Abstract
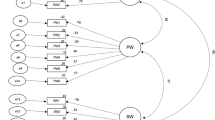
This study is the first to investigate the factor structure of the Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC-SF) in New Zealand. Towards this end, traditional Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) and the new method of Exploratory Structural Equation Modeling (ESEM) were used. Both ESEM and CFA supported the tripartite model of mental well-being in comparison to the one- and two-factor models; however, ESEM provided better fit with the data. Moreover, interfactor correlations were considerably lower in ESEM than they were in CFA, indicating greater factor distinctiveness in ESEM. ESEM also revealed a number of important cross-loadings for items in the measurement model of the MHC-SF. The results supported full metric and full scalar invariance of the MHC-SF across gender. The attenuated correlations among well-being factors obtained by ESEM here provide an important insight about the ongoing controversy regarding the failure of empirical research to identify distinct eudaimonic and hedonic factors in well-being measures. An overreliance on CFA methods may have led the field to rely on inflated estimates of shared variance between eudaimonia and hedonia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbinnett, R. (2013). Politics of happiness: Connecting the philosophical ideas of Hegel, Nietzsche and Derrida to the political ideologies of happiness. New York: Bloomsbury Publishing.
Asparouhov, T., & Muthen, B. (2009). Exploratory structural equation modeling. Structural Equation Modeling, 16, 397–438.
Bobowik, M., Basabe, N., & Páez, D. (2015). The bright side of migration: Hedonic, psychological, and social well-being in immigrants in Spain. Social Science Research, 51, 189–204.
Browne, M. W., & Cudeck, R. (1993). Alternative ways of assessing model fit. In K. A. Bollen & J. S. Long (Eds.), Testing structural equation models (pp. 136–162). Beverly Hills, CA: Sage.
Chen, F. F. (2007). Sensitivity of goodness of fit indexes to lack of measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling, 14(3), 464–504. doi:10.1080/10705510701301834.
Chen, F. F. (2008). What happens if we compare chopsticks with forks? The impact of making inappropriate comparisons in cross-cultural research. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 95(5), 1005–1017.
Cheung, G. W., & Rensvold, R. B. (2002). Evaluating goodness-of-fit indexes for testing measurement invariance. Structural Equation Modeling, 9, 233–255.
De Bruin, G. P., & Du Plessis, G. A. (2015). Bifactor analysis of the Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC-SF). Psychological Reports, 116(2), 438–446.
Deci, E. L., & Ryan, R. M. (2008). Hedonia, eudaimonia, and well-being: An introduction. Journal of Happiness Studies, 9(1), 1–11.
Demirci, I., & Akin, A. (2015). The validity and reliability of the mental health continuum short form. Egitim Bilimleri Fakultesi Dergisi, 48(1), 49–64.
Devettere, R. J. (2002). Introduction to virtue ethics: Insights of the ancient Greeks. Washington, DC: Georgetown University Press.
Diener, E., Oishi, S., & Lucas, R. E. (2015). National accounts of subjective well-being. American Psychologist, 70(3), 234.
Diener, E., Suh, E. M., Lucas, R. E., & Smith, H. L. (1999). Subjective well-being: Three decades of progress. Psychological Bulletin, 125(2), 276.
Diener, E., & Tay, L. (2015). Subjective well-being and human welfare around the world as reflected in the Gallup World Poll. International Journal of Psychology, 50(2), 135–149.
Disabato, D. J., Goodman, F. R., Kashdan, T. B., Short, J. L., & Jarden, A. (2016). Different types of well-being? A cross-cultural examination of hedonic and eudaimonic well-being. Psychological Assessment, 28(5), 471–482. doi:10.1037/pas0000209.
Fabrigar, L. R., Wegener, D. T., MacCallum, R. C., & Strahan, E. J. (1999). Evaluating the use of exploratory factor analysis in psychological research. Psychological Methods, 4(3), 272.
Gallagher, M. W., Lopez, S. J., & Preacher, K. J. (2009). The hierarchical structure of well-being. Journal of Personality, 77(4), 1025–1050.
Helliwell, J., Layard, R., & Sachs, J. (Eds.). (2015). World happiness report 2015. New York, NY: Sustainable Development Solutions Network.
Hides, L., Quinn, C., Stoyanov, S., Cockshaw, W., Mitchell, T., & Kavanagh, D. J. (2016). Is the mental wellbeing of young Australians best represented by a single, multidimensional or bifactor model? Psychiatry Research, 241, 1–7.
Hofstede, G., Hofstede, G. J., & Minkov, M. (2010). Cultures and organizations: Software of the mind (3rd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill.
Hone, L. C., Jarden, A., Schofield, G. M., & Duncan, S. (2014). Measuring flourishing: The impact of operational definitions on the prevalence of high levels of wellbeing. International Journal of Well-being, 4, 62–90.
Hu, L. T., & Bentler, P. M. (1999). Cutoff criteria for fit indexes in covariance structure analysis: Conventional criteria versus new alternatives. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 6(1), 1–55.
Joshanloo, M. (2014). Eastern conceptualizations of happiness: Fundamental differences with western views. Journal of Happiness Studies, 15, 475–493.
Joshanloo, M. (in press a). A new look at the factor structure of the MHC-SF in Iran and the United States using exploratory structural equation modeling. Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Joshanloo, M. (in press b). Revisiting the empirical distinction between hedonic and eudaimonic aspects of well-being using exploratory structural equation modeling. Journal of Happiness Studies.
Joshanloo, M., & Lamers, S. M. A. (2016). Reinvestigation of the factor structure of the MHC-SF in the Netherlands: Contributions of exploratory structural equation modeling. Personality and Individual Differences, 97, 8–12.
Joshanloo, M., Rostami, R., & Nosratabadi, M. (2006). Examining the factor structure of the Keyes’s comprehensive scale of well-being. Journal of Iranian Psychologists, 9, 35–51. (in Persian).
Joshanloo, M., Wissing, M. P., Khumalo, I. P., & Lamers, S. (2013). Measurement invariance of the Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC-SF) across three cultural groups. Personality and Individual Differences, 55(7), 755–759.
Jovanović, V. (2015). Structural validity of the Mental Health Continuum-Short Form: The bifactor model of emotional, social and psychological well-being. Personality and Individual Differences, 75, 154–159.
Karaś, D., Cieciuch, J., & Keyes, C. L. (2014). The Polish adaptation of the Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC-SF). Personality and Individual Differences, 69, 104–109.
Kashdan, T. B., Biswas-Diener, R., & King, L. A. (2008). Reconsidering happiness: The costs of distinguishing between hedonics and eudaimonia. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 3(4), 219–233.
Keyes, C. L. M. (1998). Social well-being. Social Psychology Quarterly, 61(2), 121–140.
Keyes, C. L. M. (2002). The mental health continuum: From languishing to flourishing in life. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 43(2), 207–222.
Keyes, C. L. M. (2006). The subjective well-being of America’s youth: Toward a comprehensive assessment. Adolescent and Family Health, 4(1), 3–11.
Keyes, C. L., & Annas, J. (2009). Feeling good and functioning well: Distinctive concepts in ancient philosophy and contemporary science. The Journal of Positive Psychology, 4(3), 197–201.
Keyes, C. L., Wissing, M., Potgieter, J. P., Temane, M., Kruger, A., & van Rooy, S. (2008). Evaluation of the Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC–SF) in Setswana-speaking South Africans. Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, 15(3), 181–192.
Lamers, S., Westerhof, G. J., Bohlmeijer, E. T., ten Klooster, P. M., & Keyes, C. L. (2011). Evaluating the psychometric properties of the Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC-SF). Journal of Clinical Psychology, 67(1), 99–110.
Marsh, H. W., Lüdtke, O., Muthén, B., Asparouhov, T., Morin, A. J., Trautwein, U., & Nagengast, B. (2010). A new look at the big five factor structure through exploratory structural equation modeling. Psychological Assessment, 22(3), 471.
Marsh, H. W., Morin, A. J. S., Parker, P. D., & Kaur, G. (2014). Exploratory structural equation modeling: An integration of the best features of exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 10(1), 85–110.
Marsh, H. W., Nagengast, B., Morin, A. J., Parada, R. H., Craven, R. G., & Hamilton, L. R. (2011). Construct validity of the multidimensional structure of bullying and victimization: An application of exploratory structural equation modeling. Journal of Educational Psychology, 103(3), 701–732.
Minkov, M. (2009). Predictors of differences in subjective well-being across 97 nations. Cross-Cultural Research, 43(2), 152–179.
Morin, A. J. S., Arens, A. K., & Marsh, H. W. (2016). A bifactor exploratory structural equation modeling framework for the identification of distinct sources of construct-relevant psychometric multidimensionality. Structural Equation Modeling: A Multidisciplinary Journal, 23(1), 116–139. doi:10.1080/10705511.2014.961800.
Morin, A. J. S., Marsh, H. W., & Nagengast, B. (2013). Exploratory structural equation modeling. In G. R. Hancock & R. O. Mueller (Eds.), Structural equation modeling: A second course (2nd ed.). Charlotte, NC: Information Age Publishing, Inc.
Murray, A. L., & Johnson, W. (2013). The limitations of model fit in comparing the bi-factor versus higher-order models of human cognitive ability structure. Intelligence, 41, 407–422.
OECD. (2015). The better life index. . http://www.oecdbetterlifeindex.org/.
Perrin, A. (2015). Social media usage: 2005–2015. Washington, D.C.: Pew Internet & American Life Project.
Petrillo, G., Capone, V., Caso, D., & Keyes, C. L. (2014). The Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC–SF) as a measure of well-being in the Italian context. Social Indicators Research, 121(1), 291–312.
Reise, S. P. (2012). The rediscovery of bifactor measurement models. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 47(5), 667–696.
Reise, S. P., Scheines, R., Widaman, K. F., & Haviland, M. G. (2013). Multidimensionality and structural coefficient bias in structural equation modeling: A bifactor perspective. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 73(1), 5–26.
Robitschek, C., & Keyes, C. L. M. (2009). Keyes’s model of mental health with personal growth initiative as a parsimonious predictor. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 56(2), 321–329.
Rodriguez, A., Reise, S. P., & Haviland, M. G. (2016). Applying bifactor statistical indices in the evaluation of psychological measures. Journal of Personality Assessment, 98(3), 223–237. doi:10.1080/00223891.2015.1089249.
Rosellini, A. J., & Brown, T. A. (2011). The NEO Five-Factor Inventory: latent structure and relationships with dimensions of anxiety and depressive disorders in a large clinical sample. Assessment, 18(1), 27–38.
Ryff, C. D. (1989). Happiness is everything, or is it? Explorations on the meaning of psychological well-being. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 57(6), 1069.
Singh, K., Bassi, M., Junnarkar, M., & Negri, L. (2015). Mental health and psychosocial functioning in adolescence: An investigation among Indian students from Delhi. Journal of Adolescence, 39, 59–69.
Weston, R., & Gore, P. A. (2006). A brief guide to structural equation modeling. The Counseling Psychologist, 34(5), 719–751.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joshanloo, M., Jose, P.E. & Kielpikowski, M. The Value of Exploratory Structural Equation Modeling in Identifying Factor Overlap in the Mental Health Continuum-Short Form (MHC-SF): A Study with a New Zealand Sample. J Happiness Stud 18, 1061–1074 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-016-9767-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10902-016-9767-4