Abstract
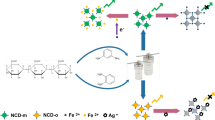
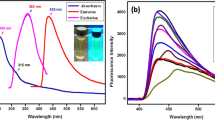
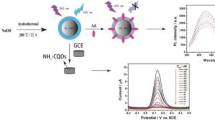
Nitrogen-sulfur co-doped carbon quantum dots (N, S-CQDs) with good photoluminescence properties were prepared by hydrothermal method using citric acid (CA) and methionine (Met) as precursors. Co-doping with N and S facilitates the electron transfer rate and coordination interaction between N,S-CQDs and Fe(III) ions which acts as a quencher of fluorescence. Based on a simple redox principle, a highly sensitive and selective method for the detection of ascorbic acid (AA) and H2O2 was successfully developed. The calibration curves obtained are linear for the current versus AA and H2O2 concentration over the range 50–500 μM and 10–140 μM, respectively. And the detection limits for AA and H2O2 are 4.2 μM and 1.9 μM, respectively. The quantitative analysis of AA and H2O2 in various juices and H2O2 disinfectant with Fe3+/CQDs or Fe2+/CQDs gave the recoveries of 87.8%–117.5% and 99.2%–106.4% with relative standard deviations (RSD) of 1.6–5.1% and 1.7–3.1%, respectively, showing satisfactory results for the determination of AA and H2O2 in actual application. The proposed strategy may provide a new pathway to developing inexpensive and sensitive way for the detection of various redox reaction–involved system.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jing-Jing Liu Z-TC, Tang D-S, Wang Y-B, Long-Tian Kang J-NY (2015) Graphene quantum dots-based fluorescent probe for turn-on sensing of ascorbic acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem 212:214–219
Meng H, Yang D, Tu Y, Yan J (2017) Turn-on fluorescence detection of ascorbic acid with gold nanolcusters. Talanta 165:346–350
Frajese GV, Benvenuto M, Fantini M, Ambrosin E, Sacchetti P, Masuelli L, Giganti MG, Modesti A, Bei R (2016) Potassium increases the antitumor effects of ascorbic acid in breast cancer cell lines in vitro. Oncol Lett 11(6):4224–4234
Pournaghi-Azar MH, Razmi-Nerbin H, Hafezi B (2001) Amperometric determination of ascorbic acid in real samples using an aluminum electrode, modified with nickel Hexacyanoferrate films by simple Electroless dipping method. Electroanal 14(3):206–212
Ntei Abudu JJM, Attaelmannan M, Levinson SS (2004) Vitamins in human arteriosclerosis with emphasis on vitamin C and vitamin E. Clin Chim Acta 339:11–25
May JM, Qu ZC (2005) Transport and intracellular accumulation of vitamin C in endothelial cells: relevance to collagen synthesis. Arch Biochem Biophy 434(1):178–186
Xiaomin QIANQZ, Ying ZHANG aYT (2010) Separation/determination of flavonoids and ascorbic acid in rat serum and excrement by capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection. Anal Sci 26(5):557–560
Khairy M, Mahmoud BG (2016) Copper oxide microstructures with hemisphere pineapple morphology for SelectiveAmperometric determination of vitamin C(L-ascorbic acid) in human fluids. Electroanal 28(10):2606–2612
Lima DRS, Cossenza M, Garcia CG, Portugal CC, Marques FFC, Paes-de-Carvalho R, Pereira Netto AD (2016) Determination of ascorbic acid in the retina during chicken embryo development using high performance liquid chromatography and UV detection. Anal Methods 8:5441–5447
Matsuoka Y, Yamato M, Yamasaki T, Mito F, Yamada K (2012) Rapid and convenient detection of ascorbic acid using a fluorescent nitroxide switch. Free Radical Bio Med 53(11):2112–2118
Danyang Ji YD, Meng H, Lin Z, Huanga Z, Hu Y, Jianjun Li FY, Li Z (2018) A novel colorimetric strategy for sensitive and rapid sensing of ascorbic acid using cobalt oxyhydroxide nanoflakes and 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 256:512–519
Nuo Duan SW, Dai S, Miao T, Jie Chen ZW (2015) Simultaneous detection of pathogenic bacteria using an aptamer based biosensor and dual fluorescence resonance energy transfer from quantum dots to carbon nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:917–923
Matsuoka Y, Yamato M, Yamada K (2016) Fluorescence probe for the convenient and sensitive detection of ascorbic acid. J Clin Biochem Nutr 58:16–22
Feng LL, Wu YX, Zhang DL, Hu XX, Zhang J, Wang P, Song ZL, Zhang XB, Tan W (2017) Near infrared graphene quantum dots-based two-photon Nanoprobe for direct bioimaging of endogenous ascorbic acid in living cells. Anal Chem 89(7):4077–4084
Tran Van Tam NBT, Kim HR, Chung JS, Choi WM (2014) One-pot synthesis of N-doped graphene quantum dots as a fluorescent sensing platform for Fe3+ ions detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 202:568–573
IGa PMC a, Yate b L, Zaera RT, Cabanero G, Grande HJ, Ruiz V (2016) Graphene quantum dot membranes as fluorescent sensing platforms for Cr (VI) detection. Carbon 109:658–665
Li N, Than A, Wang X, Xu S, Sun L, Duan H, Xu C, Chen P (2016) Ultrasensitive profiling of metabolites using tyramine-functionalized graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 10(3):3622–3629
Weng CI, Chang HT, Lin CH, Shen YW, Unnikrishnan B, Li YJ, Huang CC (2015) One-step synthesis of biofunctional carbon quantum dots for bacterial labeling. Biosens Bioelectron 68:1–6
He J, Zhang H, Zou J, Liu Y, Zhuang J, Xiao Y, Lei B (2016) Carbon dots-based fluorescent probe for "off-on" sensing of hg(II) and I. Biosens Bioelectron 79:531–535
Gong X, Liu Y, Yang Z, Shuang S, Zhang Z, Dong C (2017) An "on-off-on" fluorescent nanoprobe for recognition of chromium(VI) and ascorbic acid based on phosphorus/nitrogen dual-doped carbon quantum dot. Analy Chim Acta 968:85–96
Zhisheng Wu MF, Chen X, Tang X (2016) N-dots as a photoluminescent probe for the rapid and selective detection of Hg2+ and ag+ in aqueous solution. J Mater Chem B 4:2086
Sen Liao FZ, Zhao X, Yang H, Chen X (2018) A reusable P, N-doped carbon quantum dot fluorescent sensor for cobalt ion. Sensors Actuators B Chem 260:156–164
Siriwardana K, Nettles CB 2nd, Vithanage BC, Zhou Y, Zou S, Zhang D (2016) On-resonance fluorescence, resonance Rayleigh scattering, and Ratiometric resonance synchronous spectroscopy of molecular- and quantum dot-fluorophores. Anal Chem 88(18):9199–9206
Tang L, Ji R, Cao X, Lin J, Jiang H, Li X, Teng KS, Luk CM, Zeng S, Hao J, Lau SP (2012) Deep ultraviolet photoluminescence of water-soluble self-passivated graphene quantum dots. ACS Nano 6:5102–5110
Liu R, Wu D, Feng X, Mullen K (2011) Bottom-up fabrication of photoluminescent graphene quantum dots with uniform morphology. J Am Chem Soc 133(39):15221–15223
Mehta VN, Jha S, Basu H, Singhal RK, Kailasa SK (2015) One-step hydrothermal approach to fabricate carbon dots from apple juice for imaging of mycobacterium and fungal cells. Sensors Actuators B Chem 213:434–443
Jiang K, Zhang L, Lu J, Xu C, Cai C, Lin H (2016) Triple-mode emission of carbon dots: applications for advanced anti-counterfeiting. Angew Chem 55(25):7231–7235
Dong Sun RB, Zhang P-H, Wu G-H, Zhang J-R, Zhu J-J (2013) Hair fiber as a precursor for synthesizing of sulfur- and nitrogen-co-doped carbon dots with tunable luminescence properties. Sci Direct 64:424–434
DSa W-JN, Zhu R-H, Deng S-Y, Cosnier S, Zhang X-J (2016) Dumbbell-shaped carbon quantum dots/AuNCs nanohybrid as an efficient ratiometric fluorescent probe for sensing cadmium (II) ions and L-ascorbic acid. Carbon 96:1034–1042
Zhongqian Song FQ, Xu Y, Liu M, Cui L, Liu J (2016) Multifunctional N,S co-doped carbon quantum dots with pH- and thermo-dependent switchable fluorescent properties and highly selective detection of glutathione. Carbon 104:169–178
Jiang K, Sun S, Zhang L, Wang Y, Cai C, Lin H (2015) Bright-yellow-emissive N-doped carbon dots: preparation, cellular imaging, and bifunctional sensing. ACS Appl Mater Inter 7(41):23231–23238
Hou J, Wang W, Zhou T, Wang B, Li H, Ding L (2016) Synthesis and formation mechanistic investigation of nitrogen-doped carbon dots with high quantum yields and yellowish-green fluorescence. Nanoscale 8(21):11185–11193
Wei Li MZ, Li H, Wang K, Cheng S, Jiang K (2015) A high performance sulfur-doped disordered carbon anode for sodium ion batteries. Energ Environ Sci 8:2916
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21571191 and No. 51674292) and Key Laboratory of Hunan Province for Water Environment and Agriculture Product Safety (2018TP1003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 2092 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, K., Jiang, X. Fluorescent Carbon Quantum Dots with Fe(III/II) Irons as Bridge for the Detection of Ascorbic Acid and H2O2. J Fluoresc 29, 769–777 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-019-02395-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-019-02395-z