Abstract
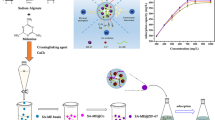
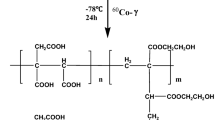
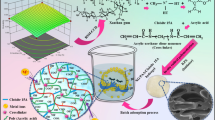
Metal–organic framework materials(ZIF-9) were loaded on Sodium alginate/polyvinyl(PVA/SA) hydrogel by in situ growth method for adsorption of heavy metal Cu (II). The structure of hydrogels composited with MOFs and polymers was designed to improve the poor mechanical properties of natural polymer gel materials and the inconvenience of powdered MOFs materials in practical applications. The adsorption results showed that the optimum adsorption process of Cu (II) pH was 5.0. The adsorption kinetics and isotherm suggest that the adsorption process follows the Freundlich isotherm and the pseudo-second-order models. The experimental maximum adsorption capacity was 98.98 mg/g, 2.6 times and 1.5 times higher than ordinary SA and PVA/SA hydrogel spheres. Synthesized hydrogel spheres were characterized by FT-IR, SEM, XRD, and XPS, which confirmed that MOF materials have grown in situ on PVA/SA hydrogel spheres. More importantly, PVA/SA@ZIF-9 exhibited exceptional mechanical stability and showed excellent recycling capability in the cyclic adsorption process.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.W. Jung, S.Y. Lee, J.W. Choi et al., A facile one-pot hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite/biochar nanocomposites: adsorption behavior and mechanisms for the removal of copper(II) from aqueous media [J]. Chem. Eng. J. 369, 529–541 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2019.03.102
T. Liu, Z. Chen, Z. Li et al., Rapid separation and efficient removal of Cd based on enhancing surface precipitation by carbonate-modified biochar. ACS Omega 28(6), 18253–18259 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c02126
C. Liu, T. Wu, P.C. Hsu et al., Direct/alternating current electrochemical method for removing and recovering heavy metal from water using graphene oxide electrode. ACS Nano 13(6), 6431–6437 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b09301
L. Yang, Y.J. Zhu, G. He et al., Multifunctional photocatalytic filter paper based on ultralong nanowires of the calcium-alendronate complex for high-performance water purification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14(7), 9464–9479 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c23180
M. Khan, A. Akhtar, S.A. Nabi, Kinetics and thermodynamics of alkaline earth and heavy metal ion exchange under particle diffusion controlled phenomenon using polyaniline-sn(iv)iodophosphate nanocomposite. J. Chem. Eng. Data 59(8), 2677–2685 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1021/je500523n
A. Mfm, B. Amgm, C. Mk et al., Adsorption of heavy metals and hardness ions from groundwater onto modified zeolite: batch and column studies. Alex. Eng. J. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aej.2021.09.041
H. Es-Sahbany, R. Hsissou, M. Hachimi et al., Investigation of the adsorption of heavy metals (Cu Co, Ni and Pb) in treatment synthetic wastewater using natural clay as a potential adsorbent (Sale-Morocco). Mater. Today (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.1100
S. Liu, S. Zhang, M. Fan et al., High-efficiency adsorption of various heavy metals by tea residue biochar loaded with nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ. Prog. Sustainable Energy (2021). https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13706
J. Kaur, P. Sengupta, S. Mukhopadhyay, Critical review of bioadsorption on modified cellulose and removal of divalent heavy metals (Cd, Pb, and Cu). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 61(5), 1921–1954 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.1c04583
Q. Zuo, H. Zheng, P. Zhang et al., Functionalized activated carbon fibers by hydrogen peroxide and polydopamine for efficient trace lead removal from drinking water. Langmuir 38(1), 253–263 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c02459
Z. Zhao, Y. Song, P. Phanlavong et al., Efficient heavy metal removal from water by polydopamine confined ZrO2 nanocrystals with improvements in nanoparticles utilization and ion diffusion. ACS EST Eng. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestengg.1c00370
S. Xue, J. Fan, K. Wan et al., Calcium-modified Fe3O4 nanoparticles encapsulated in humic acid for the efficient removal of heavy metals from wastewater. Langmuir 37, 10994–11007 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c01491
T. Jayaramudu, R.D. Pyarasani, A. Akbari-Fakhrabadi et al., Synthesis of gum acacia capped polyaniline-based nanocomposite hydrogel for the removal of methylene blue dye. J. Polym. Environ. 29, 2447–2462 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-021-02066-w
Y.Z. Yan, Q.D. An, Z.Y. Xiao et al., Flexible core-shell/bead-like alginate@PEI with exceptional adsorption capacity, recycling performance toward batch and column sorption of Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 313, 475–486 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.12.099
H.J. Choi, Assessment of the adsorption kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic for Pb(II) removal using alow-costhybrid biowaste adsorbent eggshell/coffeeground/sericite. Water Environ. Res. 91(12), 1600–1612 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/wer.1158
W. Zhang, J. Song, Q. He et al., Novel pectin based composite hydrogel derived from grapefruit peel for enhanced Cu(II) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 384, 121445 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121445
H. Ren, Z. Gao et al., Efficient Pb(II) removal using sodium alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose gel beads: preparation, characterization, and adsorption mechanis. Carbohyd. Polym. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.002
L. Yuan, Y. Wu, Q.S. Gu et al., Injectable photo crosslinked enhanced double-network hydrogels from modified sodium alginate and gelatin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 96, 569–577 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.12.058
Y. Li, S.J. Liu, F.M. Chen et al., High-strength apatite/attapulgite/alginate composite hydrogel for effective adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 64(12), 5469–5477 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.9b00616
P. Cheng, C. Wang, Y.V. Kaneti et al., Practical MOF nanoarchitectonics: new strategies for enhancing the processability of mofs for practical applications. Langmuir 36(16), 4231–4249 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.0c00236
M.R. Lohe, M. Rose, S. Kaskel, Metal-organic framework (MOF) aerogels with high micro-and macroporosity. Chem. Commun. 40, 6056–6058 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1039/b910175f
A.S. Eltaweil, I.M. Mamdouh, E.M. Abd El-Monaem et al., Highly efficient removal for methylene blue and Cu2+ onto UiO-66 metal-organic framework/carboxylated graphene oxide-incorporated sodium alginate beads. ACS Omega 6(36), 23528–23541 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c03479
J. Cao, Y. Su, Y. Liu et al., Self-assembled MOF membranes with underwater superoleophobicity for oil/water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 566, 268–277 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2018.08.068
He. Zhu, Qi. Zhang, Shiping Zhu, Alginate hydrogel: a shapeable and versatile platformfor in-situ preparation of MOF-polymer composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 8, 17395–17401 (2016)
D. Qian, L. Bai, Y. Wang et al., A bifunctional alginate-based composite hydrogel with synergistic pollutant adsorption and photocatalytic degradation performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 58(29), 13133–13144 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.9b01709
O. Maan, P. Song, N. Chen et al., An in situ procedure for the preparation of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 polyacrylamide hydrogel for adsorption of aqueous pollutants. Adv. Mater. Interfaces (2019). https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.201801895
H. Zhu, Q. Zhang, S. Zhu, Alginate hydrogel: a shapeable and versatile platform for in situ preparation of metal-organic framework-polymer composites. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8, 17395 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b04505
W. Ren, J. Gao, C. Lei et al., Recyclable metal-organic framework/cellulose aerogels for activating peroxymonosulfate to degrade organic pollutants. Chem. Eng. J. -Lausanne- (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2018.05.143
O.H. Kwon, J.O. Kim, D.W. Cho et al., Adsorption of As(III), As(V) and Cu(II) on zirconium oxide immobilized alginate beads in aqueous phase [J]. Chemosphere 160, 126–133 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.06.074
T. Hu, Q. Liu, T. Gao et al., Facile preparation of tannic acid–poly(vinyl alcohol)/sodium alginate hydrogel beads for methylene blue removal from simulated solution. ACS Omega 3(7), 7523–7531 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00577
M.A. Morsy, M.A. Al-Khaldi, A. Suwaiyan, Normal vibrational mode analysis and assignment of benzimidazole by ab initio and density functional calculations and polarized infrared and raman spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. A 106(40), 9196–9203 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0256948
X. Zhang, X. Lin, Y. He et al., Phenolic hydroxyl derived copper alginate microspheres as superior adsorbent for effective adsorption of tetracycline. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 136, 445–459 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.165
X. Zhu, Y. Liu, C. Zhou et al., A novel porous carbon derived from hydrothermal carbon for efficient adsorption of tetracycline. Carbon 77, 627–636 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2014.05.067
X. Xu, X.Y. Jiang, F.P. Jiao et al., Tunable assembly of porous three-dimensional graphene oxide-corn zein composites with strong mechanical properties for adsorption of rare earth elements. J. Taiwan Instit. Chem. Eng. 85, 106–114 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.12.024
C. Jin, X. Zhang et al., Thiol-Ene synthesis of cysteine-functionalized lignin for the enhanced adsorption of Cu(II) and Pb(II). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 57(23), 7872–7880 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b00823
X. Chen, G. Chen, L. Chen et al., Adsorption of copper and zinc by biochars produced from pyrolysis of hardwood and corn straw in aqueous solution. Bioresour. Technol. 102(19), 8877–8884 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2011.06.078
S. Periyasamy, N. Viswanathan, Hydrothermal synthesis of melamine-functionalized covalent organic polymer-blended alginate beads for iron removal from water [J]. J. Chem. Eng. Data 64, 2280–2291 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.8b01085
N. Wang, X. Xu, H. Li et al., Preparation and application of a xanthate-modified thiourea chitosan sponge for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solutions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 55(17), 4960–4968 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.6b00694
T.A. Nguyen, B.T. Dang, H. Le et al., Thiosemicarbazone-modified cellulose: synthesis, characterization, and adsorption studies on Cu(II) removal. ACS Omega 5(24), 14481–14493 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c01129
Z. Peixia et al., In-situ growth of polyvinylpyrrolidone modified Zr-MOFs thin-film nanocomposite (TFN) for efficient dyes removal. Composites Part B Eng. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107208
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the financial support from Qinghai Province Thousand Talents Program funded project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GZ: Experimentalize, Data collection, Writing-original draft. GY: Investigation, Aid with Synthesis and Preliminary Characterization. HC: Data curation, Formal analysis. HF: Supervision, Writing-review & editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, G., Chen, H., Yang, G. et al. Preparation of In Situ ZIF-9 Grown on Sodium Alginate/Polyvinyl Alcohol Hydrogels for Enhancing Cu (II) Adsorption from Aqueous Solutions. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 4576–4588 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02463-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-022-02463-1