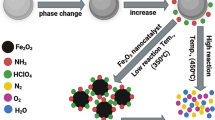
Abstract
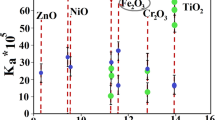
Surface oxygen of oxide catalyst has low coordination number; they are negatively charged. Surface oxygen can act active site for decomposition of energetic nitramines (i.e. HMX). Additionally hydrous catalyst surface can release active OH radicals. Colloidal oxide particles can fulfil these requirements. Furthermore oxide particles can induce thermite reaction with aluminium particles. This study reports on the facile fabrication of colloidal ferric oxide particles of 5 nm average particle size. Aluminium nanoplates of 100 nm particle size were dispersed in ferric oxide colloid. Colloidal Fe2O3/Al binary mixture was integrated into HMX matrix via co-precipitation technique. SEM micrographs demonstrated uniform dispersion of nanothermite particles into energetic matrix. Naonothermite particles experienced dramatic change in HMX thermal behaviour with increase in total heat release by 63% using DSC. The impact of thermite particles on HMX kinetic decomposition was evaluated via an integral isoconversional method using KAS, and Kissinger models. The mean value of apparent activation was reduced by 23.5 and 24.3% using Kissinger and KAS models respectively. This dramatic change in HMX decomposition could be ascribed to ferric oxide reactivity. Facile integration of colloidal thermite particles into HMX can secure high interfacial surface area.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Meyer, J. Kohler, A. Homburg, eds. EXPLOSIVES. Sixth (ed.). 2007, WILEY: Weinheim
H. Huang, Y. Shi, J. Yang, Thermal characterization of the promising energetic material TKX-50. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 121(2), 705–709 (2015)
A.M.A. Elghafour et al., Highly energetic nitramines: A novel platonizing agent for double-base propellants with superior combustion characteristics. Fuel 227, 478–484 (2018)
M. Talawar et al., New directions in the science and technology of advanced sheet explosive formulations and the key energetic materials used in the processing of sheet explosives: Emerging trends. J. Hazard. Mater. 300, 307–321 (2015)
S. Elbasuney, G.S. El-Sayyad, The potentials of TiO2 nanocatalyst on HMX thermolysis. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(17), 14930–14940 (2020)
S. Elbasuney et al., Multi-component nanocomposite infrared flare with superior infrared signature via synergism of nanothermite and reduced graphene oxide. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(14), 11520–11526 (2020)
N. Fischer et al., Pushing the limits of energetic materials–the synthesis and characterization of dihydroxylammonium 5, 5′-bistetrazole-1, 1′-diolate. J. Mater. Chem. 22(38), 20418–20422 (2012)
S. Elbasuney, M. Yehia, Ammonium Perchlorate Encapsulated with TiO2 Nanocomposite for Catalyzed Combustion Reactions. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 29(4), 1349–1357 (2019)
S. Elbasuney, M. Yehia, Ferric Oxide Colloid: A Novel Nano-catalyst for Solid Propellants. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 30(3), 706–713 (2020)
S. Elbasuney et al., Novel High Energy Density Material Based on Metastable Intermolecular Nanocomposite. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 30(10), 3980–3988 (2020)
S. Elbasuney et al., Ferric oxide colloid: novel nanocatalyst for heterocyclic nitramines. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2021
S. Elbasuney et al., Facile synthesis of RGO-Fe2O3 nanocomposite: A novel catalyzing agent for composite propellants. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(23), 20805–20815 (2020)
S. Elbasuney, Dispersion characteristics of dry and colloidal nano-titania into epoxy resin. Powder Technol. 268(0), 158–164 (2014)
S. Elbasuney, Continuous hydrothermal synthesis of AlO(OH) nanorods as a clean flame retardant agent. Particuology 22, 66–71 (2015)
S. Elbasuney, Surface engineering of layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanoparticles for polymer flame retardancy. Powder Technol. 277, 63–73 (2015)
A. Cabanas et al., A continuous and clean one-step synthesis of nano-particulate Ce1 – xZrxO2 solid solutions in near-critical water. Chemical Communications 11, 901–902 (2000)
K. Byrappa, M. Yoshimura, Hydrothermal technology—Principles and applications. Handbook of hydrothermal technology, 2001: 1–52
O. Schäf, H. Ghobarkar, P. Knauth, Hydrothermal synthesis of nanomaterials, in Nanostructured Materials. 2004, Springer. p. 23–41
Y.X. Gan et al., Hydrothermal synthesis of nanomaterials. 2020, Hindawi
A. Benhammada et al., Synthesis and characterization of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles from different precursors and their catalytic effect on the thermal decomposition of nitrocellulose. Thermochim. Acta 686, 178570 (2020)
A.F. Tarchoun et al., New insensitive nitrogen-rich energetic polymers based on amino-functionalized cellulose and microcrystalline cellulose: Synthesis and characterization. Fuel 277, 118258 (2020)
S. Hanafi et al., Catalytic effect of 2D-layered energetic hybrid crystals on the thermal decomposition of 3-nitro-2,4-dihydro-3H-1,2,4-triazol-5-one (NTO). Thermochim. Acta 692, 178747 (2020)
M.A. Khalilzadeh et al., Green Synthesis of Magnetic Nanocomposite with Iron Oxide Deposited on Cellulose Nanocrystals with Copper (Fe3O4@CNC/Cu): Investigation of Catalytic Activity for the Development of a Venlafaxine Electrochemical Sensor. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2020. 59(10): 4219–4228
S. Elbasuney et al., Novel nanocomposite decoy flare based on super-thermite and graphite particles. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(8), 6130–6139 (2020)
S. Elbasuney et al., Reduced graphene oxide: a novel black body emitter for advanced infrared decoy flares. Journal of Energetic Materials, 2020: p. 1–13
S. Elbasuney et al., Infrared Signature of Novel Super-Thermite (Fe2O3/Mg) Fluorocarbon Nanocomposite for Effective Countermeasures of Infrared Seekers. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym Mater. 28(5), 1718–1727 (2018)
S. Elbasuney et al., Infrared Spectra of Customized Magnesium/Teflon/Viton Decoy Flares. Combustion, Explosion, and Shock Waves 55(5), 1 (2019)
S. Elbasuney et al., Super-Thermite (Al/Fe2O3) Fluorocarbon Nanocomposite with Stimulated Infrared Thermal Signature via Extended Primary Combustion Zones for Effective Countermeasures of Infrared Seekers. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials, 2018. 28
D. Trache, Comments on “thermal degradation behavior of hypochlorite-oxidized starch nanocrystals under different oxidized levels”. Carbohyd. Polym. 151, 535–537 (2016)
A.F. Tarchoun et al., (2019) A Promising Energetic Polymer from Posidonia oceanica Brown Algae Synthesis, Characterization, and Kinetic Modeling Macromolecular. Chemistry Physics 2019: 220(22)
S. Elbasuney et al., Novel (MnO2/Al) thermite colloid: an opportunity for energetic systems with enhanced performance. J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 31(23), 21399–21407 (2020)
M. Starink, The determination of activation energy from linear heating rate experiments: a comparison of the accuracy of isoconversion methods. Thermochim. Acta 404(1–2), 163–176 (2003)
H.E. Kissinger, Reaction kinetics in differential thermal analysis. Analytical chemistry 29(11), 1702–1706 (1957)
S. Elbasuney, Sustainable steric stabilization of colloidal titania nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 409, 438–447 (2017)
S. Vyazovkin, C. Wight, Kinetics in solids. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 48(1), 125–149 (1997)
Q.-L. Yan et al., Thermal behavior and decomposition kinetics of Formex-bonded explosives containing different cyclic nitramines. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 111(2), 1419–1430 (2013)
Q.-L. Yan et al., The influence of the semtex matrix on the thermal behavior and decomposition kinetics of cyclic nitramines. Cent. Eur. J. Energ. Mater. 10(4), 509–528 (2013)
N.N. Thadhani, Thermal analysis instrumentation for kinetics of shocked materials. 2003, Georgia Institute of Technology
V.E. ZARKO, A.A. GROMOV (eds.), ENERGETIC NANOMATERIALS Synthesis, Characterization, and Application (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2016)
C.M. Tarver, T.D. Tran, Thermal decomposition models for HMX-based plastic bonded explosives. Combust. Flame 137(1–2), 50–62 (2004)
V.E. Zarko, A.A. Gromov, Energetic nanomaterials: Synthesis, characterization, and application. 2016: elsevier
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elbasuney, S., Hamed, A., Yehia, M. et al. The Impact of Metastable Intermolrecular Nanocomposite Particles on Kinetic Decomposition of Heterocyclic Nitramines Using Advanced Solid‐Phase Decomposition Models. J Inorg Organomet Polym 31, 3665–3676 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02007-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-021-02007-z