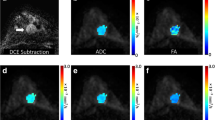
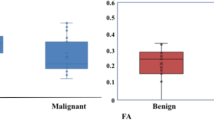
Abstract
Lactation and the return to the pre-conception state during post-weaning are regulated by hormonal induced processes that modify the microstructure of the mammary gland, leading to changes in the features of the ductal / glandular tissue, the stroma and the fat tissue. These changes create a challenge in the radiological workup of breast disorder during lactation and early post-weaning. Here we present non-invasive MRI protocols designed to record in vivo high spatial resolution, T2-weighted images and diffusion tensor images of the entire mammary gland. Advanced imaging processing tools enabled tracking the changes in the anatomical and microstructural features of the mammary gland from the time of lactation to post-weaning. Specifically, by using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) it was possible to quantitatively distinguish between the ductal / glandular tissue distention during lactation and the post-weaning involution. The application of the T2-weighted imaging and DTI is completely safe, non-invasive and uses intrinsic contrast based on differences in transverse relaxation rates and water diffusion rates in various directions, respectively. This study provides a basis for further in-vivo monitoring of changes during the mammary developmental stages, as well as identifying changes due to malignant transformation in patients with pregnancy associated breast cancer (PABC).




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hovey RC, Trott JF, Vonderhaar BK. Establishing a framework for the functional mammary gland: from endocrinology to morphology. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2002;7(1):17–38. Review
Neville MC, McFadden TB, Forsyth I. Hormonal regulation of mammary differentiation and milk secretion. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2002;7(1):49–66.
Kent JC. How breast feeding works. J Midwifery Women’s Heal. 2007;52:564–70.
Neville MC, Allen JC, Archer PC, et al. Studies in human lactation: milk volume and nutrient composition during weaning and lactogenesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991;54:81–92.
McDaniel SM, Rumer KK, Biroc SL, et al. Remodeling of the mammary microenvironment after lactation promotes breast tumor cell metastasis. Am J Pathol. 2006;168:608–20.
Schedin P, O’Brien J, Rudolph M, Stein T, Borges V. Microenvironment of the involuting mammary gland mediates mammary cancer progression. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2007;12:71–82.
Cooper A. Anatomy of the breast. London: Longman, Orme, Green, Browne and Longmans; 1840.
Ramsay DT, Kent JC, Hartmann RA, Hartmann PE. Anatomy of the lactating human breast redefined with ultrasound imaging. J Anat. 2005;206:525–34.
Gooding MJ, Finlay J, Shipley JA, Halliwell M, Duck FA. Three-dimensional ultrasound imaging of mammary ducts in lactating women: a feasibility study. J Ultrasound Med. 2010;29:95–103.
Markiewicz E, Fan X, Mustafia D, Zamoraa M, Roman BB, Jansen SA, Macleod K, Conzen SD, and Karczmara GS, High resolution 3D MRI of mouse mammary glands with intra-ductal injection of contrast media. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 33(1):161–165, doi:10.1016/j.mri.2014.08.035
Physics of MRI: a primer, DB Plewes, W Kucharczyk - J Magn Reson Imaging 2012; 35:1038–1054. doi:10.1002/jmri.23642
Santyr GE. MR imaging of the breast. Imaging and tissue characterization without intravenous contrast. Rev Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 1994;2(4):673–90.
Iima MD, Le Bihan MD. Clinical Intravoxel incoherent motion and diffusion MR imaging: past, present, and future. Radiology. 2016;278(1):13–32. doi:10.1148/radiol.2015150244. Review
Vashi R, Hooley R, Butler R, Geisel J, Philpotts L. Breast imaging of the pregnant and lactating patient: imaging modalities and pregnancy-associated breast cancer. Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200(2):321–8.
Ayyappan AP, Kulkarni S, Crystal P. Pregnancy-associated breast cancer: spectrum of imaging appearances. Br J Radiol. 2010;83(990):529–34. doi:10.1259/bjr/17982822.
Turnbull LW. Dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI in the diagnosis and management of breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2009;22(1):28–39. doi:10.1002/nbm.1273. Review
Moon M, Cornfeld D, Weinreb J. Dynamic contrast-enhanced breast MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009;17(2):351–62. doi:10.1016/j.mric.2009.01.010. Review
Pinker K, Helbich TH, Morris EA. The potential of multiparametric MRI of the breast. Br J Radiol. 2017;90(1069):20160715. doi:10.1259/bjr.20160715. Review
Sundgren PC, Leander P. Is administration of gadolinium-based contrast media to pregnant women and small children justified? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011;34(4):750–7. Review
Kanal E, Barkovich AJ, Bell C, et al. ACR guidance document on MR safe practices. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37(3):501–30.
Boivin G, de Korvin B, Marion J, Duvauferrier R. Is a breast MRI possible and indicated in case of suspicion of breast cancer during lactation? Diagn Interv Imaging. 2012;93(11):823–7. doi:10.1016/j.diii.2012.05.013.
Talele AC, Slanetz PJ, Edmister WB, Yeh ED, Kopans DB. The lactating breast: MRI findings and literature review. The lactating breast: MRI findings and literature review. Breast J. 2003;9(3):237–40.
Espinosa LA, Daniel BL, Vidarsson L, Zakhour M, Ikeda DM, Herfkens RJ. The lactating breast: contrast-enhanced MR imaging of normal tissue and cancer. Radiology. 2005;237(2):429–36.
Spick C, Pinker-Domenig K, Rudas M, Helbich TH. Baltzer PA.MRI-only lesions: application of diffusion weighted imaging obviates unnecessary MR-guided breast biopsies. Eur Radiol. 2014;24(6):1204–10. doi:10.1007/s00330-014-3153-6.
Partridge SC, McDonald ES. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: protocol optimization, interpretation, and clinical applications. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2013;21(3):601–24. doi:10.1016/j.mric.2013.04.007. and references cited therein)
Sah RG, Agarwal K, Sharma U, Parshad R, Seenu V, Jagannathan NR. Characterization of malignant breast tissue of breast cancer patients and the normal breast tissue of healthy lactating women volunteers using diffusion MRI and in vivo 1H MR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015;41:169–74.
Paran Y, Bendel P, Margalit R, Degani H. Water diffusion in the different microenvironments of breast cancer. NMR Biomed. 2004;17:170–80.
Jiang R, Ma Z, Dong H, Sun S, Zeng X, Li X. Diffusion tensor imaging of breast lesions: evaluation of apparent diffusion coefficient and fractional anisotropy and tissue cellularity. Br J Radiol. 2016;89(1064):20160076. doi:10.1259/bjr.20160076.
Le Bihan D, Mangin JF, Poupon C, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging: concepts and applications. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001;13:534–46.
Westin CF, Maier SE, Mamata H, Nabavi A, Jolesz FA, Kikinis R. Processing and visualization for diffusion tensor MRI. Med Image Anal. 2002;6:93–108.
Furman-Haran E, Grobgeld D, Nissan N, Shapiro-Feinberg M, Degani H. Can diffusion tensor anisotropy indices assist in breast cancer detection? J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016;44(6):1624–32. doi:10.1002/jmri.25292.
Eyal E, Shapiro-Feinberg M, Furman-Haran E, et al. Parametric diffusion tensor imaging of the breast. Investig Radiol. 2012;47:284–91.
Partridge SC, Ziadloo A, Murthy R, et al. Diffusion tensor MRI: preliminary anisotropy measures and mapping of breast tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2010;31:339–47.
PAT B, Schäfer A, Dietzel M, et al. Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging of the breast: a pilot study. Eur Radiol. 2011;21:1–10.
Cakir O, Arslan A, Inan N, et al. Comparison of the diagnostic performances of diffusion parameters in diffusion weighted imaging and diffusion tensor imaging of breast lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2013;82:e801–6.
Onaygil C, Kaya H, Ugurlu MU. Aribal E diagnostic performance of diffusion tensor imaging parameters in breast cancer and correlation with the prognostic factors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017;45(3):660–72. doi:10.1002/jmri.25481.
Nissan N, Furman-Haran E, Shapiro-Feinberg M, Grobgeld D, Degani H. Diffusion-tensor MR imaging of the breast: hormonal regulation. Radiology. 2014;271:672–80.
Just N. Improving tumour heterogeneity MRI. Br J Cancer. 2014;111:2205–13. doi:10.1038/bjc.2014.512.
Geddes DT. Inside the lactating breast: the latest anatomy research. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2007;52:556–63.
Mortazavi SN, Hassiotou F, Geddes D, Hassanipour F. Mathematical modeling of mammary ducts in lactating human females. J Biomech Eng. 2015;137(7):071009 Paper No: BIO-14-1167. doi:10.1115/1.4028967.
Panaritis V, Despotidis P, Kyriakidis A. Diameter of mammary terminal ducts as an additional tool in evaluation of women with polycystic ovarium disease. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2004;270:252–4. doi:10.1007/s00404-003-0555-0.
Mayr NA, Staples JJ, Robinson RA, Vanmetre JE, Hussey DH. Morphometric studies in intraductal breast carcinoma using computerized image analysis. Cancer. 1991;67(11):2805–12.
Reisert M, Weigel M, Eyal E, Grobgeld D, Degani H, Hennig J. Diffusion tensor based reconstruction of the ductal tree. In: Proc Intl Soc Mag Reson Med. 2011;19:1011.
Dewey KG, Finley DA, Lönnerdal B. Breast milk volume and composition during late lactation (7-20 months). J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1984;3:713–20.
Shapiro-Feinberg M, Weisenberg N, Zehavi T, et al. Clinical results of DTI. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:S151–2.
Middleton LP, Amin M, Gwyn K, Theriault R, Sahin A. Breast carcinoma in pregnant women: assessment of clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical features. Cancer. 2003;98(5):1055–60.
Kakoulidis I, Skagias L, Politi E. Pregnancy associated breast cancer (PABC): aspects in diagnosis. Breast Dis. 2015;35:157–66. Review
Nissan N, Furman-Haran E, Feinberg-Shapiro M, et al. Tracking the mammary architectural features and detecting breast cancer with magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging. J Vis Exp. 2014:e52048. doi:10.3791/52048.
Acknowledgements
The professional work of the MR imaging technicians, Fanny Attar and Nachum Stern, is gratefully acknowledged. H. Degani holds the Fred and Andrea Fallek Chair for Breast Cancer Research. E. Furman-Haran holds the Calin and Elaine Rovinescu Research Fellow Chair for Brain Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
No conflict of interest declared.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nissan, N., Furman-Haran, E., Shapiro-Feinberg, M. et al. Monitoring In-Vivo the Mammary Gland Microstructure during Morphogenesis from Lactation to Post-Weaning Using Diffusion Tensor MRI. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia 22, 193–202 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-017-9383-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10911-017-9383-x