Abstract
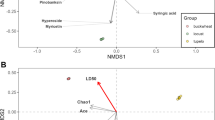
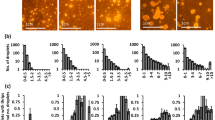
Determination of the safety of agents prior to release is one of the most important research goals in biological control. In addition to concerns for the safety of non-target plants, determination of the potential toxic properties of new agents needs to be assessed. Numerous phytophagous insects are defended by chemicals against the attack of natural enemies. Some of these defensive compounds could pose an environmental risk if an agent is released. Here, larval populations of two pergid sawflies, Heteroperreyia hubrichi and H. jorgenseni, were analyzed by LC-MS/MS to investigate whether they contain alleged toxic peptides. The first species is a potential candidate for biological control of the invasive weed Brazilian peppertree in Florida and Hawaii. The chemical analyses revealed the presence of the peptides pergidin (Perg), 4-valinepergidin (VPerg), dephosphorylated pergidin (dpPerg), lophyrotomin (LGln and LGlu). The effect of sawfly population for each species was significantly influencing peptide concentration. All peptides occurred at lower concentrations compared with purportedly toxic species of this sawfly family. However, the concentrations of the peptides are of concern for the welfare of wildlife and livestock that would be exposed to these species. These results demonstrate that release of this biological control agent in the invaded range may pose an environmental threat.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boevé J-L, Rozenberg R, Shinohara A, Schmidt S (2014) Toxic peptides occur frequently in pergid and argid sawfly larvae. PLoS One 9(8):e105301. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0105301
Cuda JP, Habeck DH, Hight SD, et al (2004) Brazilian Peppertree. In: Combs EM, Clark JK, Piper GL, Cofrancesco jr. AF (eds) Biological Control of Invasive Plants in the United States. Oregon State University Press, Corvallis, Oregon, pp 439–441
Cuda JP, Medal JC, Vitorino MD, Habeck DH (2005) Supplementary host specificity testing of the sawfly Heteroperryia hubrichi, a candidate for classical biological control of Brazilian peppertree, Schinus terebinthifolius, in the USA. BioControl 50:195–201. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-004-0459-3
Dittrich RL, Macedo JHP, Cuda J, Biondo AW (2004) Brazilian peppertree sawfly larvae toxicity in bovines. Vet Clin Pathol 33:191. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1939-165X.2001.tb00424.x
Dutra F, Riet-Correa F, Mendez MC, Paiva N (1997) Poisoning of cattle and sheep in Uruguay by sawfly (Perreyia flavipes) larvae. Vet Hum Toxicol 39:281–286
Ewel J (1986) Invasibility: lessons from South Florida. In: Mooney HA, Drake JA (eds) Ecology of biological invasions of North America and Hawaii, Mooney. H. Springer-Verlag, New York, pp 214–230
Gann GD, Bradley K, Woodmansee SW (2018) Floristic inventory of South Florida database online. In: Inst. Reg. Conserv. Delray Beach, Florida. http://regionalconservation.org/ircs/database/database.asp
Hight SD, Horiuchi I, Vitorino MD, Wikler C, Pedrosa-Macedo JH (2003) Biology, host specificity tests, and risk assessment of the sawfly Heteroperreyia hubrichi, a potential biological control agent of Schinus terebinthifolius in Hawaii. Biocontrol Sci Tech 48:461–476
Le Bourgeois T, Baret S, de Chenon RD (2011) Biological control of Rubus alceifolius (Rosaceae) in La Réunion Island (Indian Ocean): from investigations on the plant to the release of the biological control agent Cibdela janthina (Argidae). In: XIII International Symposium on Biological Control of Weeds - 2011. pp 153–160
MacLeod JK, Braybrook C, Simmonds PM, Oelrichs PB (2000) A unique toxic peptide from the larvae of the south American sawfly, Perreyia flavipes. Aust J Chem 53:293–297
Mathieu A, Dumont Y, Chiroleu F et al (2014) Predicting the altitudinal distribution of an introduced phytophagous insect against an invasive alien plant from laboratory controlled experiments: case of Cibdela janthina (Hymenoptera: Argidae) and Rubus alceifolius (Rosaceae) in La Réunion. BioControl 59:461–471. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10526-014-9574-y
Mc Kay F, Oleiro M, Cabrera Walsh G et al (2009) Natural enemies of Brazilian peppertree (Sapindales: Anacardiaceae) from Argentina: their possible use for biological control in the USA. Fla Entomol 92:292–303. https://doi.org/10.1653/024.092.0213
Medal JC, Vitorino MD, Habeck DH et al (1999) Host specificity of Heteroperreyia hubrichi malaise (Hymenoptera: Pergidae), a potential biological control agent of Brazilian peppertree (Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi). Biol Control 14:60–65. https://doi.org/10.1006/bcon.1998.0670
Mytinger L, Williamson GB (1987) The invasion of Schinus into saline communities of Everglades National Park. Florida Scientist 50:7–12
Oelrichs PB, MacLeod JK, Seawright AA et al (1999) Unique toxic peptides isolated from sawfly larvae in three continents. Toxicon 37:537–544
Oelrichs PB, MacLeod JK, Seawright AA, Grace PB (2001) Isolation and identification of the toxic peptides from Lophyrotoma zonalis (Pergidae) sawfly larvae. Toxicon 39:1933–1936
Raymundo DL, Bezerra PS, Bandarra PM et al (2008) Spontaneous poisoning by larvae of Perreyia flavipes (Pergidae) in sheep. Pesqui Vet Bras 28:19–22. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-736X2008000100003
Rodgers L, Pernas T, Hill SD (2014) Mapping invasive plant distributions in the Florida everglades using the digital aerial sketch mapping technique. Invasive Plant Science and Management 7:360–374
Schmidt S, Smith DR (2018) Pergidae of the world – an online catalogue of the sawfly family Pergidae (Insecta, Hymenoptera, Symphyta). In: World Wide Web Electron. Publ. http://pergidae.snsb-zsm.de. Accessed 25 Jul 2016
Schmitz DC, Simberloff D, Hofstetter RL et al (1997) The ecological impact of nonindigenous plants. In: Simberloff D, Schmitz DC, Brown TC (eds) Strangers in paradise: impact and management of nonindigenous species in Florida. Island Press, Washington, DC, pp 39–61
Smith DR (1990) A synopsis of the sawflies (Hymenoptera, Symphyta) of America south of the United States: Pergidae. Revista Brasileira de Entomologia 34:7–200
Taeger A, Blank SM, Liston AD (2010) World catalog of Symphyta (Hymenoptera). Zootaxa 2580:1–1064
Thamsborg SM, Jørgensen RJ, Brummerstedt E (1987) Sawfly poisoning in sheep and goats. Vet Rec 121:253–255
Wheeler G, Mc Kay F, Vitorino M et al (2016) Biological control of the invasive weed, Brazilian peppertree, Schinus terebinthifolia: a review of the project with an update on the proposed agents. Southeast Nat 15:15–34
Yoshioka ER, Markin GP (1991) Efforts of biological control of Christmas berry Schinus terebinthifolius in Hawaii. In: Center TD, Doren RF, Hofstetter RL, et al. (eds) Proceedings of the Symposium on Exotic Pest Plants. pp 377–385
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank K. Dyer, S. Hight (USDA-ARS) and Frederik Hendrickx (Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences, RBINS) for assistance, as well as two anonymous reviewers for comments on the manuscript. This project was partially funded by the RBINS, the Florida Fish and Wildlife Conservation Commission (#08250, TA:088), and the United States Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. We also thank the Ministry of Ecology of Misiones Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boevé, JL., Rozenberg, R., Mc Kay, F. et al. Toxic Peptides in Populations of Two Pergid Sawflies, Potential Biocontrol Agents of Brazilian Peppertree. J Chem Ecol 44, 1139–1145 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-018-1021-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10886-018-1021-6