Abstract
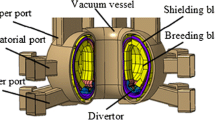
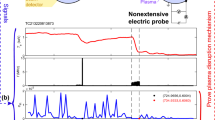
The magnitude of the damaging effects on the vacuum vessel (VV) components caused by the plasma disruptions increases with the quantity of the thermal energy and poloidal magnetic energy dissipated inside the VV. This paper focuses on the poloidal magnetic energy flow across the VV during the plasma disruptions in J-TEXT tokamak, which helps to calculate the quantity of the magnetic energy dissipated inside the VV (W dis ). The value of W dis can be used to evaluate the relevant damage. W dis equals the initial magnetic energy stored inside the VV before disruption (W ini ) plus the magnetic energy flowing into the VV during disruption (ΔW flow ). W ini is calculated by a Maxwell simulation model while ΔW flow is measured based on the Poynting theory. W ini takes 52 % of the total magnetic energy (W tot ) while ΔW flow takes 43.3 % according to the measurement results, leading to 95.3 % of the W tot dissipating inside the VV during disruption. The characteristic of the magnetic energy flow and its analyzing method in J-TEXT provide reference for the other fusion devices.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
ITER Physics Expert Group on Disruptions, Plasma control, and MHD. Nucl. Fusion 39, 2253 (1999)
T.C. Hender et al., Chapter 3: MHD stability, operational limits and disruptions. Nucl. Fusion 47(6), S128–S202 (2007)
J.I. Paley et al., Energy flow during disruptions in JET. J. Nucl. Mater. 337–339, 702–706 (2005)
Yu.L. Igitkhanov et al., Conversion of magnetic energy of runaway electrons during disruption termination. Contrib. Plasma Phys. 54(4–6), 585–590 (2014)
A. Loarte et al., Magnetic energy flows during the current quench and termination of disruptions with runaway current plateau formation in JET and implications for ITER. Nucl. Fusion 51, 073004 (2011)
A.W. Hyatt, et al., Magnetic and thermal energy flow during disruptions in DIII-D, in Proceedings of 23rd European Conference on Controlled Fusion and Plasma Physics (Kiev, Ukraine, vol. 20C, 1996) (Petit-Lancy: European Physical Society)
G. Zhuang et al., Recent research work on the J-TEXT tokamak. Nucl. Fusion 53, 104014 (2013)
Z. Ge et al., Reconstruction of the TEXT-U Tokamak in China. Plasma Sci. Technol. 11, 439 (2009)
J. Chen, G. Zhuang et al., Equilibrium reconstruction based on core magnetic measurement and its applications on equilibrium transition in Joint-TEXT tokamak. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 85, 103501 (2014)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the National ITER Project of China (No. 2013GB113003) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST: cx-15-061.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Zhang, J., Rao, B. et al. The Magnetic Energy Flow During Plasma Disruptions in J-TEXT. J Fusion Energ 34, 1411–1416 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-015-9985-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10894-015-9985-5