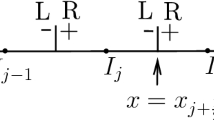
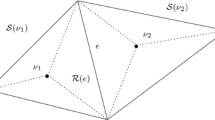
Abstract
A high-order quasi-conservative discontinuous Galerkin (DG) method is proposed for the numerical simulation of compressible multi-component flows. A distinct feature of the method is a predictor-corrector strategy to define the grid velocity. A Lagrangian mesh is first computed based on the flow velocity and then used as an initial mesh in a moving mesh method (the moving mesh partial differential equation or MMPDE method ) to improve its quality. The fluid dynamic equations are discretized in the direct arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian framework using DG elements and the non-oscillatory kinetic flux while the species equation is discretized using a quasi-conservative DG scheme to avoid numerical oscillations near material interfaces. A selection of one- and two-dimensional examples are presented to verify the convergence order and the constant-pressure-velocity preservation property of the method. They also demonstrate that the incorporation of the Lagrangian meshing with the MMPDE moving mesh method works well to concentrate mesh points in regions of shocks and material interfaces.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abgrall, R.: How to prevent pressure oscillations in multicomponent flow calculations: A quasi conservative approach. J. Comput. Phys. 125, 150–160 (1996)
Addessio, F. L., Carroll, D. E., Dukowicz, J. K., Harlow, F. H., Johnson, J. N., Kashiwa, B. A., Maltrud, M. E., Ruppel, H.: CAVEAT: A computer code for fluid dynamics problems with large distortion and internal slip, Los Alamos National Laboratory LA-10613-MSREVISED, (1990)
Baines, M.J.: Moving Finite Elements. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1994)
Baines, M.J., Hubbard, M.E., Jimack, P.K.: Velocity-based moving mesh methods for nonlinear partial differential equations. Comm. Comput. Phys. 10, 509–576 (2011)
Boscheri, W.: High order direct Arbitrary-Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) finite volume schemes for hyperbolic systems on unstructured meshes. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 24, 751–801 (2017)
Budd, C.J., Huang, W., Russell, R.D.: Adaptivity with moving grids. Acta Numer. 18, 111–241 (2009)
Chen, Y.: A study of GKS method for multi-component flows (in Chinese), Ph.D thesis, Beijing, China Academy of Engineering Physics (2010)
Chen, Y., Jiang, S.: A non-oscillatory kinetic scheme for multi-component flows with the equation of state for a stiffened gas. J. Comput. Math. 29, 661–683 (2011)
Chen, Y., Jiang, S.: Modified kinetic flux vector splitting schemes for compressible flows. J. Comput. Phys. 228, 3582–3604 (2009)
Cheng, J., Zhang, F., Liu, T.G.: A discontinuous Galerkin method for the simulation of compressible gas-gas and gas-water two-medium flows. J. Comput. Phys. 403, 109059 (2020)
Cheng, J., Shu, C.-W.: A high order ENO conservative Lagrangian type scheme for the compressible Euler equations. J. Comput. Phys. 227, 1567–1596 (2007)
Cheng, J., Shu, C.-W.: Positivity-preserving Lagrangian scheme for multi-material compressible flow. J. Comput. Phys. 257, 143–168 (2014)
Cockburn, B., Hou, S., Shu, C.-W.: The Runge-Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws IV: The multidimensional case. Math. Comp. 54, 545–581 (1990)
Cockburn, B., Lin, S.-Y., Shu, C.-W.: TVB Runge-Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws III: One dimensional systems. J. Comput. Phys. 84, 90–113 (1989)
Cockburn, B., Shu, C.-W.: TVB Runge-Kutta local projection discontinuous Galerkin finite element method for conservation laws II: General framework. Math. Comp. 52, 411–435 (1989)
Cockburn, B., Shu, C.-W.: The Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method for conservation laws V: Multidimensional systems. J. Comput. Phys. 141, 199–224 (1998)
Farhat, C., Geuzaine, P., Granndmont, C.: The discrete geometric conservation law and the nonlinear stability of ALE schemes for the solution of flow problems on moving grids. J. Comput. Phys. 174, 669–694 (2001)
Fu, P., Schnücke, G., Xia, Y.: Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian discontinuous Galerkin method for conservation laws on moving simplex meshes. Math. Comp. 88, 2221–2255 (2019)
Henry de Frahan, M. T., Varadan, S., Johnsen, E.: A new limiting procedure for discontinuous Galerkin methods applied to compressible multiphase flows with shocks and interfaces, J. Comput. Phys. 280, 489-509 (2015)
Hirt, C.W., Amsden, A.A., Cook, J.L.: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian computing method for all flow speed. J. Comput. Phys. 14, 227–253 (1974)
Huang, W., Kamenski, L.: A geometric discretization and a simple implementation for variational mesh generation and adaptation. J. Comput. Phys. 301, 322–337 (2015)
Huang, W., Kamenski, L.: On the mesh nonsingularity of the moving mesh PDE method. Math. Comput. 87, 1887–1911 (2018)
Huang, W., Ren, Y., Russell, R.D.: Moving mesh methods based on moving mesh partial differential equations. J. Comput. Phys. 113, 279–290 (1994)
Huang, W., Ren, Y., Russell, R.D.: Moving mesh partial differential equations (MMPDEs) based upon the equidistribution principle. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 31, 709–730 (1994)
Huang, W., Russell, R.D.: Adaptive moving mesh methods. Springer-Verlag, New York (2011)
Huang, W.: Mathematical principles of anisotropic mesh adaptation. Comm. Comput. Phys. 1, 276–310 (2006)
Huang, W.: Variational mesh adaptation: isotropy and equidistribution. J. Comput. Phys. 174, 903–924 (2001)
Huang, W.: Variational mesh adaptation II: error estimates and monitor functions. J. Comput. Phys. 184, 619–648 (2003)
Jimack, P., Wathen, A.: Temporal derivatives in the finite-element method on continuously deforming grids. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 28, 990–1003 (1991)
Klingenberg, C., Schnücke, G., Xia, Y.: Arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian discontinuous Galerkin method for conservation laws: analysis and application in one dimension. Math. Comp. 86, 1203–1232 (2017)
Kucharik, M., Shashkov, M.J.: One-step hybrid remapping algorithm for multi-material arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian methods. J. Comput. Phys. 231, 2851–2864 (2012)
Lesoinne, M., Farhat, C.: Geometric conservation laws for flow problems with moving boundaries and deformable meshes, and their impact on aeroelastic computations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 134, 71–90 (1996)
Liu, H., Xu, K.: A Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method for viscous flow equations. J. Comput. Phys. 224, 1223–1242 (2007)
Liu, N., Xu, X., Chen, Y.: High-order spectral volume scheme for multi-component flows using non-oscillatory kinetic flux. Comput. Fluids 152, 120–133 (2017)
Lomtev, I., Kirby, R.M., Karniadakis, G.E.: A discontinuous Galerkin ALE method for compressible viscous flows in moving domains. J. Comput. Phys. 155, 128–159 (1999)
Luo, D., Huang, W., Qiu, J.X.: A quasi-Lagrangian moving mesh discontinuous Galerkin method for hyperbolic conservation laws. J. Comput. Phys. 396, 544–578 (2019)
Luo, D., Qiu, J.X., Zhu, J., Chen, Y.: A quasi-conservative discontinuous Galerkin method for multi-component flows using the non-oscillatory kinetic flux. J. Sci. Comput. 87, 1–32 (2021)
Maire, P.H., Breil, J., Galera, S.: A cell-centered arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian (ALE) method. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 56, 1161–1166 (2008)
Maire, P.H., Abgrall, R., Breil, J., Ovadia, J.: A cell-centered Lagrangian scheme for two-dimensional compressible flow problems. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 29, 1781–1824 (2007)
Miller, K., Miller, R.N.: Moving finite elements I. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 18, 1019–1032 (1981)
Nguyen, V.T.: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian discontinuous Galerkin method for simulations of flows over variable geometries. J. Fluids Struct. 26, 312–329 (2010)
Pandare, A. K., Wang, C., Luo, H.: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian reconstructed discontinuous Galerkin method for compressible multiphase flows, 46th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference (2016)
Persson, P.O., Bonet, J., Peraire, J.: Discontinuous Galerkin solution of the Navier-Stokes equations on deformable domains. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 198, 1585–1595 (2009)
Qiu, J.X., Liu, T.G., Khoo, B.C.: Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin methods for compressible two-medium flow simulations: one-dimensional case. J. Comput. Phys. 222, 353–373 (2007)
Qiu, J.X., Liu, T.G., Khoo, B.C.: Simulations of compressible two-medium flow by Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin methods with the ghost fluid method. Comm. Comput. Phys. 3, 479–504 (2008)
Qiu, J.X., Shu, C.-W.: Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method using WENO limiters. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 26, 907–929 (2005)
del Razo, M.J., Leveque, R.J.: Numerical methods for interface coupling of compressible and almost incompressible media. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 39, B486–B507 (2017)
Reed, W. H., Hill, T. R.: Triangular mesh methods for neutron transport equation, Los Alamos Scientific Laboratory Report LA-UR-73-479 (1973)
Ren, X., Xu, K., Shyy, W.: A multi-dimensional high-order DG-ALE method based on gas-kinetic theory with application to oscillating bodies. J. Comput. Phys. 316, 700–720 (2016)
Saleem, M.R., Ali, I., Qamar, S.: Application of discontinuous Galerkin method for solving a compressible five-equation two-phase flow model. Results Phys. 8, 379–390 (2018)
Shu, C.-W.: Total-variation-diminishing time discretizations. SIAM J. Sci. Stat. Comput. 9, 1073–1084 (1988)
Shu, C.-W., Osher, S.: Efficient implementation of essentially non-oscillatory shock capturing schemes II. J. Comput. Phys. 83, 32–78 (1989)
Shyue, K.M.: An efficient shock-capturing algorithm for compressible multicomponent problems. J. Comput. Phys. 142, 208–242 (1998)
Shyue, K.M.: A wave-propagation based volume tracking method for compressible multicomponent flow in two space dimensions. J. Comput. Phys. 215, 219–244 (2006)
Tang, T.: Moving mesh methods for computational fluid dynamics flow and transport, Recent Advances in Adaptive Computation (Hangzhou, 2004), Volume 383 of AMS Contemporary Mathematics, pages 141-173. Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI, (2005)
Wang, C.-W., Shu, C.-W.: An interface treating technique for compressible multi-medium flow with Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin method. J. Comput. Phys. 229, 8823–8843 (2010)
Xu, K.: BGK-based scheme for multicomponent flow calculations. J. Comput. Phys. 134, 122–133 (1997)
Xu, X., Ni, G., Jiang, S.: A high-order moving mesh kinetic scheme based on WENO reconstruction for compressible flows on unstructured meshes. J. Sci. Comput. 57, 278–299 (2013)
Zhang, Z., Naga, A.: A new finite element gradient recovery method: superconvergence property. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 26, 1192–1213 (2005)
Zhao, X., Yu, X., Qiu, M., Qing, F., Zou, S.: An arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian RKDG method for multi-material flows on adaptive unstructured meshes. Comput. Fluids 207, 104589 (2020)
Zhu, J., Qiu, J.X., Liu, T.G., Khoo, B.C.: High-order RKDG methods with WENO type limiters and conservative interfacial procedure for one-dimensional compressible multi-medium flow simulations. Appl. Numer. Math. 61, 554–580 (2011)
Zhu, J., Qiu, J.X., Shu, C.-W.: High-order Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin methods with a new type of multi-resolution WENO limiters. J. Comput. Phys. 404, 109105 (2020)
Zhu, J., Shu, C.-W., Qiu, J.X.: High-order Runge-Kutta discontinuous Galerkin methods with a new type of multi-resolution WENO limiters on triangular meshes. Appl. Numer. Math. 153, 519–539 (2020)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The research is supported partly by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 12101063, 11901044 and 12071392), Science Challenge Project (China), No. TZ2016002, National Key Project (GJXM92579)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, D., Li, S., Huang, W. et al. A Quasi-Conservative Discontinuous Galerkin Method for Multi-component Flows Using the Non-oscillatory Kinetic Flux II: ALE Framework. J Sci Comput 90, 46 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01732-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-021-01732-4