Abstract
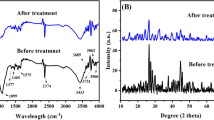
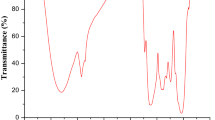
There is a need to develop effective and inexpensive methods for removal of heavy metals from contaminated water in developing countries. In this study, a novel microporous, microcrystalline, zeolite-type X high silica (NaX-500) sorbent was synthesized using hydrothermal method followed by calcination at 500 °C. Its sorption capacity to remove Cu(II) was tested in reconstituted water with and without humic acid (HA). Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, chemical elemental composition, scanning electron microscopy, N2 adsorption–desorption measurement and X-ray diffraction analyses confirmed that NaX-500 has a micro-crystalline structure with micrometer-sized pores and a specific area of about 336 m2/g. The results showed that sorption of Cu(II) below 20 mg/L was described by pseudo-first-order kinetic model and above 500 mg/L by the second order model, whereas Dubinin–Radushkevich model (for all cases R2 values > 0.810) described best the sorption of copper(II) on NaX-500. The presence of HA was found to influence the adsorption efficiency as copper formed a complex with zeolite–HA, thus improving the adsorption capacities. This study shows that, the newly developed material is rapid and effective for the removal of copper from contaminated water both at low and moderate concentrations including from water with moderate concentration of humic substances.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Jaishankar, T. Tseten, N. Anbalagan, B.B. Mathew, K.N. Beeregowda, Toxicity, mechanism and health effects of some heavy metals. Interdiscip. Toxicol. 7(2), 60–72, 2014
S. Chowdhury, M.A.J. Mazumder, O. Al-attas, T. Husain, Science of the total environment heavy metals in drinking water: occurrences, implications, and future needs in developing countries. Sci. Total Environ. 569–570, 476–488 (2016)
Y. Zhang, Y. Han, J. Yang, L. Zhu, W. Zhong, Toxicities and risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Taihu Lake, China, based on sediment quality guidelines. J. Environ. Sci. 62, 31–38 (2017)
R.B. Suami et al., Concentration of heavy metals in edible fishes from Atlantic Coast of Muanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo. J. Food Compos. Anal. 73, 1–9 (2018)
N.A. Fakhre, B.M. Ibrahim, The use of new chemically modified cellulose for heavy metal ion adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 343, 324–331 (2018)
I.M. Kenawy, M.A.H. Hafez, M.A. Ismail, M.A. Hashem, Adsorption of Cu(II), Cd(II), Hg(II), Pb(II) and Zn(II) from aqueous single metal solutions by guanyl-modified cellulose. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 107, 1538–1549 (2018)
T.S. Anirudhan, P.S. Suchithra, Humic acid-immobilized polymer/bentonite composite as an adsorbent for the removal of copper(II) ions from aqueous solutions and electroplating industry wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 16(1), 130–139 (2010)
Ö Gök, A. Özcan, B. Erdem, A.S. Özcan, Prediction of the kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamic parameters of adsorption of copper(II) ions onto 8-hydroxy quinoline immobilized bentonite. Colloids Surf. A 317(1–3), 174–185 (2008)
S.S. Banerjee, D.H. Chen, Fast removal of copper ions by gum arabic modified magnetic nano-adsorbent. J. Hazard. Mater. 147(3), 792–799 (2007)
H. Chen, G. Dai, J. Zhao, A. Zhong, J. Wu, H. Yan, Removal of copper(II) ions by a biosorbent-Cinnamomum camphora leaves powder. J. Hazard. Mater. 177(1–3), 228–236 (2010)
J. Hao, L. Ji, C. Li, C. Hu, K. Wu, Rapid, efficient and economic removal of organic dyes and heavy metals from wastewater by zinc-induced in-situ reduction and precipitation of graphene oxide. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 88, 137–145 (2018)
V. Yogeshwaran, A. Priya, Removal of hexavalent chromium by adsorption using natural wastes-a review. Adv. Recycl. Waste Manag. 2(4), 4–6 (2017)
M.A. Renu, K. Singh, S. Upadhyaya, R.K. Dohare, Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using modified agricultural adsorbents. Mater. Today Proc. 4(9), 10534–10538, 2017
Z. Elouear, J. Bouzid, N. Boujelben, M. Feki, F. Jamoussi, A. Montiel, Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions by activated phosphate rock. J. Hazard. Mater. 156(1–3), 412–420 (2008)
E. Kaprara et al., Cu-Zn powders as potential Cr(VI) adsorbents for drinking water. J. Hazard. Mater. 262, 606–613 (2013)
I. Aloma, M.A. Martin-Lara, I.L. Rodriguez, G. Blazquez, M. Calero, Removal of nickel (II) ions from aqueous solutions by biosorption on sugarcane bagasse. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 43(2), 275–281 (2012)
H. Yin, J. Zhu, In situ remediation of metal contaminated lake sediment using naturally occurring, calcium-rich clay mineral-based low-cost amendment. Chem. Eng. J. 285, 112–120 (2016)
M. Ghasemi, H. Javadian, N. Ghasemi, S. Agarwal, V.K. Gupta, Microporous nanocrystalline NaA zeolite prepared by microwave assisted hydrothermal method and determination of kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic parameters of the batch sorption of Ni (II). J. Mol. Liq. 215, 161–169 (2016)
N. Arancibia-Miranda et al., Nanoscale zero valent supported by zeolite and montmorillonite: template effect of the removal of lead ion from an aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 301, 371–380 (2016)
X. Kong, Z. Han, W. Zhang, L. Song, H. Li, Synthesis of zeolite-supported microscale zero-valent iron for the removal of Cr 6þ and Cd 2þ from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Manag. 169, 84–90 (2016)
O.O. Ltaief, S. Siffert, S. Fourmentin, M. Benzina, Synthesis of Faujasite type zeolite from low grade Tunisian clay for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous waste by batch process: kinetic and equilibrium study ` partir d’ une argile commune ` se d’ une ze ´ olithe de type faujasite a ´ limination. C. R. Chim. 18, 1123–1133 (2015)
X. Zhang, D. Tong, J. Zhao, X. Li, Synthesis of NaX zeolite at room temperature and its characterization. Mater. Lett. 104, 80–83 (2013)
R. Han et al., Characterization and properties of iron oxide-coated zeolite as adsorbent for removal of copper (II) from solution in fixed bed column. Chem. Eng. J. 149, 123–131 (2009)
K. Menad, A. Feddag, M. Abd, E. Hasnaoui, A. Elkader, Synthesis and modification by ion exchange of the composite core-shell. J. Sci. Innov. Res. 3(4), 419–425 (2014)
Y. Bouizi, Micro-composites formed a continuous layer of zeolite covering a core zeolite-study training process, in Thesis, pp. 6, 12, 39 (2005)
M.M.J. Treacy, J.B. Higgins, Collection of Simulated XRD Powder Patterns for Zeolites (Elsevier, London, 2001), pp. 11–15
H. Tanaka, A. Fujii, Effect of stirring on the dissolution of coal fly ash and synthesis of pure-form Na-A and -X zeolites by two-step process. Adv. Powder Technol. 20(5), 473–479 (2009)
D. Nibou, H. Mekatel, S. Amokrane, M. Barkat, M. Trari, Adsorption of Zn2+ ions onto NaA and NaX zeolites: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Hazard. Mater. 173(1–3), 637–646 (2010)
V. Ndira, Substances humiques du sol et du compost: analyse elementaire et groupements atomiques fictifs: vers une approche thermodynamique (2006)
Y. Zhan, Z. Zhu, J. Lin, Y. Qiu, J. Zhao, Removal of humic acid from aqueous solution by cetylpyridinium bromide modified zeolite. J. Environ. Sci. 22(9), 1327–1334 (2010)
S.V. Mohan, J. Karthikeyan, Removal of lignin and tannin colour from aqueous solution by adsorption onto activated charcoal. Environ. Pollut. 97(1–2), 183–187 (1997)
A.O. Dada, A.P. Olalekan, A.M. Olatunya, O. Dada, Langmuir, Freundlich, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich isotherms studies of equilibrium sorption of Zn2+ unto phosphoric acid modified rice husk. IOSR J. Appl. Chem. 3(1), 38–45 (2012)
A. Günay, E. Arslankaya, I. Tosun, Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J. Hazard. Mater. 146(1–2), 362–371 (2007)
G. Asgari, B. Roshani, G. Ghanizadeh, The investigation of kinetic and isotherm of fluoride adsorption onto functionalize pumice stone, J. Hazard. Mater. 217–218, 123–132 (2012)
H.K. Boparai, M. Joseph, D.M. O’Carroll, Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles. J. Hazard. Mater. 186(1), 458–465 (2011)
I. Kuźniarska-Biernacka, A.M. Fonseca, I.C. Neves, Manganese complexes with triazenido ligands encapsulated in NaY zeolite as heterogeneous catalysts. Inorg. Chim. Acta 394, 591–597 (2013)
J. Lin, Y. Zhan, Z. Zhu, Adsorption characteristics of copper (II) ions from aqueous solution onto humic acid-immobilized surfactant-modified zeolite. Colloids Surf. A 384, 9–16 (2011)
T.C. Nguyen, P. Loganathan, T.V. Nguyen, S. Vigneswaran, J. Kandasamy, R. Naidu, Simultaneous adsorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Pb, and Zn by an iron-coated Australian zeolite in batch and fixed-bed column studies. Chem. Eng. J. 270, 393–404 (2015)
C. Wang, L. Lippincott, I. Yoon, X. Meng, Modeling, rate-limiting step investigation, and enhancement of the direct bio-regeneration of perchlorate laden anion-exchange resin. Water Res. 43(1), 127–136 (2009)
S. Wang, T. Terdkiatburana, M.O. Tadé, Single and co-adsorption of heavy metals and humic acid on fly ash. Sep. Purif. Technol. 58(3), 353–358 (2008)
S. Rangabhashiyam, N. Anu, M.S. Giri Nandagopal, N. Selvaraju, Relevance of isotherm models in biosorption of pollutants by agricultural byproducts. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2(1), 398–414 (2014)
W.S.W. Ngah, S. Fatinathan, Adsorption characterization of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions onto chitosan-tripolyphosphate beads: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J. Environ. Manag. 91(4), 958–969 (2010)
J.P. Hobson, Physical adsorption isotherms extending from ultrahigh vacuum to vapor pressure. J. Phys. Chem. 309(22), 2720–2727 (1969)
M.M. Dubinin, The potential theory of adsorption of gases and vapors for adsorbents with energetically nonuniform surfaces. Chem. Rev. 60(2), 235–241 (1960)
Acknowledgements
Corresponding author is thankful to Dr. A. FEDDAG, MCA, Mostaganem University and Prof. T. JUHNA, Director, Water Research laboratory, Riga Technical University for constant encouragement and providing infrastructure.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See Table 6.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Menad, K., Feddag, A. & Juhna, T. Copper(II)–Humic Acid Adsorption Process Using Microporous-Zeolite Na-X. J Inorg Organomet Polym 29, 1–16 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0958-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-018-0958-9