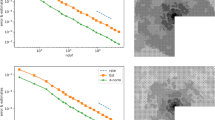
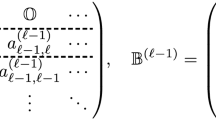Abstract
In this paper, a fully non-conforming least-squares spectral element method for fourth order elliptic problems on smooth domains is presented. The proposed method works for a general fourth order elliptic operator with non-homogeneous data in two dimensions and gives exponentially accurate solutions. We derive differentiability estimates and prove our main stability estimate theorem using a non-conforming spectral element method. We then formulate a numerical scheme using a block diagonal preconditioner. Error estimates are also proven for the proposed method. We provide the computational complexity of our method and present results of numerical simulations that have been performed to validate the theory.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altas, I., Dym, J., Gupta, M.M., Manohar, R.: Mutigrid solution of automatically generated high-order discretizations for the biharmonic equation. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 19, 1575–1585 (1998)
Babuška, I., Guo, B.: Approximation properties of the \(h-p\) version of the finite element method. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 133, 319–346 (1996)
Babuška, I., Guo, B.: Regularity of the solutions of elliptic problems with piecewise analytic data, part I: boundary value problems for linear elliptic equation of second order. SIAM J. Math. Anal. 19(1), 172–203 (1988)
Babuška, I., Guo, B.: The \(h-p\) version of the finite element method on domains with curved boundaries. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 25, 837–861 (1988)
Babuška, I., Guo, B.: The \(h\)-\(p\) version of the finite element method, part I: the basic approximation results. Comput. Mech. 1, 21–41 (1986)
Babuška, I., Guo, B.: The \(h-p\) version of the finite element method, part II: general results and applications. Comput. Mech. 1, 203–220 (1986)
Bernardi, C., Coppoletta, G., Maday, Y.: Some spectral approximations of two-dimensional fourth-order problems. Math. Comput. 59(199), 63–76 (1992)
Bernardi, C., Maday, Y.: Spectral methods. Handb. Numer. Anal. 5, 209–485 (1997)
Ben-Artzi, M., Croisille, J.P., Fishelov, D.: A fast direct solver for the biharmonic problem in a rectangular grid. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 31(1), 303–333 (2008)
Bialecki, B., Karageorghis, A.: A Legendre spectral Galerkin method for the biharmonic Dirichlet problem. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 22(5), 1549–1569 (2001)
Bialecki, B.: A Legendre spectral collocation method for the biharmonic Dirichlet problem. ESAIM: Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 34(3), 637–662 (2000)
Bialecki, B.: A fast solver for the orthogonal spline collocation solution of the biharmonic Dirichlet problem on rectangles. J. Comput. Phys. 191, 601–621 (2003)
Bjørstad, P.: Fast numerical solution of the biharmonic Dirichlet problem on rectangles. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 20(1), 59–71 (1983)
Buzzbee, B.L., Dorr, F.W.: The direct solution of the biharmonic equation on rectangular regions and the Poisson equation on irregular regions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 11(4), 753–763 (1974)
Canuto, C., Hussaini, M.Y., Quarteroni, A., Zang, T.A.: Spectral Methods in Fluid Dynamics. Springer, Berlin (1988)
Ciarlet, P.G.: The finite element method for elliptic problems, classics in applied mathematics. SIAM. 40 (2002). doi:10.1137/1.9780898719208
Dutt, P., Biswas, P., Raju, G.N.: Preconditioners for spectral element methods for elliptic and parabolic problems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 215(1), 152–166 (2008)
Dutt, P.K., Kumar, N.K., Upadhyay, C.S.: Non-conforming \(h-p\) spectral element methods for elliptic problems. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.) 117(1), 109–145 (2007)
Dutt, P., Tomar, S.: Stability estimates for \(h-p\) spectral element methods for general elliptic problems on curvilinear domains. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math. Sci.) 113(4), 395–429 (2003)
Dutt, P., Tomar, S., Kumar, B.V.R.: Stability estimates for \(h-p\) spectral element methods for elliptic problems. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Math Sci.) 112(4), 601–639 (2002)
Gerritsma, M., Maerschalck, D.B.: Least-squares spectral element methods in computational fluid dynamics. Advanced Computational Methods in Science and Engineering Lecture Notes in Computational Science and Engineering, vol. 71, pp. 179–227 (2010)
Grisvard, P.: Elliptic problems in nonsmooth domains, classics in applied mathematics. SIAM, 69 (2011). doi:10.1137/1.9781611972030
Husain, A., Khan, A.: Least-squares spectral element preconditioners for fourth order elliptic problems. arXiv:1608.08416
Karniadakis, G., Sherwin, J.: Spectral/h-p Element Methods for CFD. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1999)
Khan, A., Upadhyay, C.S.: Exponentially accurate nonconforming least-squares spectral element method for elliptic problems on unbounded domain. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 305, 607–633 (2016)
Kumar, N.K., Nagaraju, G.: Least-squares \(hp\)/spectral element method for elliptic problems. Appl. Numer. Math. 60(1–2), 38–54 (2010)
Kumar, N.K., Dutt, P.K., Upadhyay, C.S.: Nonconforming spectral/\(h-p\) element methods for elliptic systems. J. Numer. Math. 17(2), 119–142 (2009)
Mandel, J.: Iterative methods for \(p-\)version finite elements: preconditioning thin solids. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 133, 247–257 (1996)
Meleshko, V.V.: Selected topics in the history of the two-dimensional biharmonic problem. Appl. Mech. Rev. 56(1), 3385 (2003)
Pathria, D., Karniadakis, G.E.: Spectral element methods for elliptic problems in non-smooth domains. J. Comput. Phys. 122, 83–95 (1995)
Pontaza, J.P., Reddy, J.N.: Spectral/hp least-squares finite element formulation for the incompressible Navier-Stokes equation. J. Comput. Phys. 190(2), 523–549 (2003)
Proot, M.M.J., Gerritsma, M.I.: A least-squares spectral element formulation for Stokes problem. J. Comput. Phys. 17(1–4), 285–296 (2002)
Schwab, C.: \(p\) and \(h-p\) Finite Element Methods. Clarendon Press, Oxford (1998)
Shen, J.: Efficient spectral-Galerkin method I. Direct solvers for the second and fourth order equations using Legendre polynomials. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 15(6), 1489–1505 (1994)
Shen, J., Tang, T.: Spectral and High-order Methods with Applications. Science Press, Beijing (2006)
Shen, J., Tang, T., Wang, L.L.: Spectral Methods: Algorithms, Analysis and Applications. Springer, Berlin (2011)
Tomar, S.K.: \(h-p\) Spectral element methods for elliptic problems over non-smooth domains using parallel computers. Computing 78, 117–143 (2006)
Tomar, S.K., Dutt, P., Kumar, B.V.R.: An efficient and exponentially accurate parallel \(h-p\) spectral element method for elliptic problems on polygonal domains—the Dirichilet case. Lecture Notes in Computer Science 2552, High Performance Computing. Springer, Berlin (2002)
Yu, X.H., Guo, B.Y.: Spectral element method for mixed inhomogeneous boundary value problems of fourth order. J. Sci. Comput. 61(3), 673–701 (2014)
Yu, X.H., Guo, B.Y.: Spectral method for fourth-order problems on quadrilaterals. J. Sci. Comput. 66(2), 1–27 (2015)
Zhang, S., Xu, J.: Optimal solvers for fourth-order PDEs discretized on unstructured grids. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 52(1), 282–307 (2014)
Zhao, J.: Multigrid methods for fourth order problems. Ph.D. Thesis, University of South Carolina. www.math.sc.edu/~fem/zhaodiss.pdf (2004)
Zhu, Z.: The least-squares spectral element method solution of the gas-liquid multi-fluid model coupled with the population balance equation. Ph.D. Thesis, NTNU Norway. www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:297012/FULLTEXT03.pdf (2009)
Žitňan, P.: Discrete weighted least-squares method for the Poisson and biharmonic problems on domains with smooth boundary. Appl. Math. Comput. 217(22), 8973–8982 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The first author is thankful to the LNM Institute of Information Technology (LNMIIT), Jaipur for supporting his visits to carry out this work and also thankful to IIT Kanpur for providing the parallel computers facilities to compute the numerical results. Research is also supported by Mathematics Center Heidelberg (MATCH), Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany.
This work was carried out during the second author’s stay at the LNM Institute of Information Technology (LNMIIT), Jaipur as assistant professor.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Husain, A. Exponentially Accurate Spectral Element Method for Fourth Order Elliptic Problems. J Sci Comput 71, 303–328 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0300-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10915-016-0300-z