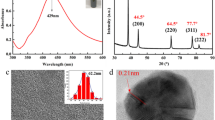
Abstract
Conductive ink is used in many areas of the industry. There are many studies on the production of conductive ink. In this study, mixtures of 2–40 nm silver nanoparticles with a minimum shelf life of 3–4 months were prepared with polyvinyl alcohol and polyaniline. The shelf life of many conductive inks known in the literature cannot be mentioned. We measured the resistance of the films formed on the surface. In the study, we characterized the materials via FTIR, SEM, EDX, and Zetasizer analyzes. The current–voltage measurement of the films was performed by the two-point method. Compared to the literature, we achieved to reach a resistance level of 10–6 Ω cm. Moreover, the solutions we produce can be preserved for one year at room temperature without collapse or deterioration. This also enables conductive ink production, which is very suitable for industrial production.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Omri, I. Najeh, L. El Mir, Influence of annealing temperature on the microstructure and dielectric properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 42, 8940–8948 (2016)
K. Omri, A. Bettaibi, K. Khirouni, L. El Mir, The optoelectronic properties and role of Cu concentration on the structural and electrical properties of Cu doped ZnO nanoparticles. Physica B 537, 167–175 (2018)
K. Omri, S. Gouadria, Dielectric investigation and effect of low copper doping on optical and morphology properties of ZO-Cu nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 17021–17031 (2021)
K. Omri, A. Alyamani, L. El Mir, Surface morphology, microstructure and electrical properties of Ca-doped ZnO thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 16606–16612 (2019)
P. Sungmee, S. Jayaraman, Enhancing the quality of life through wearabletechnology. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Magn. 22, 41–48 (2003)
İA. Kariper, T. Özpozan, Optical and electrical properties of nickel xanthate thin films. Bull. Mater. Sci. 37(3), 553–561 (2014)
İA. Kariper, T. Özpozan, Cobalt xanthate thin film with chemical bath deposition. J. Nanomater. 2013, 19 (2013)
X. Nie, H. Wang, J. Zou, Inkjet printing of silver citrate conductive ink on PET substrate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 261, 554 (2012)
J. Kastner, T. Faury, H.M. Außerhuber, T. Obermuller, H. Leichtfried, M.J. Haslinger, E. Liftinger, J. Innerlohinger, I. Gnatiuk, D. Holzinger, T. Lederer, Silver-based reactive ink for inkjet-printing of conductive lines on textiles. Microelectron. Eng. 176, 84 (2017)
J.S. Kang, H.S. Kim, J. Ryu, H.T. Hahn, S. Jang, J.W. Joung, Inkjet printed electronics using copper nanoparticle ink. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 21, 1213 (2010)
A. Capasso, A.E. Del Rio Castillo, H. Sun, A. Ansaldo, V. Pellegrini, F. Bonaccorso, Ink-jet printing of graphene for flexible electronics: an environmentally-friendly approach. Solid State Commun. 224, 53 (2015)
K. Arapov, R. Abbel, G. de With, H. Friedrich, Inkjet printing of graphene. Faraday Discuss. 173, 323 (2014)
Z. Wanga, W. Wanga, Z. Jiang, D. Yu, Low temperature sintering nano-silver conductive ink printed oncotton fabric as printed electronics. Prog. Org. Coat. 101, 604–611 (2016)
D.S. Saıdına, N. Eawwıboonthanakıt, M. Marıattı, S. Fontana, C. Herold, Recent development of graphene-based ink and other conductive material-based inks for flexible electronics. J. Electron. Mater. 48(6), 3428–3450 (2019)
C. Hepokur, İA. Kariper, S. Mısır, E. Ay, S. Tunoğlu, M.S. Ersezd, Ü. Zeybek, S.E. Kuruca, İ Yaylım, Silver nanoparticle/capecitabine for breast cancer cell treatment. Toxicol. Vitro 61, 104600 (2019)
B.S. Singu, P. Srinivasan, S. Pabba, benzoyl peroxide oxidation route to nano form polyaniline saltcontaining dual dopants for pseudocapacitor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 159(1), A6–A13 (2012)
H.S. Mansur, C.M. Sadahira, A.N. Souza, A.A.P. Mansur, FTIR spectroscopy characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel with different hydrolysis degree and chemically crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 28, 539–548 (2008)
L. Mo, D. Liu, W. Li, L. Li, L. Wang, X. Zhou, Effects of dodecylamine and dodecanethiol on the conductive properties ofnano-Ag films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 5746–5753 (2011)
Q. Huang, W. Shen, W. Song, Synthesis of colourless silver precursor ink for printing conductive patterns on silicon nitride substrates. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 7384–7388 (2012)
J. E. Corona, A. I. Oliva, Morphological effects and their relation with the electrical resistivity measured during the initial stages of growth of Au/glass films, 2nd International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ICEEE) and XI Conference on Electrical Engineering (CIE 2005), Mexico City, Mexico. September 7–9 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kariper, İ.A. Conductive Ink Next Generation Materials: Silver Nanoparticle/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Polyaniline. J Inorg Organomet Polym 32, 1277–1286 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02179-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02179-8