Abstract
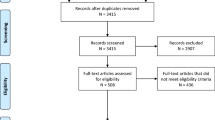
The main objective of this systematic review is to assess the reliability of alternative positions of processed electroencephalogram sensors for depth of anesthesia monitoring and its applicability in clinical practice. A systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, Clinical trial.gov in accordance with reporting guidelines of PRISMA statement together with the following sources: Google and Google Scholar. We considered eligible prospective studies, written in the English language. The last search was run on the August 2023. Risk of bias and quality assessment were performed. Data extraction was performed by two authors and results were synthesized narratively owing to the heterogeneity of the included studies. Thirteen prospective observational studies (438 patients) were included in the systematic review after the final assessment, with significant diversity in study design. Most studies had a low risk of bias but due to lack of information in one key domain of bias (Bias due to missing data) the overall judgement would be No Information. However, there is no clear indication that the studies are at serious or critical risk of bias. Bearing in mind, the heterogeneity and small sample size of the included studies, current evidence suggests that the alternative infraorbital sensor position is the most comparable for clinical use when the standard sensor position in the forehead is not possible.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Shafer SL, Stanski DR. Defining depth of anesthesia. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2008;182:409–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-74806-9_19.
Sleigh JW. Depth of anesthesia: perhaps the patient isn’t a submarine. Anesthesiology. 2011;115(6):1149–50. https://doi.org/10.1097/aln.0b013e3182390396.
Shander A, Lobel GP, Mathews DM. Brain monitoring and the depth of anesthesia: another goldilocks dilemma. Anesth Analg. 2018;126(2):705–9. https://doi.org/10.1213/ANE.0000000000002383.
Lobo FA, Shander A. Modern anesthetic noninvasive monitoring: a deep look into perioperative care. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2019;33(Suppl 1):S1–2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jvca.2019.03.037.
Li Y, Bohringer C, Liu H. Double standard: why electrocardiogram is standard care while electroencephalogram is not? Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2020;33(5):626–32. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000902.
Sepúlveda PO, Vera R, Fernández MS, Lobo FA. Linear thinking does not reflect the newer 21st-century anesthesia concepts. A narrative review. J Clin Monit Comput. 2023;37(5):1133–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-023-01021-5.
Zanner R, Pilge S, Kochs EF, Kreuzer M, Schneider G. Time delay of electroencephalogram index calculation: analysis of cerebral state, bispectral, and Narcotrend indices using perioperatively recorded electroencephalographic signals. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103(3):394–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aep198.
Dahaba AA. Different conditions could result in the bispectral index indicating an incorrect hypnotic state. Anesth Analg. 2005;101(3):765–73. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000167269.62966.af.
Lobo FA, Schraag S. Limitations of anaesthesia depth monitoring. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2011;24(6):657–64. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0b013e32834c7aba.
Buzsáki G, Anastassiou CA, Koch C. The origin of extracellular fields and currents–EEG, ECoG. LFP and spikes Nat Rev Neurosci. 2012;13(6):407–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn3241.
Blum, Rutkove SB. The clinical neurophysiology primer edited by Andrew S. Blum, Seward B. Rutkove. Humana. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-271-7
Fisch BJ. Fisch and Spehlmann EEG primer: basic principles of digital and analog EEG. 3rd ed. Elsevier Science B.V. 1999.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 2021;372:n71. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.n71.
International prospective register of systematic reviews, PROSPERO, Available from https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/. Accessed 6 July 2022.
Sterne JAC, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, et al. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomized studies of interventions. BMJ. 2016;355:4919. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i4919.
Moola S, Munn Z, Tufanaru C, Aromataris E, Sears K, et al. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In: Aromataris E, Munn Z, editors. Joanna Briggs Institute Reviewer’s Manual. The Joanna Briggs Institute. 2017. Available from https://reviewersmanual.joannabriggs.org/. Accessed 6 July 2022.
Gagnier JJ, Kienle G, Altman DG, Moher D, Sox H, Riley D. The CARE guidelines: consensus-based clinical case reporting guideline development. Headache: J Head Face Pain. 2013;53(10):1541–7.
Kim YS, Lim BG, Lee IO. False elevation of bispectral index with a mandibular position in a patient undergoing craniotomy. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2014;26(3):265–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANA.0000000000000011.
Ayub A, Balakrishnan I, Lalwani P, Rath GP. Index of consciousness monitoring is possible with placement of electrodes in the occipital region J Neuroanaesth. Crit Care. 2014;01(02):153–4. https://doi.org/10.4103/2348-0548.130413.
Sinha PK, Suneel PR, Unnikrishnan KP, Smita V, Rathod RC. An alternative site for entropy sensor placement. Anesth Analg. 2006;102(4):1291.
Hemmerling TM, Deschamps S, Michaud G, Trager G. An unusual site for BIS monitoring. Anesth Analg. 2004;99(4):1264–5. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ANE.0000133945.35317.4B.
Dubey JK, Goel N, Chawla R, Gupta M, Bhardwaj M. Supralabial site: an alternative site for bispectral index monitoring: a cross-sectional study. J Neuroanaesthesiol Crit Care. 2022;9(3):149–54. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-1756430.
Tufegdzic B, Lamperti M, Khozenko A, Achi E, Jayaprakasam S, St John TL. Validation of a nasal SedLine® sensor placement: Going beyond the forehead when depth of anesthesia is important. Interdiscip Neurosurg. 2021;26:101310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.inat.2021.101310.
Romito JW, Folefac DA, Manjunath A, Yang A, Romito BT, et al. Comparison of bispectral index monitor data between standard frontal-temporal position and alternative nasal dorsum position in the intensive care unit: a pilot study. J Neurosci Nurs. 2022;54(1):30–4. https://doi.org/10.1097/JNN.0000000000000635.
Hajiyeva K, Meco BC, Guclu CY, Yorukoglu D, Doganay B, et al. Comparison of nasal and frontal BIS monitoring in neurosurgery: does the site of sensor placement affect the BIS values? Int J Clin Med. 2021;12:108–14. https://doi.org/10.4236/ijcm.2021.123012.
Vachnadze DI, Akselrod BA, Guskov DA, Goncharova AV. Anesthesia depth monitoring using alternative placement of entropy sensors: a prospective study. J Clin Monit Comput. 2019;33(5):871–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-018-00238-z.
Puente-Barbas JA, Navarro-Suay R, Gutiérrez-Ortega C, Gilsanz-Rodríguez F. Comparative study of concordance between bispectral index recordings obtained from the standard frontal and infra-orbital sensor position. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2018;35(9):714–6. https://doi.org/10.1097/EJA.0000000000000795.
Akavipat P, Hungsawanich N, Jansin R. Alternative placement of bispectral index electrode for monitoring depth of anesthesia during neurosurgery. Acta Med Okayama. 2014;68(3):151–5. https://doi.org/10.18926/AMO/52655.
Brigid JB. The acceptability of auricular versus frontal Bispectral Index Values. BJA: British J Anaesthesia 113(eLetters Supplement): No Pagination Specified. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/el_11327
Lee SY, Kim YS, Lim BG, Kim H, Kong MH, Lee IO. Comparison of bispectral index scores from the standard frontal sensor position with those from an alternative mandibular position. Korean J Anesthesiol. 2014;66(4):267–73. https://doi.org/10.4097/kjae.2014.66.4.267.
Nelson P, Nelson JA, Chen AJ, Kofke WA. An alternative position for the BIS-Vista montage in frontal approach neurosurgical cases. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2013;25(2):135–42. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANA.0b013e31826ca3a0.
Dahaba AA, Xue JX, Zhao GG, Liu QH, Xu GX, et al. BIS-vista occipital montage in patients undergoing neurosurgical procedures during propofol-remifentanil anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2010;112(3):645–51. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181cf4111.
Horiuchi T, Kawaguchi M, Kurita N, Inoue S, Furuya H. The validity of bispectral index values from a dislocated sensor: a comparison with values from a sensor located in the commercially recommended position. Anesth Analg. 2007;104(4):857–9. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ane.0000258764.37968.bb.
Shiraishi T, Uchino H, Sagara T, Ishii N. A comparison of frontal and occipital bispectral index values obtained during neurosurgical procedures. Anesth Analg. 2004;98(6):1773–5. https://doi.org/10.1213/01.ANE.0000121344.69058.09.
McGuinness LA, Higgins JPT. Risk-of-bias VISualization (robvis): An R package and Shiny web app for visualizing risk-of-bias assessments. Res Syn Meth. 2020;12:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.1411.
Seeck M, Koessler L, Bast T, Leijten F, Michel C, et al. The standardized EEG electrode array of the IFCN. Clin Neurophysiol. 2017;128(10):2070–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2017.06.254.
Kochs E, Bischoff P, Pichlmeier U, Schulte am Esch J. Surgical stimulation induces changes in brain electrical activity during isoflurane/nitrous oxide anesthesia A topographic electroencephalographic analysis. Anesthesiology. 1994;80(5):1026–34. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-199405000-00012.
Bruhn J, Bouillon TW, Shafer SL. Electromyographic activity falsely elevates the bispectral index. Anesthesiology. 2000;92(5):1485–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-200005000-00042.
Schuller PJ, Newell S, Strickland PA, Barry JJ. Response of bispectral index to neuromuscular block in awake volunteers. British J Anaesthesia. 2015;115(1):95–103. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aev072.
Zanner R, Pilge S, Kochs EF, Kreuzer M, Schneider G. Time delay of electroencephalogram index calculation: analysis of cerebral state, bispectral, and Narcotrend indices using perioperatively recorded electroencephalographic signals. Br J Anaesth. 2009;103(3):394–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aep198.
Abdelrahman AMF, Elbadry AA, Omara AF. Comparison of post-auricular and frontal bispectral index values obtained during renal surgeries. BMC Anesthesiol. 2023;23(1):417. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-023-02372-x.
Isik OG, Chauhan V, Ahmed MT, Chang BA, Cassim TZ, et al. Alternate electrode placements to facilitate frontal electroencephalography monitoring in anesthetized and critically Ill patients. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 2024. ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1097/ANA.0000000000000955
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge Philip Anderson for his contribution to the grammar and spelling revision of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the authorship and publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions to the study and manuscript preparation include the following. Conception and design: all authors; Drafting the article: all authors; Data collection: Saba Motta; Critically revising the article: all authors; Reviewed submitted version of manuscript: all authors; Approved the final version of the manuscript on behalf of all authors: Boris Tufegdzic; Study supervision: Boris Tufegdzic.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics and dissemination
The proposed systematic review does not require ethical approval, as it is conducted at the study level and does not involve individual patient-level data. Results will be disseminated by data sharing via academically established means, presentation at local and national scientific meetings and publication as a peer-reviewed manuscript.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tufegdzic, B., Lobo, F., Achi, E. et al. Alternative sensor montage for Index based EEG monitoring. A systematic review. J Clin Monit Comput (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-024-01162-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-024-01162-1