Abstract
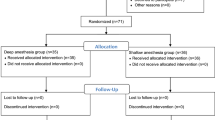
Previous studies have shown that sugammadex decreases the anesthetic depth when administered to reverse the neuromuscular blockade produced by rocuronium/vecuronium. The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of sugammadex alone on anesthetic depth and hemodynamics. Sixty patients scheduled for abdominal surgery participated in the study. Anesthesia was induced with thiopental/fentanyl and maintained with N2O/oxygen and sevoflurane concentrations adjusted to maintain Entropy and Bispectral Index (BIS) values between 40 and 50. Cis-atracurium 0.2 mg/kg was administered for neuromuscular blockade which was monitored with a TOF-Watch® SX acceleromyograph. State entropy (SE), response entropy (RE), Bispectral Index (BIS), systolic (SAP) and diastolic blood pressure (DAP), heart rate (HR), SpO2, end-tidal CO2 and sevoflurane concentrations were recorded every 3 min intraoperatively. Sugammadex 2 mg/kg (Group-2), 4 mg/kg (Group-4) or 16 mg/kg (Group-16) was given intravenously when a count of two responses of the train-of-four (TOF) or a post-tetanic count (PTC) 1-3 appeared or when no response at all (PTC = 0) was observed, respectively. The overall SE values, thus the primary outcome of the study, were 44 ± 11, 43 ± 10 and 43 ± 11 for Group-2, Group-4 and Group-16, respectively (p = 0.812). Also, the secondary endpoints, namely RE, BIS, SAP and DAP, HR and SpO2 did not differ between the three groups. Comparisons between Group-2 versus Group-4, Group-2 versus Group-16 and Group-4 versus Group-16 showed no differences (p > 0.05) for all the studied variables. Sugammadex alone at low, medium or high clinical doses has no effect on anesthetic depth as assessed by Entropy and BIS or on hemodynamics.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jones RK, Caldwell JE, Brull SJ, Soto RG. Reversal of profound rocuronium-induced blockade with sugammadex. Anesthesiology. 2008;109:816–24.
Aho AJ, Kamata K, Yli-Hankala A, Lyytikainen L-P, Kulkas A, Jantti V. Elevated BIS and Entropy values after sugammadex or neostigmine: an electroencephalographic or electromyographic phenomenon? Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2012;56:465–73.
Dahaba AA, Bornemann H, Hopfgartner E, Ohran M, Kocher K, Liebmann M, Wilfinger G, Metzler H. Effect of sugammadex or neostigmine neuromuscular block reversal on bispectral index monitoring of propofol/remifentanil anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2012;108:602–6.
Sparr HJ, Vermeyen KM, Beaufort AM, Rietbergen H, Proost JH, Saldien V, Velik-Salchner C, Wierda JMKH. Early reversal of profound rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade by sugammadex in a randomized multicenter study efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics. Anesthesiology. 2007;106:935–43.
Forbes AR, Cohen NH, Eger EI. Pancuronium reduces halothane requirement in man. Anesth Analg. 1979;58:497–9.
Lanier WL, Iaizzo PA, Milde JH, Sharbrough FW. The cerebral and systemic effects of movement in response to a noxious stimulus in lightly anesthetized dogs. Possible modulation of cerebral function by muscle afferents. Anesthesiology. 1994;80:392–401.
Illman H, Antila H, Olkkola KT. Reversal of neuromuscular blockade by sugammadex does not affect EEG derived indices of depth of anesthesia. J Clin Monit Comput. 2010;24:371–6.
Dahl V, Pendeville PE, Hollmann MW, Heier T, Abels EA, Blobner M. Safety and efficacy of sugammadex for the reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade in cardiac (heart failure) patients undergoing noncardiac surgery. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2009;26:874–84.
Cammu G, Coart D, De Graeve K, Beelen R. Reversal of rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block with sugammadex in heart failure patients: a prospective observational study. Acta Anaesthesiol Belg. 2012;63:69–73.
Musizza B, Ribaric S. Monitoring the depth of anaesthesia. Sensors. 2010;10:10896–935.
Vasella FC, Frascarolo P, Spahn DR, Magnusson L. Antagonism of neuromuscular blockade but not muscle relaxation affects depth of anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth. 2005;94:742–7.
Ekman A, Fink R, Eriksson L, Brudin L, Sandin R, Sundman E. Neuromuscular block and the electroencephalogram during sevofurane anaesthesia. NeuroReport. 2007;18:1817–20.
Greif R, Greenwald S, Schweitzer E, Laciny S, Rajek A, Caldwell JE, Sessler DI. Muscle relaxation does not alter hypnotic level during propofol anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2002;94:604–8.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Mrs. Aikaterini Dimitriou for helping in the statistical analysis of the data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Registration: ClinTrials.gov NCT01301261.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fassoulaki, A., Chondrogiannis, K. & Staikou, C. Sugammadex at both high and low doses does not affect the depth of anesthesia or hemodynamics: a randomized double blind trial. J Clin Monit Comput 31, 297–302 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-016-9844-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10877-016-9844-6