Abstract
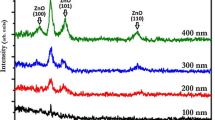
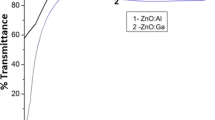
Improved properties of aluminum zinc oxide (AZO) thin films deposited by the magnetron sputtering at room temperature are reported. AZO is one of the most promising transparent conducting oxide materials, which widely used in thin film solar cells. In this study the optimization process of the DC magnetron sputtered AZO films was carried out at room temperature by studying its structural, optical, electrical and morphological properties at different deposition times (5, 10, 15, 20 and 25 min). It can be utilized as a front contact for the cadmium telluride (CdTe) based thin film solar cells. The structural study shows that the preferred orientation of grains is along plane (002), with a hexagonal structure of the grains. The electrical and optical characteristics show that the films has an average transmission of 70 % and a resistivity of the order of 10−4 Ω cm. The morphology analysis suggests the formation of packed grains with a homogeneous surface.






Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
30 December 2023
This article has been retracted. Please see the Retraction Notice for more detail: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-023-02987-0
References
A.R. Silva, J.O. Rossi, L.P.S. Neto, M. Ueda, Adherence enhancement of metallic film on PZT type ceramic using nitrogen plasma implantation. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 42(10), 3173–3179 (2014)
I.B. Matveev, L.A. Rosocha, Guest editorial: classification of plasma systems for plasma-assisted combustion. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 38(12), 3257–3264 (2010)
P.I. Vysikaylo, V.S. Mitin, A.V. Mitin, N.N. Krasnobaev, V.V. Belyaev, Theoretical model of ceramic heat sinks. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 43(3), 892–895 (2015)
W.B. Choi, D.S. Chung, J.H. Kang, H.Y. Kim, Y.W. Jin, I.T. Han, Y.H. Lee, J.E. Jung, N.S. Lee, G.S. Park, J.M. Kim, Fully sealed, high-brightness carbon-nanotube field-emission display. Appl. Phys. Lett. 75, 3129–3131 (1999)
I.C. Chen, L.H. Chen, X.R. Ye, C. Daraio, S. Jin, C.A. Orme, A. Quist, R. Lal, Extremely sharp carbon nanocone probes for atomic force microscopy imaging. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 153102–153104 (2006)
S.S. Wong, A.T. Woolley, E. Joselevich, C.M. Lieber, Functionalization of carbon nanotube AFM probes using tip-activated gases. Chem. Phys. Lett. 306, 219–225 (1999)
R. Martel, T. Schmidt, H.R. Shea, T. Hertel, P. Avouris, Singleand multi-wall carbon nanotube field-effect transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 2447–2449 (1998)
Q.H. Wang, T.D. Corrigan, J.Y. Dai, R.P.H. Chang, A.R. Krauss, Field emission from nanotube bundle emitters at low fields. Appl. Phys. Lett. 70, 3308–3310 (1997)
S. Fan, M.G. Chapline, N.R. Franklin, T.W. Tombler, A.M. Cassell, H. Dai, Self-oriented regular arrays of carbon nanotubes and their field emission properties. Science 283, 512–514 (1990)
C.S. Huang, C.Y. Yeh, Y.H. Chang, Y.M. Hsieh, C.Y. Ku, Q.T. Lai, Field emission properties of CNT–ZnO composite materials. Diam. Relat. Mater. 18, 452–456 (2009)
W.A. de Heer, A. Chatelain, D. Ugarte, A carbon nanotube field emission electron source. Science 270, 1179–1180 (1995)
A.G. Rinzler, J.H. Hafner, P. Nikolaev, P. Nordlander, D.T. Colbert, R.E. Smalley, L. Lou, S.G. Kim, D. Tomanek, Unraveling nanotubes: field emission from an atomic wire. Science 269, 1550–1553 (1995)
N. de Jonge, Y. Lamy, K. Schoots, T.H. Oosterkamp, High brightness electron beam from a multi-walled carbon nanotube. Nature 420, 393–395 (2002)
J. Jiao, L.F. Dong, D.W. Tuggle, C.L. Mosher, S. Foxley, J. Tawdekar, Fabrication and characterization of carbon nanotube field emitters. Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 706, 113–117 (2002)
P.I. Vysikaylo, V.S. Mitin, A.V. Mitin, N.N. Krasnobaev, V.V. Belyaev, Plasma metallization coating and its adhesion to microwave transistor substrate Pt.1. methods of experimental research. IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. 43(4), 1088–1092 (2015)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Ghorannevis, Z., Akbarnejad, E., Salar Elahi, A. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: Magnetron Sputtered AZO Thin Film Preparation for the Solar Cells Applications. J Inorg Organomet Polym 25, 1486–1489 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-015-0265-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10904-015-0265-7