Abstract
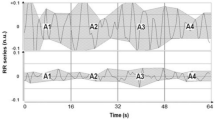
Hypnosis has shown an effect on the regulation of the autonomic nervous system by increasing parasympathetic activity. The Analgesia/Nociception Index (ANI) is derived from heart rate variability and represents the relative parasympathetic tone. We investigated the effects of hypnosis on ANI in healthy volunteers. Participants to the 2016 International Hypnosis congress, Saint Malo, France were recruited in this prospective observational study. After comfortable positioning of the subject in the sitting position (T0), the hypnotic trance was induced (T1) then conducted with suggestions of comfort (T2) before return to normal consciousness (T3). The ANI, heart rate (HR) and respiratory rate (RR) were recorded at the different time-points. Forty subjects were enrolled (31 women, 9 men). The mean ± SD ANI at T2 (84 ± 12) was significantly greater than at T0 (60 ± 10), T1 (62 ± 9) and T3 (59 ± 11). The median [25th–75th percentile] ANI values at T2 were significantly greater in women (90 [83–95]) than in men (74 [68–83]). There were no significant variations of HR during time. The median [25th–75th percentile] RR at T1 (16 [14–18] breaths/min) and T2 (14 [12–16] breaths/min) were significantly smaller than at T0 (18 [16–20] breaths/min) and T3 (18 [16–20] breaths/min). This study shows that hypnosis induces an increase in the relative parasympathetic tone assessed by ANI in healthy volunteers, with greater ANI values observed in women. These results suggest that ANI monitoring may provide an objective tool for the measurement of the intensity of the hypnotic process, although this should be confirmed by further studies.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Montgomery GH, David D, Winkel G, Silverstein JH, Bovbjerg DH. The effectiveness of adjunctive hypnosis with surgical patients: a meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 2002;94:1639–45.
Saadat H, Drummond-Lewis J, Maranets I, Kaplan D, Saadat A, Wang SM, Kain ZN. Hypnosis reduces preoperative anxiety in adult patients. Anesth Analg. 2006;102:1394–6.
Stoelb BL, Molton IR, Jensen MP, Patterson DR. The efficacy of hypnotic analgesia in adults: a review of the literature. Contemp Hypn. 2009;26:24–39.
Tefikow S, Barth J, Maichrowitz S, Beelmann A, Strauss B, Rosendahl J. Efficacy of hypnosis in adults undergoing surgery or medical procedures: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Psychol Rev. 2013;33:623–36.
Lang EV, Benotsch EG, Fick LJ, Lutgendorf S, Berbaum ML, Berbaum KS, Logan H, Spiegel D. Adjunctive non-pharmacological analgesia for invasive medical procedures: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2000;355:1486–90.
Kendrick C, Sliwinski J, Yu Y, Johnson A, Fisher W, Kekecs Z, Elkins G. Hypnosis for acute procedural pain: a critical review. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2016;64:75–115.
Vanhaudenhuyse A, Laureys S, Faymonville ME. Neurophysiology of hypnosis. Neurophysiol Clin. 2014;44:343–53.
DeBenedittis G, Cigada M, Bianchi A, Signorini MG, Cerutti S. Autonomic changes during hypnosis: a heart rate variability power spectrum analysis as a marker of sympatho-vagal balance. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 1994;42:140–52.
Aubert AE, Verheyden B, Beckers F, Tack J, Vandenberghe J. Cardiac autonomic regulation under hypnosis assessed by heart rate variability: spectral analysis and fractal complexity. Neuropsychobiology. 2009;60:104–12.
Yüksel R, Ozcan O, Dane S. The effects of hypnosis on heart rate variability. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2013;61:162–71.
Diamond SG, Davis OC, Howe RD. Heart-rate variability as a quantitative measure of hypnotic depth. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2008;56:1–18.
Boselli E, Bouvet L, Allaouchiche B. Analgesia monitoring using Analgesia/Nociception Index: results of clinical studies in awake and anesthetized patients. Le Praticien en Anesthésie Réanimation. 2015;19:78–86.
Boselli E, Daniela-Ionescu M, Bégou G, Bouvet L, Dabouz R, Magnin C, Allaouchiche B. Prospective observational study of the non-invasive assessment of immediate postoperative pain using the analgesia/nociception index (ANI). Br J Anaesth. 2013;111:453–9.
De Jonckheere J, Logier R, Jounwaz R, Vidal R, Jeanne M. From pain to stress evaluation using heart rate variability analysis: development of an evaluation platform. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:3852–5.
De Jonckheere J, Rommel D, Nandrino J, Jeanne M, Logier R. Heart rate variability analysis as an index of emotion regulation processes: interest of the Analgesia Nociception Index (ANI). Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2012;2012:3432–5.
Boselli E, Musellec H, Bernard F, Guillou N, Hugot P, Augris-Mathieu C, Diot-Junique N, Bouvet L, Allaouchiche B. Effects of conversational hypnosis on relative parasympathetic tone assessed by Analgesia/Nociception Index (ANI) and on patient comfort during axillary brachial plexus blocks for ambulatory upper limb surgery: a quasiexperimental pilot study. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2017 (in press).
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ, Gøtzsche PC, Vandenbroucke JP. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. Lancet. 2007;370:1453–7.
Barabasz A, Barabasz M. Induction technique: beyond simple response to suggestion. Am J Clin Hypn. 2016;59:204–13.
Musellec H, Bernard F, Houssel P, Guillou N, Hugot P, Martin L, Hamelin H, Lanchou J, Gentili ME, Devins C, Virot C. Ambulatory Essure implant placement sterilization procedure for women: prospective study comparing general anesthesia versus hypnosis combined with sedation. Ann Fr Anesth Réanim. 2010;29:889–96.
Logier R, Jeanne M, De Jonckheere J, Dassonneville A, Delecroix M, Tavernier B. PhysioDoloris: a monitoring device for analgesia/nociception balance evaluation using heart rate variability analysis. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:1194–7.
De Jonckheere J, Bonhomme V, Jeanne M, Boselli E, Gruenewald M, Logier R, Richebé P. Physiological signal processing for individualized anti-nociception management during general anesthesia: a review. Yearb Med Inform. 2015;10:95–101.
Jeanne M, Clement C, De Jonckheere J, Logier R, Tavernier B. Variations of the analgesia nociception index during general anaesthesia for laparoscopic abdominal surgery. J Clin Monit Comput. 2012;26:289–94.
Boselli E, Bouvet L, Bégou G, Dabouz R, Davidson J, Deloste JY, Rahali N, Zadam A, Allaouchiche B. Prediction of immediate postoperative pain using the analgesia/nociception index: a prospective observational study. Br J Anaesth. 2014;112:715–21.
Boselli E, Bouvet L, Bégou G, Torkmani S, Allaouchiche B. Prediction of hemodynamic reactivity during total intravenous anesthesia for suspension laryngoscopy using Analgesia/Nociception Index (ANI): a prospective observational study. Minerva Anestesiol. 2015;81:288–97.
Boselli E, Logier R, Bouvet L, Allaouchiche B. Prediction of hemodynamic reactivity using dynamic variations of Analgesia/Nociception Index (ANI). J Clin Monit Comput. 2016;30:977–84.
Jess G, Pogatzki-Zahn EM, Zahn PK, Meyer-Frieem CH. Monitoring heart rate variability to assess experimentally induced pain using the analgesia nociception index: a randomised volunteer study. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2015;33:118–25
Page RA, Green JP. An update on age, hypnotic suggestibility, and gender: a brief report. Am J Clin Hypn. 2007;49:283–7.
Gruenewald M, Ilies C, Herz J, Schoenherr T, Fudickar A, Hocker J, Bein B. Influence of nociceptive stimulation on analgesia nociception index (ANI) during propofol-remifentanil anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2013;110:1024–30.
Jeanne M, Delecroix M, De Jonckheere J, Keribedj A, Logier R, Tavernier B. Variations of the analgesia nociception index during propofol anesthesia for total knee replacement. Clin J Pain. 2014;30:1084–8.
Le Guen M, Jeanne M, Sievert K, Al Moubarik M, Chazot T, Laloe PA, Dreyfus JF, Fischler M. The Analgesia Nociception Index: a pilot study to evaluation of a new pain parameter during labor. Int J Obstet Anesth. 2012;21:146–51.
Ledowski T, Tiong WS, Lee C, Wong B, Fiori T, Parker N. Analgesia nociception index: evaluation as a new parameter for acute postoperative pain. Br J Anaesth. 2013;111:627–9.
Kekecs Z, Bowers J, Johnson A, Kendrick C, Elkins G. The Elkins Hypnotizability Scale: assessment of reliability and validity. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2016;64:285–304.
Funding
The study was funded by institutional sources only. Three ANI monitors® were loaned ex gratia by MDoloris Medical Systems (Lille, France) for the duration of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Emmanuel Boselli has received travel grants and speaker honorarium form MDoloris Medical Systems (Lille, France). Hervé Musellec, Laure Martin, Franck Bernard, Nicolas Fusco, Nicolas Guillou, Pierre Hugot, Xavier Paqueron, Thomas Yven and Claude Virot declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boselli, E., Musellec, H., Martin, L. et al. Effects of hypnosis on the relative parasympathetic tone assessed by ANI (Analgesia/Nociception Index) in healthy volunteers: a prospective observational study. J Clin Monit Comput 32, 487–492 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-017-0056-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-017-0056-5