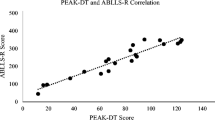
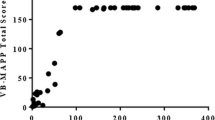
Abstract
The present investigation sought to examine the efficacy of the instructional curriculum described in the Direct Training Module of the PEAK Relational Training System on the language repertoires, as measured by the PEAK direct assessment, of children diagnosed with autism or related developmental disabilities. Twenty-seven children diagnosed with pervasive developmental disorders were evaluated using the PEAK direct training assessment protocol prior to assignment to control and experimental groups. Participants in the experimental group received additional language instruction derived from the curriculum programs of the Direct Training Module, while participants in the control group received treatment as usual. Both groups were then re-assessed using the PEAK direct assessment after 1 month. A repeated measures ANOVA indicated that participants in the experimental group made significantly more gains in language skills than those who were assigned to the control group, F(1, 22) = 9.684, p = .005. Implications for evidence-based practice and future research are discussed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dixon, M. R. (2014a). PEAK relational training system: Direct training module. Carbondale, IL: Shawnee Scientific Press.
Dixon, M. R. (2014b). PEAK relational training system: Generalization learning module. Carbondale, IL: Shawnee Scientific Press.
Dixon, M. R. (in press-a). PEAK relational training system: Equivalence. Carbondale, IL: Shawnee Scientific Press.
Dixon, M. R. (in press-b). PEAK relational training system: Transformation. Carbondale, IL: Shawnee Scientific Press.
Dixon, M. R., Carman, J., Tyler, P. A., Whiting, S. W., Enoch, M. R., & Daar, J. H. (2014a). PEAK relational training system for children with autism and developmental disabilities: Correlations with peabody picture vocabulary test and assessment reliability. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 26(5), 603–614. doi:10.1007/s10882-014-9384-2.
Dixon, M. R., Small, S. L., & Rosales, R. (2007). Extended analysis of empirical citations with Skinner’s verbal behavior: 1984–2004. The Behavior Analyst, 30(2), 197–209.
Dixon, M. R., Whiting, S. W., & Daar, J. H. (2014). The direct training module. In M. R. Dixon (Ed.), PEAK relational training system: Direct training module. Carbondale, IL: Shawnee Scientific Press.
Dixon, M. R., Whiting, S. W., Rowsey, K., & Belisly, J. (2014c). Assessing the relationship between intelligence and the PEAK relational training system. Research in Autism Spectrum Disorders, 8(9), 1208–1213. doi:10.1016/j.rasd.2014.05.005.
Hayes, S. C., Barnes-Holmes, D., & Roche, B. (2001). Relational frame theory: A post-Skinnerian account of human language and cognition. New York: Plenum.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act of 2004 (2004). Retrieved from http://idea.ed.gov/download/statute.html.
LeBlanc, L. A., Esch, J., Sidener, T. M., & Firth, A. M. (2006). Behavioral language interventions for children with autism: Comparing applied verbal behavior and naturalistic teaching approaches. Analysis of Verbal Behavior, 22, 2249–2260.
Lovaas, O. I. (2003). Teaching individuals with developmental delays: Basic intervention techniques. Austin, TX: Pro-Ed.
Martin, N., & Brownell, R. (2011a). Expressive one-word picture test: Manual 4. Novato, CA: ATP Assessments.
Martin, N., & Brownell, R. (2011b). Receptive one-word picture vocabulary test: Manual 4. Novato, CA: ATP Assessments.
National Autism Center (2009). National Standards Report. Retrieved from http://www.nationalautismcenter.org/pdf/NAC%20Standards%20Report.pdf.
Partington, J. W. (2008). The assessment of basic language and learning skills—Revised (the ABLLS-R). Pleasant Hill, CA: Behavior Analysts.
Skinner, B. F. (1957). Verbal Behavior. Acton, MA: Copley Publishing Group.
Sundberg, M. L. (2008). Verbal behavior milestones assessment and placement program: The VB-MAPP. Concord, CA: AVB Press.
Sundberg, M. L., & Michael, J. (2001). The benefits of Skinner’s analysis of verbal behavior for children with autism. Behavior Modification, 25(5), 698–724. doi:10.1177/0145445501255003.
Tiger, J. H., Hanley, G. P., & Bruzek, J. (2008). Functional communication training: A review and practical guide. Behavior Analysis In Practice, 1(1), 16–23.
United States Surgeon General. (1998). Mental health: A report of the surgeon general. Washington, DC: Author.
U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics (2011). Retrieved from http://nces.ed.gov/.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McKeel, A.N., Dixon, M.R., Daar, J.H. et al. Evaluating the Efficacy of the PEAK Relational Training System Using a Randomized Controlled Trial of Children with Autism. J Behav Educ 24, 230–241 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-015-9219-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10864-015-9219-y