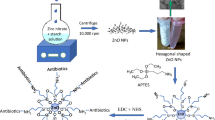
Abstract
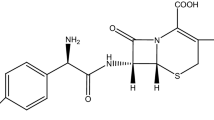
Infections caused by multi-drug resistant Staphylococcus aureus, are considered as a universal health threat. The aim of this study was to synthesize zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles (NPs), functionalization of them by glutamic acid (Glu) and conjugation with thiosemicarbazid (TSC) to enhance their antibacterial effect against ciprofloxacin resistant S. aureus. The synthesized ZnO@Glu–TSC NPs were characterized using energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and transmission electron microscopy. The physicochemical assays confirmed the synthesis of ZnO@Glu–TSC NPs. Antibacterial potential of ZnO@Glu–TSC NPs against S. aureus was investigated using well diffusion, Minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination and checkerboard titration methods. MIC values of functionalized NPs reduced by two to eightfolds against each respected strain in comparison with the ZnO nanoparticles (alone). Our results revealed the synergistic activity of ZnO@Glu–TSC NPs and ciprofloxacin (CIP) against ciprofloxacin resistant S. aureus. In this study, improved antimicrobial activity of ZnO@Glu–TSC NPs and their synergism with CIP against drug resistant S. aureus was observed. Thus, ZnO@Glu–TSC NPs could be regarded as a promising new antibacterial agent to be used for therapeutic and preventive purposes. However, further investigation needs to be performed to evaluate the safety of these NPs for medical applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Patra, S. Mitra, N. Debnath, P. Pramanik, and A. Goswami (2014). Bull. Mater. Sci. 37, 199.
M. R. Hesari, A. Salehzadeh, and R. Darsanaki (2017). Acta Microbiol. Immunol. Hung. 1, 14.
S. H. Zhang, R. X. Zhao, G. Li, H. Y. Zhang, C. L. Zhang, and G. Muller (2014). RSC Adv. 4, 54837.
V. Srivastava, D. Gusain, and Y. C. Sharma (2013). Ceram. Int. 39, 9803.
T. Szabo, J. Nemeth, and I. Dekany (2003). Coll. Surf. A. 230, 23.
L. S. Reddy, M. M. Nisha, M. Joice, and P. N. Shilpa (2014). Pharm. Biol. 52, 1388.
S. Mitra, S. Chandra, D. Laha, P. Patra, N. Debnath, A. Pramanik, P. Pramanik, and A. Goswami (2012). Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 586.
E. Taylor and T. J. Webster (2011). Int. J. Nanomed. 6, 1463.
J. S. Casas, M. S. Garcıa-Tasende, and J. Sordo (2000). Coordin. Chem. Rev. 209, 197.
Q. X. Li, H. A. Tang, Y. Z. Li, M. Wang, L. F. Wang, and C. G. Xia (2000). J. Inorg. Biochem. 78, 167.
H. Barrak, T. Saied, P. Chevallier, G. Laroche, A. M. Nif, and A. H. Hamzaoui (2016). Arab. J. Chem. 1, 1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.04.019.
S. A. S. Shandiz, A. Montazeri, M. Abdolhosseini, S. H. Shahrestani, M. Hedayati, Z. Moradi-Shoeili, and A. Salehzadeh (2018). J. Clust. Sci. 29, 1107.
The Clinical & Laboratory Standards Institute [CLSI] (2015), 76.
L. He, Y. Liu, A. Mustapha, and M. Lin (2011). Microbiol. Res. 166, 207.
S. Chaudhary, Y. Kaur, A. Umar, and G. R. Chaudhary (2016). J. Mol. Liq. 220, 1013.
G. Xiong, U. Pal, J. G. Serrano, K. B. Ucer, and R. T. Williams (2006). Phys. Status Solidi 3, 3577.
D. M. Wiles and T. Suprunchuk (1969). Can. J. Chem. 47, 1087.
L. Jin and Y. Wang (2017). Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 19, 12992.
J. L. Navarrete, V. Hernandez, and F. J. Ramirez (1995). J. Mol. Struct. 348, 249.
K. C. Barick, A. Sharma, N. G. Shetake, R. S. Ningthoujam, R. K. Vatsa, P. D. Babu, B. N. Pandey, and P. A. Hassan (2015). Dalton Trans. 44, 14686.
S. K. Sinha, S. Ram, and O. P. Lamba (1988). Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Spectrosc. 44, 713.
K. R. Raghupathi, R. T. Koodali, and A. C. Manna (2011). Langmuir. 27, 4020.
Y. Xie, Y. He, P. L. Irwin, T. Jin, and X. Shi (2011). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77, 2325.
N. C. Kasuga, K. Sekino, M. Ishikawa, A. Honda, M. Yokoyama, S. Nakano, N. Shimada, C. Koumo, and K. Nomiya (2003). J. Inorg. Biochem. 96, 298.
J. A. Rufian-Henares and S. P. de la Cueva (2009). J. Agric. Food Chem. 57, 432.
Q. X. Li, H. A. Tang, Y. Z. Li, M. Wang, L. F. Wang, and C. G. Xia (2000). J. Inorg. Biochem. 78, 174.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the university of Guilan and Islamic Azad university (Rasht branch) for providing facilities to carry out this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest exist.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nejabatdoust, A., Salehzadeh, A., Zamani, H. et al. Synthesis, Characterization and Functionalization of ZnO Nanoparticles by Glutamic Acid (Glu) and Conjugation of ZnO@Glu by Thiosemicarbazide and Its Synergistic Activity with Ciprofloxacin Against Multi-drug Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Clust Sci 30, 329–336 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-01487-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10876-018-01487-3