Abstract
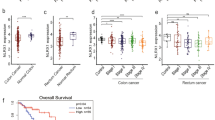
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAAD) is the third leading cause of cancer-related deaths, with a 5-year relative survival rate of 6%. Hence, novel therapeutic targets need to be urgently explored for PAAD. Recently, oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) has been identified to contribute to the development of PAAD. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide + hydrogen (NADH) dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) 1 alpha subcomplex 4 (NDUFA4) is known to affect the mitochondrial respiration pathway. However, the function of NDUFA4 in PAAD remains unclear. In this study, NDUFA4 expression was examined in samples from patients with PAAD using real-time polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical staining. Furthermore, cell proliferation and cell cycle were analyzed using Cell Counting Kit-8 assay and flow cytometry. A xenograft tumor model derived from a PAAD cell line was developed to validate the in vitro findings. NDUFA4 was observed to be upregulated in the PAAD samples, and high levels were associated with a poor survival rate. NDUFA4 knockdown reduced cell proliferation by inducing G1 arrest in SW1990 cells. Mechanistically, NDUFA4 knockdown decreased the oxygen consumption rate, cellular adenosine triphosphate level, mitochondrial complex IV activity, and protein levels of COX6C and COX5B, which indicated the suppression of OXPHOS. In contrast, NDUFA4 overexpression exerted the opposite effects. Finally, NDUFA4 knockdown significantly inhibited the growth of the xenograft tumor derived from the SW1990 cell line in vivo. Therefore, NDUFA4 contributes to PAAD proliferation by enhancing OXPHOS.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets generated during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Balsa E, Marco R, Perales-Clemente E, Szklarczyk R, Calvo E, Landazuri MO, Enriquez JA (2012) NDUFA4 is a subunit of complex IV of the mammalian electron transport chain. Cell Metab 16(3):378–386. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.07.015
Chen D, Hou Y, Cai X (2021) MiR-210-3p enhances cardiomyocyte apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction by targeting the NDUFA4 gene in sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction. Int Heart J 62(3):636–646. doi:https://doi.org/10.1536/ihj.20-512
Cui S, Yang X, Zhang L, Zhao Y, Yan W (2018) LncRNA MAFG-AS1 promotes the progression of colorectal cancer by sponging miR-147b and activation of NDUFA4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 506(1):251–258. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.112
Gyorffy B, Surowiak P, Budczies J, Lanczky A (2013) Online survival analysis software to assess the prognostic value of biomarkers using transcriptomic data in non-small-cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 8(12):e82241. doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0082241
Hirst J, Carroll J, Fearnley IM, Shannon RJ, Walker JE (2003) The nuclear encoded subunits of complex I from bovine heart mitochondria. Biochim Biophys Acta 1604(3):135–150. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/s0005-2728(03)00059-8
Kadenbach B (2017) Regulation of mammalian 13-subunit cytochrome c oxidase and binding of other proteins: role of NDUFA4. Trends Endocrinol Metab 28(11):761–770. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2017.09.003
Kadenbach B (2021) Complex IV - The regulatory center of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. Mitochondrion 58:296–302. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2020.10.004
Ko AH (2015) Progress in the treatment of metastatic pancreatic cancer and the search for next opportunities. J Clin Oncol 33(16):1779–1786. doi:https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.59.7625
Koritzinsky M (2015) Metformin: A novel biological modifier of tumor response to radiation Therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 93(2):454–464. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.06.003
Lei L, Chen C, Zhao J, Wang H, Guo M, Zhou Y, Luo J, Zhang J, Xu L (2017) Targeted expression of miR-7 operated by TTF-1 promoter inhibited the growth of human lung cancer through the NDUFA4 pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 6:183–197. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2016.12.005
Li L, Li Y, Huang Y, Ouyang Y, Zhu Y, Wang Y, Guo X, Yuan Y, Gong K (2018) Long non-coding RNA MIF-AS1 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis to upregulate NDUFA4. Cancer Sci 109(12):3714–3725. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13801
Malkas LH, Herbert BS, Abdel-Aziz W, Dobrolecki LE, Liu Y, Agarwal B, Hoelz D, Badve S, Schnaper L, Arnold RJ, Mechref Y, Novotny MV, Loehrer P, Goulet RJ, Hickey RJ (2006) A cancer-associated PCNA expressed in breast cancer has implications as a potential biomarker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(51):19472–19477. doi:https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604614103
Mishmar D, Ruiz-Pesini E, Mondragon-Palomino M, Procaccio V, Gaut B, Wallace DC (2006) Adaptive selection of mitochondrial complex I subunits during primate radiation. Gene 378:11–18. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2006.03.015
Muller FE, Braun M, Syring I, Klumper N, Schmidt D, Perner S, Hauser S, Muller SC, Ellinger J (2015) NDUFA4 expression in clear cell renal cell carcinoma is predictive for cancer-specific survival. Am J Cancer Res 5(9):2816–2822
Puissegur MP, Mazure NM, Bertero T, Pradelli L, Grosso S, Robbe-Sermesant K, Maurin T, Lebrigand K, Cardinaud B, Hofman V, Fourre S, Magnone V, Ricci JE, Pouyssegur J, Gounon P, Hofman P, Barbry P, Mari B (2011) miR-210 is overexpressed in late stages of lung cancer and mediates mitochondrial alterations associated with modulation of HIF-1 activity. Cell Death Differ 18(3):465–478. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2010.119
Rahib L, Smith BD, Aizenberg R, Rosenzweig AB, Fleshman JM, Matrisian LM (2014) Projecting cancer incidence and deaths to 2030: the unexpected burden of thyroid, liver, and pancreas cancers in the United States. Cancer Res 74(11):2913–2921. doi:https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0155
Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin 64(1):9–29. doi:https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21208
Sinn M, Sinn BV, Striefler JK, Lindner JL, Stieler JM, Lohneis P, Bischoff S, Blaker H, Pelzer U, Bahra M, Dietel M, Dorken B, Oettle H, Riess H, Denkert C (2014) SPARC expression in resected pancreatic cancer patients treated with gemcitabine: results from the CONKO-001 study. Ann Oncol 25(5):1025–1032. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdu084
Spanknebel K, Conlon KC (2001) Advances in the surgical management of pancreatic cancer. Cancer J 7(4):312–323
Tang Z, Li C, Kang B, Gao G, Li C, Zhang Z (2017) GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res 45(W1):W98–W102. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx247
Wang W, Karamanlidis G, Tian R (2016) Novel targets for mitochondrial medicine. Sci Transl Med 8(326):326rv323. doi:https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aac7410
Weinberg SE, Chandel NS (2015) Targeting mitochondria metabolism for cancer therapy. Nat Chem Biol 11(1):9–15. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1712
Yang D, Li R, Xia J, Li W, Ma L, Ye L, Xue H (2020) Long noncoding RNA PCAT18 upregulates SPRR3 to promote colorectal cancer progression by binding to miR-759. Cancer Manag Res 12:11445–11452. doi:https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S272652
Zacksenhaus E, Shrestha M, Liu JC, Vorobieva I, Chung PED, Ju Y, Nir U, Jiang Z (2017) Mitochondrial OXPHOS Induced by RB1 deficiency in breast cancer: implications for anabolic metabolism, stemness, and metastasis. Trends Cancer 3(11):768–779. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trecan.2017.09.002
Zhu J, Vinothkumar KR, Hirst J (2016) Structure of mammalian respiratory complex I. Nature 536(7616):354–358. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19095
Zong S, Wu M, Gu J, Liu T, Guo R, Yang M (2018) Structure of the intact 14-subunit human cytochrome c oxidase. Cell Res 28(10):1026–1034. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0071-1
Funding
This work was supported by the Applied Basic Research of Changzhou Technology Bureau (CJ20200095).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xuemin Chen, Xinquan Wu, and Yue Zhang contributed to the conception and design of the study. Material preparation and data collection and analysis were performed by Yue Zhang, Mengchen Ge, Yuxiang Chen, Yan Yang, Weibo Chen, Di Wu, and Huihua Cai. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Yue Zhang, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript to be submitted.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Animal experiments were performed according to the institutional animal welfare guidelines and were approved by the Animal Care Committee of the Third Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University.
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or nonfinancial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Yue Zhang and Mengchen Ge are the co-first author, they contribute equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Ge, M., Chen, Y. et al. NDUFA4 promotes cell proliferation by enhancing oxidative phosphorylation in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Bioenerg Biomembr 54, 283–291 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-022-09949-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10863-022-09949-0