Abstract
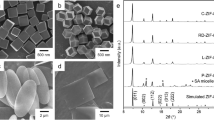
ZIFs of different morphologies were synthesized by different solvents. Three types of ZIFs with different morphologies, ZIF-M, ZIF-P, and ZIF-L, were prepared using anhydrous methanol, polyethylene glycol-400, and water as solvents, respectively. The morphologies of ZIF-M and ZIF-L are rhombic dodecahedron and blade-like, respectively. Wherein the ZIF-M sample using methanol as solvent has an unusual morphology of high internal specific surface and pore volume. The ZIFs were characterized by XRD, SEM, AAS, N2 adsorption isotherms, pore size distribution, and evaluated with S. aureus and E. coli to gain antibacterial activity. Using the determination of growth curves, plate counting method and circle of inhibition method, the results showed that ZIF-M like has high antibacterial properties for ZIF-L and ZIF-P. Folding and rupture of the cell walls of dead bacteria was found by measuring the SEM of the bacteria. ZIF-M has the largest specific surface area, better potential properties and highest Zn2+ release, which leads to the high antibacterial effect of ZIF-M.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
X. Zhao, M. Zheng, X. Gao et al., The application of MOFs-based materials for antibacterial adsorption. Coord. Chem. Rev. 440, 213970 (2021)
M. Zhang, S. Ye, J. Wang, K.Y.J. Cao, G. Li, X. Liao, In situ growth zeolite imidazole framework materials on chitosan for greatly enhanced antibacterial effect. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 186, 639–648 (2021)
Y. Kong, W. Zhang, T. He, X. Yang, W. Bi, J. Li, W. Yang, W. Chen, Asymmetric wettable polycaprolactone-chitosan/chitosan oligosaccharide nanofibrous membrane as antibacterial dressings. Carbohydr. Polym. 304, 120485 (2023)
D. Saliba, M. Ammar, M. Rammal et al., Crystal growth of ZIF-8, ZIF-67, and their mixed-metal derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140(5), 1812–1823 (2018)
R. Douaihy, M. Ghoul, M.L. Hmadeh, Banding for controlled size and growth of zeolitic-imidazolate frameworks. Small 15(28), e1901605 (2019)
P. Yao, Y. Liu, X. Tang, S. Lu, Y. Yao, Synthesis of reusable NH2-MIL-125(Ti)@polymer monolith as efficient adsorbents for dyes wastewater remediation. Green. Chem. Eng. 4 (2023) 439-446.
G. Guan, L. Zhang, J. Zhu, H. Wu, W. Li, Q. Sun, Antibacterial properties and mechanism of biopolymer-based films functionalized by CuO/ZnO nanoparticles against Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus. J. Hazard Mater. 402, 123542 (2021)
G. Huang, Y. Li, Z. Qin, Q. Liang, C. Xu, B. Lin, Hybridization of carboxymethyl chitosan with MOFs to construct recyclable, long-acting and intelligent antibacterial agent carrier. Carbohydr. Polym. 233, 115848 (2020)
H. Ma, S. Yang, M. Li et al., Preparation and photocatalytic antibacterial mechanism of porous metastable beta-Bi2O3 nanosheets. Ceram. Int. 47(24), 34092–34105 (2021)
S. Khattak, X. Qin, L. Huang et al., Preparation and characterization of antibacterial bacterial cellulose/chitosan hydrogels impregnated with silver sulfadiazine. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 189, 483–493 (2021)
J. Deng, Z. Dai, L. Deng, Effects of the morphology of the ZIF on the CO2 separation performance of MMMs. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 59(32), 14458–14466 (2020)
Y. Li, P. Li, C. Zhang, K. He, Y. Chen, X. Liao, Dual zn source strategy for synthesizing ZIFs: zero discharge, less raw material, high output, and better adsorptive performance. CrystEngComm 25, 4325–4332 (2023)
M. Malekmohammadi, S. Fatemi, M. Razavian, A. Nouralishahi, A comparative study on ZIF-8 synthesis in aqueous and methanolic solutions: effect of temperature and ligand content. Solid State Sci. 91, 108–112 (2019)
M. Jian, B. Liu, R. Liu, J. Qu, H. Wang, X. Zhang, Water-based synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 with high morphology level at room temperature. RSC Adv. 5, 48433–48441 (2015)
H. Zhang, X. Hu, T. Li et al., MIL series of metal organic frameworks (MOFs) as novel adsorbents for heavy metals in water: a review. J. Hazard Mater. 429, 128271 (2022)
M. Shahmirzaee, A. Hemmati-Sarapardeh, M. Husein, M. Schaffie, M. Ranjbar, Development of a powerful zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8)/carbon fiber nanocomposite for separation of hydrocarbons and crude oil from wastewater. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 307, 110463 (2020)
W. Cai, W. Zhang, Z. Chen, Magnetic Fe3O4@ZIF-8 nanoparticles as a drug release vehicle: pH-sensitive release of norfloxacin and its antibacterial activity. Colloids Surf. B 223, 113170 (2023)
Y. Feng, H. Wang, J. Yao, Synthesis of 2D nanoporous zeolitic imidazolate framework nanosheets for diverse applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 431, 213677 (2020)
G.P. Chuy, P.C.L. Muraro, A.R. Viana, G. Pavoski, D.C.R. Espinosa, B.S. Vizzotto, W.L. da Silva, Green nanoarchitectonics of silver nanoparticles for antimicrobial activity against resistant pathogens. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 32, 1213–1222 (2022)
A. Karimi, A. Khataee, V. Vatanpour et al., High-flux PVDF mixed matrix membranes embedded with size-controlled ZIF-8 nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 229(C), 115838 (2019)
Q. Deng, R. Zhai, B. Chen, X. Jiang, H. Li, C. Li, M. Jin, One-pot synthesis of rod-like lignin@zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 with enhanced immobilization of β-glucosidase. Ind. Crops Prod. 196, 116473 (2023)
S. Dursun, H. Akyıldız, V. Kalem, Production of CuCoO2 nanoparticle/SnO2 nanofiber heterostructures for visible light photocatalytic applications. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 434, 114233 (2023)
D. Ma, P. Li, X. Duan et al., A hydrolytically stable vanadium(IV) metal-organic framework with photocatalytic bacteriostatic activity for autonomous indoor humidity control. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 59(10), 3905–3909 (2020)
L.D. Pompeu, P.C.L. Muraro, G. Chuy, B.S. Vizzotto, G. Pavoski, D.C.R. Espinosa, L. da Silva Fernandes, W.L. da Silva, Adsorption for rhodamine b dye and biological activity of nano-porous chitosan from shrimp shells. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 29, 49858–49869 (2022)
S. Dursun, Production of novel hazelnut shell-based semi-IPN biocomposite absorbents and their use in removing heavy metal ions from water. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 30, 44276–44291 (2023)
S. Ghosh, D. Ghosh, P. Bag et al., Aqueous synthesis of ZnTe/dendrimer nanocomposites and their antimicrobial activity: implications in therapeutics. Nanoscale 3(3), 1139–1148 (2011)
J. Chen, Z. Huang, H. Zhang et al., Three-dimensional layered nanofiber sponge with in situ grown silver-metal organic framework for enhancing wound healing. Chem. Eng. J. 443, 136234 (2022)
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CZ: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—review & editing. XL: Investigation, Writing—review & editing, ZZ: Data curation, Validation. KT: Investigation, Validation. YY: Investigation, Validation. XL: Project administration, Writing—review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no confict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Li, X., Zhang, Z. et al. Morphological Effect of ZIFs as the Promotion of Surface-Potential-Adsorption for Antibacterial Performance. J Inorg Organomet Polym (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02971-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02971-8