostics of lung nodules using minimal characteristics extraction technique. Diagnostics 6(1):13, 2016.
Penedo, M. G., Carreira, M. J., Mosquera, A., et al., Computer-aided diagnosis: a neural-network-based approach to lung nodule detection. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 17(6):872–880, 1998.
Akram, S., Javed, M. Y., Akram, M. U., et al., Pulmonary nodules detection and classification using hybrid features from computerized tomographic images. J. Med. Imag. Health Inform. 6(1):252–259, 2016.
Santos, A. M., de Carvalho Filho, A. O., Silva, A. C., et al., Automatic detection of small lung nodules in 3D CT data using Gaussian mixture models, Tsallis entropy and SVM. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 36:27–39, 2014.
Teramoto, A., and Fujita, H., Fast lung nodule detection in chest CT images using cylindrical nodule-enhancement filter. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 8(2):193–205, 2013.
Gonçalves, L., Novo, J., and Campilho, A., Hessian based approaches for 3D lung nodule segmentation. Expert Syst. Appl. 61:1–15, 2016.
Jiang, H. Y., Ma, H., Qian, W., et al., Risk analysis for pathological changes in pulmonary parenchyma based on lung computed tomography images. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 40(3):357–363, 2016.
Messay, T., Hardie, R. C., and Rogers, S. K., A new computationally efficient CAD system for pulmonary nodule detection in CT imagery. Med. Image Anal. 14(3):390–406, 2010.
Zhang, F., Song, Y., Cai, W., et al., Lung nodule classification with multilevel patch-based context analysis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 61(4):1155–1166, 2014.
Feng, Z., Jiulun, F. A. N., Xiaoying, P. A. N., et al., Two-dimensional Otsu’s curve thresholding segmentation method based on gray and non-local spatial gray feature. Appl. Res. Comput. 5:104, 2012.
Chunying, P., Jikui, L., and Lixi, H., White blood cells image classification based on improving the connection of FCM and LFP. J. Imag. Graph. 18(5):545–551, 2013.
Wang, H., Guo, X. H., Jia, Z. W., et al., Multilevel binomial logistic prediction model for malignant pulmonary nodules based on texture features of CT image. Eur. J. Radiol. 74(1):124–129, 2010.
Ye, X., Lin, X., Dehmeshki, J., et al., Shape-based computer-aided detection of lung nodules in thoracic CT images. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 56(7):1810–1820, 2009.
Gonzales, R. C., Woods, R. E., and Eddins, S. L., Digital image processing using MATLAB. Pearson Prentice Hall, New Jersey, 2004.
Lee, S. L. A., Kouzani, A. Z., and Hu, E. J., Random forest based lung nodule classification aided by clustering. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 34(7):535–542, 2010.
Saien, S., Pilevar, A. H., and Moghaddam, H. A., Refinement of lung nodule candidates based on local geometric shape analysis and Laplacian of Gaussian kernels. Comput. Biol. Med. 54:188–198, 2014.
Lu, L., Tan, Y., Schwartz, L. H., et al., Hybrid detection of lung nodules on CT scan images. Med. Phys. 42(9):5042–5054, 2015.
Guo, W., and Li, Q., High performance lung nodule detection schemes in CT using local and global information. Med. Phys. 39(8):5157–5168, 2012.
Choi, W. J., and Choi, T. S., Automated pulmonary nodule detection system in computed tomography images: a hierarchical block classification approach. Entropy 15(2):507–523, 2013.
Netto, S. M. B., Silva, A. C., Nunes, R. A., et al., Automatic segmentation of lung nodules with growing neural gas and support vector machine. Comput. Biol. Med. 42(11):1110–1121, 2012.
Choi, W. J., and Choi, T. S., Automated pulmonary nodule detection based on three-dimensional shape-based feature descriptor. Comput. Meth. Programs Biomed. 113(1):37–54, 2014.
He, C., Fan, X., and Li, Y., Toward ubiquitous healthcare services with a novel efficient cloud platform. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 60(1):230–234, 2013.
Wang, D., He, D., Wang, P., et al., Anonymous two-factor authentication in distributed systems: certain goals are beyond attainment. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secur. Comput. 12(4):428–442, 2015.
Wang, D., Wang, N., Wang, P., et al., Preserving privacy for free: efficient and provably secure two-factor authentication scheme with user anonymity. Inf. Sci. 321:162–178, 2015.
He, C. G., Bao, S. D., and Li, Y., A novel tri-factor mutual authentication with biometrics for wireless body sensor networks in healthcare applications. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 6(3):910–931, 2013.
He, C. G., Cao, C. Z, Bao S. D. An enhanced role-based access control mechanism for hospital information systems. Int. Conf. Comput. Intell. 1001-1005, 2011
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National 863 project of China (SS2015AA020109), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61502472 and No. 31300816) and STS funding from Chinese Academy of Sciences (JCYJ20140417113430655 and JCYJ20140417113430619).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Patient Facing Systems
Ji-kui Liu and Hong-yang Jiang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Jk., Jiang, Hy., Gao, Md. et al. An Assisted Diagnosis System for Detection of Early Pulmonary Nodule in Computed Tomography Images. J Med Syst 41, 30 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0669-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-016-0669-0