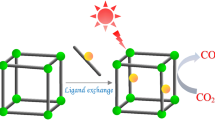
Abstract
Carbon dioxide (CO2) transformation is a cutting-edge technology to eliminate greenhouse effects and produce valuable chemicals as well as fuels. Herein, we report an elaborate engineering for improving the efficiency of Zr-based Bipy-UiO-67 metal–organic framework (ZBU) in CO2 transformations. As demonstrated, tuning the catalytic performance by incorporating Co into ZBU (ZBU-Co) was realized as a practical strategy to affect the CO2 insertion to epoxides in terms of conversion, green procedure, recyclability, chemical/thermal stability, time, and energy. Also, extending the diversity of the reaction to bulky epoxides showed that increasing temperature is an effective remedy for achieving complete conversion. Importantly, in comparison with the homogeneous and heterogeneous counterparts, ZBU-Co illustrated superior results. On the other hand, ZBU-Co exhibited potential application in photocatalytic reduction of CO2, endowing bi-functional feature to the catalytic system. Accordingly, higher CO2 adsorption capacity and CO evolution were recorded for ZBU-Co compared to the pristine ZBU. Furthermore, the ability to recover the catalyst for four cycles is a valuable characteristic from environmentally/eco-friendly aspects, which further proves the versatility of the modified MOF in the photocatalytic reaction. Overall, ZBU-Co is considered a promising candidate for CO2 transformations due to the several advantages in CO2 insertion and photocatalytic reduction.
Graphical Abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
V. Humphrey, J. Zscheischler, P. Ciais, L. Gudmundsson, S. Sitch, S.I. Seneviratne, Sensitivity of atmospheric CO2 growth rate to observed changes in terrestrial water storage. Nature 560, 628–631 (2018)
B.J. Soden, W.D. Collins, D.R. Feldman, Reducing uncertainties in climate models. Science 361, 326–327 (2018)
P. Yaashikaa, P.S. Kumar, S.J. Varjani, A. Saravanan, A review on photochemical, biochemical and electrochemical transformation of CO2 into value-added products. J. CO2 Util. 33, 131–147 (2019)
N.L. Panwar, S.C. Kaushik, S. Kothari, Role of renewable energy sources in environmental protection: a review. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev 15, 1513–1524 (2011)
S. Chu, Y. Cui, N. Liu, The path towards sustainable energy. Nat. Mater. 16, 16–22 (2017)
J. Raven, K. Caldeira, H. Elderfield, O. Hoegh-Guldberg, P. Liss, U. Riebesell, J. Shepherd, C. Turley, A. Watson, Ocean acidification due to increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide, R. Soc. (2005).
L. Kapsenberg, S. Alliouane, F. Gazeau, L. Mousseau, J.-P. Gattuso, Coastal ocean acidification and increasing total alkalinity in the northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Ocean Sci. 13, 411–426 (2017)
E. Rabinowitch, Photosynthesis, US Atomic Energy Commission (1949).
J. Barber, Photosynthetic energy conversion: natural and artificial. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 185–196 (2009)
C. Yoo, Y.-E. Kim, Y. Lee, Selective transformation of CO2 to CO at a single nickel center. Acc. Chem. Res. 51, 1144–1152 (2018)
G. Mele, C. Annese, A. De Riccardis, C. Fusco, L. Palmisano, G. Vasapollo, L. D’Accolti, Turning lipophilic phthalocyanines/TiO2 composites into efficient photocatalysts for the conversion of CO2 into formic acid under UV–vis light irradiation. Appl. Catal. A Catal A 481, 169–172 (2014)
C. Wu, F. Irshad, M. Luo, Y. Zhao, X. Ma, S. Wang, Ruthenium complexes immobilized on an azolium based metal organic framework for highly efficient conversion of CO2 into formic acid. ChemCatChem 11, 1256–1263 (2019)
Y. Zhang, T. Zhang, S. Das, Catalytic transformation of CO 2 into C1 chemicals using hydrosilanes as a reducing agent. Green Chem. 22, 1800–1820 (2020)
D. Hidalgo, J. Martín-Marroquín, Power-to-methane, coupling CO2 capture with fuel production: an overviewRenew. Sust. Energ. Rev 132, 110057 (2020)
A. Yahaya, M. Gondal, A. Hameed, Selective laser enhanced photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into methanol. Chem. Phys. Lett. 400, 206–212 (2004)
K. Yang, J. Jiang, Transforming CO2 into methanol with N-heterocyclic carbene-stabilized coinage metal hydrides immobilized in a metal–organic framework UiO-68. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13, 58723–58736 (2021)
J.A. Rodriguez, P. Liu, D.J. Stacchiola, S.D. Senanayake, M.G. White, J.G. Chen, Hydrogenation of CO2 to methanol: importance of metal–oxide and metal–carbide interfaces in the activation of CO2. ACS Catal.Catal 5, 6696–6706 (2015)
L. Wang, L. Wang, J. Zhang, X. Liu, H. Wang, W. Zhang, Q. Yang, J. Ma, X. Dong, S.J. Yoo, Selective hydrogenation of CO2 to ethanol over cobalt catalysts. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 57, 6104–6108 (2018)
L. Liu, A.V. Puga, J. Cored, P. Concepción, V. Pérez-Dieste, H. García, A. Corma, Sunlight-assisted hydrogenation of CO2 into ethanol and C2+ hydrocarbons by sodium-promoted Co@ C nanocomposites. Appl. Catal. B 235, 186–196 (2018)
R. Motterlini, B.E. Mann, R. Foresti, Therapeutic applications of carbon monoxide-releasing molecules. Expert Opin. Invest. Drugs 14, 1305–1318 (2005)
A. Nakao, Y. Toyoda, Application of carbon monoxide for transplantation. Curr Pharma Biotec 13, 827–836 (2012)
E.V. Gusevskaya, J. Jiménez-Pinto, A. Börner, Hydroformylation in the realm of scents. ChemCatChem 6, 382–411 (2014)
X. Yu, P.G. Pickup, Recent advances in direct formic acid fuel cells (DFAFC). J. Power. Sources 182, 124–132 (2008)
J. Hietala, A. Vuori, P. Johnsson, I. Pollari, W. Reutemann, H. Kieczka, Formic acid. Ullmann’s Encycl. Ind. Chem. 1, 1–22 (2016)
G. Maggio, S. Freni, S. Cavallaro, Light alcohols/methane fuelled molten carbonate fuel cells: a comparative study. J. Power. Sources 74, 17–23 (1998)
L. Spadaccini, M.C. Iii, Ignition delay characteristics of methane fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. Energy Combust. Sci 20, 431–460 (1994)
S. Ma, P.J. Kenis, Electrochemical conversion of CO2 to useful chemicals: current status, remaining challenges, and future opportunities. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2, 191–199 (2013)
M. Aresta, A. Dibenedetto, Utilisation of CO2 as a chemical feedstock: opportunities and challenges. Dalton Trans. 15, 2975–2992 (2007)
E. Alper, O.Y. Orhan, CO2 utilization: developments in conversion processes. Petroleum 3, 109–126 (2017)
S. Klaus, M.W. Lehenmeier, C.E. Anderson, B. Rieger, Recent advances in CO2/epoxide copolymerization: new strategies and cooperative mechanisms. Coord. Chem. Rev. 255, 1460–1479 (2011)
N. Fanjul-Mosteirín, C. Jehanno, F. Ruipérez, H. Sardon, A.P. Dove, Rational study of DBU salts for the CO2 insertion into epoxides for the synthesis of cyclic carbonates. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 7, 10633–10640 (2019)
F. Norouzi, H.R. Khavasi, Diversity-oriented metal decoration on UiO-type metal–organic frameworks: an efficient approach to increase CO2 uptake and catalytic conversion to cyclic carbonates. ACS Omega 4, 19037–19045 (2019)
L. Mohammadi, H.R. Khavasi, Anthracene-tagged UiO-67-MOF as highly selective aqueous sensor for nanoscale detection of arginine amino acid. Inorg. Chem. 59, 13091–13097 (2020)
R. Babu, R. Roshan, A.C. Kathalikkattil, D.W. Kim, D.-W. Park, Rapid, microwave-assisted synthesis of cubic, three-dimensional, highly porous MOF-205 for room temperature CO2 fixation via cyclic carbonate synthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 33723–33731 (2016)
Z. Qin, H. Li, X. Yang, L. Chen, Y. Li, K. Shen, Heterogenizing homogeneous cocatalysts by well-designed hollow MOF-based nanoreactors for efficient and size-selective CO2 fixation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 307, 121163 (2022)
S.L. James, Metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 32, 276–288 (2003)
P. Horcajada, C. Serre, M. Vallet-Regí, M. Sebban, F. Taulelle, G. Férey, Metal–organic frameworks as efficient materials for drug delivery. Angew. Chem. Chem 118, 6120–6124 (2006)
J. Lee, O.K. Farha, J. Roberts, K.A. Scheidt, S.T. Nguyen, J.T. Hupp, Metal–organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38, 1450–1459 (2009)
K. Lu, T. Aung, N. Guo, R. Weichselbaum, W. Lin, Nanoscale metal–organic frameworks for therapeutic, imaging, and sensing applications. Adv. Mater. 30, 1707634 (2018)
F. Norouzi, H.R. Khavasi, Iodine decorated-UiO-67 MOF as a fluorescent sensor for the detection of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. New J. Chem. 44, 8937–8943 (2020)
Q. Qian, P.A. Asinger, M.J. Lee, G. Han, K.M. Rodriguez, S. Lin, F.M. Benedetti, A.X. Wu, W.S. Chi, Z.P. Smith, MOF-based membranes for gas separations. Chem. Rev. 120, 8161–8266 (2020)
C. Petit, Present and future of MOF research in the field of adsorption and molecular separation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 20, 132–142 (2018)
J.H. Cavka, S. Jakobsen, U. Olsbye, N. Guillou, C. Lamberti, S. Bordiga, K.P. Lillerud, A new zirconium inorganic building brick forming metal organic frameworks with exceptional stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 13850–13851 (2008)
A.H. Vahabi, F. Norouzi, E. Sheibani, M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, Functionalized Zr-UiO-67 metal-organic frameworks: Structural landscape and application. Coord. Chem. Rev. 445, 214050 (2021)
A. Helal, F. Alahmari, M. Usman, Z.H. Yamani, Chalcopyrite UiO-67 metal-organic framework composite for CO2 fixation as cyclic carbonates. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 10, 108061 (2022)
L.-G. Ding, B.-J. Yao, W.-L. Jiang, J.-T. Li, Q.-J. Fu, Y.-A. Li, Z.-H. Liu, J.-P. Ma, Y.-B. Dong, Bifunctional imidazolium-based ionic liquid decorated UiO-67 type MOF for selective CO2 adsorption and catalytic property for CO2 cycloaddition with epoxides. Inorg. Chem. 56, 2337–2344 (2017)
E.S. Gutterød, S. Øien-Ødegaard, K. Bossers, A.-E. Nieuwelink, M. Manzoli, L. Braglia, A. Lazzarini, E. Borfecchia, S. Ahmadigoltapeh, B. Bouchevreau, B.T. Lønstad-Bleken, R. Henry, C. Lamberti, S. Bordiga, B.M. Weckhuysen, K.P. Lillerud, U. Olsbye, CO2 Hydrogenation over Pt-containing UiO-67 Zr-MOFs: the base case. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 56, 13206–13218 (2017)
D. Jiang, Y. Shi, G. Zhao, X. Gong, J. Liu, D. Lan, L. Zhang, J. Ge, H. Fang, D. Cheng, Pt–Ni alloy nanobead chains catalysts embedded in UiO-67 membrane for enhanced CO2 conversion to CO. Mater. Today Energy 28, 101051 (2022)
X. Zhao, M. Xu, X. Song, X. Liu, W. Zhou, H. Wang, P. Huo, Tailored linker defects in UiO-67 with high ligand-to-metal charge transfer toward efficient photoreduction of CO2. Inorg. Chem. 61, 1765–1777 (2022)
H. Xu, X. Luo, J. Wang, Y. Su, X. Zhao, Y. Li, Spherical sandwich Au@ Pd@ UIO-67/Pt@ UIO-n (n= 66, 67, 69) core–shell catalysts: Zr-based metal–organic frameworks for effectively regulating the reverse water–gas shift reaction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 11, 20291–20297 (2019)
X. Gao, B. Guo, C. Guo, Q. Meng, J. Liang, J. Liu, Zirconium-based metal–organic framework for efficient photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO: the influence of doped metal ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 12, 24059–24065 (2020)
S. Subudhi, D. Rath, K. Parida, S. Satyabrata, D. Rath, K.M. Parida, A mechanistic approach towards the photocatalytic organic transformations over functionalised metal organic frameworks: a review. Catal. Sci. Technol.. Sci. Technol 8, 679–696 (2018)
P. Behera, S. Subudhi, S.P. Tripathy, K. Parida, MOF derived nano-materials: A recent progress in strategic fabrication, characterization and mechanistic insight towards divergent photocatalytic applications. Coord. Chem. Rev.. Chem. Rev 456, 214392 (2022)
J. Panda, S.P. Tripathy, S. Dash, A. Ray, P. Behera, S. Subudhi, K. Parida, Inner transition metal-modulated metal organic frameworks (IT-MOFs) and their derived nanomaterials: a strategic approach towards stupendous photocatalysis. Nanoscale 15, 7640–7675 (2023)
S.P. Tripathy, S. Subudhi, K. Parida, Inter-MOF hybrid (IMOFH): a concise analysis on emerging core–shell based hierarchical and multifunctional nanoporous materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 434, 213786 (2021)
J. Qin, S. Wang, X. Wang, Visible-light reduction CO2 with dodecahedral zeolitic imidazolate framework ZIF-67 as an efficient co-catalyst. Appl. Catal. B 209, 476–482 (2017)
W. Liu, L. Zhang, W. Yan, X. Liu, X. Yang, S. Miao, W. Wang, A. Wang, T. Zhang, Single-atom dispersed Co–N–C catalyst: structure identification and performance for hydrogenative coupling of nitroarenes. Chem. Sci. 7, 5758–5764 (2016)
Y. Shi, S. Hou, X. Qiu, B. Zhao, MOFs-based catalysts supported chemical conversion of CO2. Metal-Organic Framew. 8, 373–426 (2020)
Q.-L. Zhu, J. Li, Q. Xu, Immobilizing metal nanoparticles to metal–organic frameworks with size and location control for optimizing catalytic performance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 10210–10213 (2013)
H. Li, Y. Gao, Z. Xiong, C. Liao, K. Shih, Enhanced selective photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CH4 over plasmonic Au modified g-C3N4 photocatalyst under UV–vis light irradiation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 439, 552–559 (2018)
Y. Gao, L. Ye, H. Chen, L. Sun, Highly efficient photocatalytic reduction of CO2 and H2O to CO and H2 with a cobalt bipyridyl complex. J. Energy Chem. 27, 502–506 (2018)
T. Ouyang, H.H. Huang, J.W. Wang, D.C. Zhong, T.B. Lu, A dinuclear cobalt cryptate as a homogeneous photocatalyst for highly selective and efficient visible-light driven CO2 reduction to CO in CH3CN/H2O solution. Angew. Chem. 129, 756–761 (2017)
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed equally for producing the materials and contents for the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in the submitted manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-dolaimy, F., Kzar, M.H., Hussein, S.A. et al. Incorporating of Cobalt into UiO-67 Metal–Organic Framework for Catalysis CO2 Transformations: An Efficient Bi-functional Approach for CO2 Insertion and Photocatalytic Reduction. J Inorg Organomet Polym 34, 864–873 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02860-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02860-0