Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate mortality risk factors in pediatric-onset common variable immunodeficiency disorders (CVID), we evaluated the largest single-institution cohort of pediatric-onset CVID patients. Previous publications on CVID have provided valuable descriptive data, but lack risk stratification to guide physicians in management of these patients.
Methods
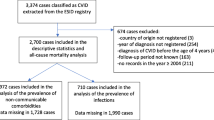
Retrospective chart review of 198 subjects with CVID at a single institution, of whom 91 had disease onset at a pediatric age. Clinical and laboratory data were collected at diagnosis and in follow-up. Odds ratios and Fisher tests were utilized to examine trends. This study was approved by an institutional review board.
Results
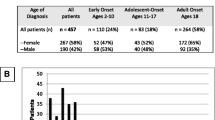
Clinical features and laboratory results for subjects diagnosed with CVID at a pediatric age are similar to those who had adult-onset CVID. However, majority of the deceased subjects (13/18) were at a pediatric age at CVID symptom onset. These subjects had a lower age at mortality, multiple comorbidities, and often depression. The most common cause of death was infection. Lung disease (OR 5, p < 0.05) and infection with severe/opportunistic organisms (OR 9, p < 0.05) are directly related to increased mortality. Delay in diagnosis of CVID is also correlated with mortality. Intermediary markers correlating with mortality include anemia, GERD, and depression.
Conclusions
There are many similarities between patients with pediatric- and adult-onset CVID; however, the mortality of pediatric CVID in our cohort is striking. This is the first study to identify specific factors correlated with mortality in pediatric-onset CVID to guide pediatricians and subspecialists in managing these immunodeficient patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CVID:
-
Common variable immunodeficiency disorders
- ESID:
-
European Society for Immunodeficiencies
- GLILD:
-
Granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease
- GERD:
-
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
- LOCID:
-
Late-onset combined immune deficiency
- MRSA:
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- USIDNET:
-
United States Immunodeficiency Network
- VRE:
-
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus
- IRB:
-
Institutional review board
References
Boyle JM, Buckley RH. Population prevalence of diagnosed primary immunodeficiency diseases in the United States. J Clin Immunol. 2007;27(5):497–502.
Sullivan KE, Boyle M, Nauman E, Carton T. Health care utilization by patients with common variable immune deficiency defined by International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision code 279.06. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015 Sep;115(3):248–50.
Quinti I, Pulvirenti F, Giannantoni P, Hajjar J, Canter DL, Milito C, et al. Development and initial validation of a questionnaire to measure health-related quality of life of adults with common variable immune deficiency: the CVID_QoL questionnaire. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2016;4(6):1169–79 e4.
Tcheurekdjian H, Palermo T, Hostoffer R. Quality of life in common variable immunodeficiency requiring intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2004 Aug;93(2):160–5.
Conley ME, Park CL, Douglas SD. Childhood common variable immunodeficiency with autoimmune disease. J Pediatr. 1986 Jun;108(6):915–22.
Hausser C, Virelizier JL, Buriot D, Griscelli C. Common variable hypogammaglobulinemia in children. Clinical and immunologic observations in 30 patients. Am J Dis Child. 1983;137(9):833–7.
Sanchez LA, Maggadottir SM, Pantell MS, Lugar P, Rundles CC, Sullivan KE, et al. Two sides of the same coin: pediatric-onset and adult-onset common variable immune deficiency. J Clin Immunol. 2017;37(6):592–602.
Grimbacher B, Party ERW. The European Society for Immunodeficiencies (ESID) registry 2014. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014;178(Suppl 1):18–20.
Hartono S, Motosue MS, Khan S, Rodriguez V, Iyer VN, Divekar R, et al. Predictors of granulomatous lymphocytic interstitial lung disease in common variable immunodeficiency. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017 May;118(5):614–20.
Mouillot G, Carmagnat M, Gerard L, Garnier JL, Fieschi C, Vince N, et al. B-cell and T-cell phenotypes in CVID patients correlate with the clinical phenotype of the disease. J Clin Immunol. 2010;30(5):746–55.
Resnick ES, Moshier EL, Godbold JH, Cunningham-Rundles C. Morbidity and mortality in common variable immune deficiency over 4 decades. Blood. 2012;119(7):1650–7.
Wehr C, Kivioja T, Schmitt C, Ferry B, Witte T, Eren E, Vlkova M, Hernandez M, Detkova D, Bos PR, Poerksen G, von Bernuth H, Baumann U, Goldacker S, Gutenberger S, Schlesier M, Bergeron-van der Cruyssen F, le Garff M, Debre P, Jacobs R, Jones J, Bateman E, Litzman J, van Hagen PM, Plebani A, Schmidt RE, Thon V, Quinti I, Espanol T, Webster AD, Chapel H, Vihinen M, Oksenhendler E, Peter HH, Warnatz K The EUROclass trial: defining subgroups in common variable immunodeficiency. Blood. 2008 1;111(1):77–85.
Bates CA, Ellison MC, Lynch DA, Cool CD, Brown KK, Routes JM. Granulomatous-lymphocytic lung disease shortens survival in common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004 Aug;114(2):415–21.
Gathmann B, Mahlaoui N, Ceredih GL, Oksenhendler E, Warnatz K, et al. Clinical picture and treatment of 2212 patients with common variable immunodeficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2014;134(1):116–26.
Chapel H, Lucas M, Lee M, Bjorkander J, Webster D, Grimbacher B, et al. Common variable immunodeficiency disorders: division into distinct clinical phenotypes. Blood. 2008;112(2):277–86.
Urschel S, Kayikci L, Wintergerst U, Notheis G, Jansson A, Belohradsky BH. Common variable immunodeficiency disorders in children: delayed diagnosis despite typical clinical presentation. J Pediatr. 2009 Jun;154(6):888–94.
Esolen LM, Fasano MB, Flynn J, Burton A, Lederman HM. Pneumocystis carinii osteomyelitis in a patient with common variable immunodeficiency. N Engl J Med. 1992 Apr 9;326(15):999–1001.
Malphettes M, Gerard L, Carmagnat M, Mouillot G, Vince N, Boutboul D, et al. Late-onset combined immune deficiency: a subset of common variable immunodeficiency with severe T cell defect. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49(9):1329–38.
Michel M, Chanet V, Galicier L, Ruivard M, Levy Y, Hermine O, et al. Autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura and common variable immunodeficiency: analysis of 21 cases and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004;83(4):254–63.
Cunningham-Rundles C, Bodian C. Common variable immunodeficiency: clinical and immunological features of 248 patients. Clin Immunol. 1999;92(1):34–48.
Cadranel J, Bouvry D, Wislez M. Respiratory manifestations of common variable immunodeficiency in adults. Rev Mal Respir. 2003;20(1 Pt 1):126–33 Manifestations respiratoires au cours du deficit immunitaire commun variable de l’adulte.
Tabolli S, Giannantoni P, Pulvirenti F, La Marra F, Granata G, Milito C, et al. Longitudinal study on health-related quality of life in a cohort of 96 patients with common variable immune deficiencies. Front Immunol. 2014;5:–605.
Hajjar J, Kutac C, Rider NL, Seeborg FO, Scalchunes C, Orange J. Fatigue and the wear-off effect in adult patients with common variable immunodeficiency. Clin Exp Immunol. 2018;194(3):327–38.
Farmer JR, Ong MS, Barmettler S, Yonker LM, Fuleihan R, Sullivan KE, et al. Common variable immunodeficiency non-infectious disease endotypes redefined using unbiased network clustering in large electronic datasets. Front Immunol. 2017;8:–1740.
Funding
All phases of this study were financially supported by 1T32HG008955-01A1 and the Steifel Family Immunology Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Duke University Institutional Review Board, and as this was a retrospective chart review involving existing data and posing no more than minimal risks to subjects, the need for individual consent was waived.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
ESM 1
(PDF 230 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baloh, C., Reddy, A., Henson, M. et al. 30-Year Review of Pediatric- and Adult-Onset CVID: Clinical Correlates and Prognostic Indicators. J Clin Immunol 39, 678–687 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-019-00674-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-019-00674-9