Abstract
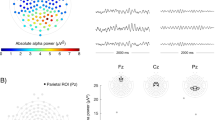
Autistic traits lie on a continuously distributed spectrum ranging from non-clinical to clinical conditions. Indeed, autistic traits have been observed in general population at sub-threshold levels. Here, the main aim was to investigate differences in resting state (RS) electroencephalographic (EEG) power spectrum in individuals with high vs. low autistic traits. Fifty undergraduates completed the Autism-Spectrum Quotient (AQ) and the Empathy Quotient (EQ). For each participant five minutes of RS-EEG were recorded and analysed by means of the exact Low-Resolution Electromagnetic Tomography software (eLORETA). A Two-Step Cluster Analysis revealed two groups: high autistic traits (AT+) and low autistic traits (AT−) group. Compared to AT−, AT+ individuals showed an increase of delta power in parietal/occipital and cortico-limbic areas. No alterations were observed in other frequency bands. Furthermore, both AQ and EQ total scores were positively correlated with delta EEG power after controlling for sex, age, and subclinical psychopathological traits. Results show that AT+ individuals exhibit an increase in slow RS EEG power in regions involved in self-referential processes, suggesting a reduction in these internally directed mental activities and adding new evidence on the existence of a continuum in the autistic spectrum which spreads from clinical to non-clinical significance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Akel, A., Allison, C., Baron-Cohen, S., & Heinke, D. (2019). The distribution of autistic traits across the autism spectrum: Evidence for discontinuous dimensional subpopulations underlying the autism continuum. Molecular Autism, 10, 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13229-019-0275-3.
Adenzato, M., Brambilla, M., Manenti, R., De Lucia, L., Trojano, L., Garofalo, S., et al. (2017). Gender differences in cognitive theory of mind revealed by transcranial direct current stimulation on medial prefrontal cortex. Scientific Reports, 7, 41219. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep41219.
Adenzato, M., Imperatori, C., Ardito, R. B., Valenti, E. M., Marca, G. D., D'Ari, S., et al. (2019a). Activating attachment memories affects default mode network in a non-clinical sample with perceived dysfunctional parenting: An EEG functional connectivity study. Behavioural Brain Research, 372, 112059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112059.
Adenzato, M., Manenti, R., Gobbi, E., Enrici, I., Rusich, D., & Cotelli, M. (2019b). Aging, sex and cognitive theory of mind: A transcranial direct current stimulation study. Scientific Reports, 9, 18064. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-54469-4.
Andrews-Hanna, J. R. (2012). The brain's default network and its adaptive role in internal mentation. Neuroscientist, 18(3), 251–270. https://doi.org/10.1177/1073858411403316.
Andrews-Hanna, J. R., Reidler, J. S., Sepulcre, J., Poulin, R., & Buckner, R. L. (2010). Functional-anatomic fractionation of the brain's default network. Neuron, 65(4), 550–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2010.02.005.
Arnold, H. J., & Feldman, D. C. (1981). Social desirability response bias in self-report choice situations. Academy of Management Journal, 24(2), 377–385. https://doi.org/10.5465/255848.
Association, A. P. (2013). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). Arlington: American Psychiatric Pub.
Austin, E. J. (2005). Personality correlates of the broader autism phenotype as assessed by the autism Spectrum quotient (AQ). Personality and Individual Differences, 38(2), 451–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2004.04.022.
Baio, J., Wiggins, L., Christensen, D. L., Maenner, M. J., Daniels, J., Warren, Z., et al. (2018). Prevalence of autism Spectrum disorder among children aged 8 years - autism and developmental disabilities monitoring network, 11 sites, United States, 2014. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. Surveillance summaries, 67(6), 1-23, https://doi.org/10.15585/mmwr.ss6706a1.
Bara, B. G., Ciaramidaro, A., Walter, H., & Adenzato, M. (2011). Intentional minds: A philosophical analysis of intention tested through fMRI experiments involving people with schizophrenia, people with autism, and healthy individuals. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 5, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2011.00007.
Baron-Cohen, S., & Wheelwright, S. (2004). The empathy quotient: An investigation of adults with Asperger syndrome or high functioning autism, and normal sex differences. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 34(2), 163–175. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:JADD.0000022607.19833.00.
Baron-Cohen, S., Wheelwright, S., Hill, J., Raste, Y., & Plumb, I. (2001a). The "Reading the mind in the eyes" test revised version: A study with normal adults, and adults with Asperger syndrome or high-functioning autism. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 42(2), 241–251. https://doi.org/10.1111/1469-7610.00715.
Baron-Cohen, S., Wheelwright, S., Skinner, R., Martin, J., & Clubley, E. (2001b). The autism-spectrum quotient (AQ): Evidence from Asperger syndrome/high-functioning autism, males and females, scientists and mathematicians. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 31(1), 5–17. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005653411471.
Barttfeld, P., Amoruso, L., Ais, J., Cukier, S., Bavassi, L., Tomio, A., et al. (2013). Organization of brain networks governed by long-range connections index autistic traits in the general population. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 5(1), 16. https://doi.org/10.1186/1866-1955-5-16.
Buckner, R. L., Andrews-Hanna, J. R., & Schacter, D. L. (2008). The brain's default network: Anatomy, function, and relevance to disease. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1124, 1–38. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1440.011.
Carter Leno, V., Tomlinson, S. B., Chang, S. A., Naples, A. J., & McPartland, J. C. (2018). Resting-state alpha power is selectively associated with autistic traits reflecting behavioral rigidity. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 11982. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-30445-2.
Cauvet, E., Van't Westeinde, A., Toro, R., Kuja-Halkola, R., Neufeld, J., Mevel, K., et al. (2019). Sex differences along the autism continuum: A twin study of brain structure. Cerebral Cortex, 29(3), 1342–1350. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhy303.
Chan, A. S., Sze, S. L., & Cheung, M. C. (2007). Quantitative electroencephalographic profiles for children with autistic spectrum disorder. Neuropsychology, 21(1), 74–81. https://doi.org/10.1037/0894-4105.21.1.74.
Cherkassky, V. L., Kana, R. K., Keller, T. A., & Just, M. A. (2006). Functional connectivity in a baseline resting-state network in autism. Neuroreport, 17(16), 1687–1690. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.wnr.0000239956.45448.4c.
Ciaramidaro, A., Adenzato, M., Enrici, I., Erk, S., Pia, L., Bara, B. G., et al. (2007). The intentional network: How the brain reads varieties of intentions. Neuropsychologia, 45(13), 3105–3113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.05.011.
Constantino, J. N., & Todd, R. D. (2003). Autistic traits in the general population: A twin study. Archives of General Psychiatry, 60(5), 524–530. https://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.60.5.524.
Constantino, J. N., & Todd, R. D. (2005). Intergenerational transmission of subthreshold autistic traits in the general population. Biological Psychiatry, 57(6), 655–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2004.12.014.
De Leo, D., Frisoni, G. B., Rozzini, R., & Trabucchi, M. (1993). Italian community norms for the brief symptom inventory in the elderly. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 32(Pt 2), 209–213. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2044-8260.1993.tb01045.
De Ridder, D., Vanneste, S., Kovacs, S., Sunaert, S., & Dom, G. (2011). Transient alcohol craving suppression by rTMS of dorsal anterior cingulate: An fMRI and LORETA EEG study. Neuroscience Letters, 496(1), 5–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2011.03.074.
Derogatis, L. R., & Melisaratos, N. (1983). The brief symptom inventory: An introductory report. Psychological Medicine, 13(3), 595–605. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291700048017.
Dinsdale, N. L., Hurd, P. L., Wakabayashi, A., Elliot, M., & Crespi, B. J. (2013). How are autism and schizotypy related? Evidence from a non-clinical population. PLoS One, 8(5), e63316. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063316.
Enrici, I., Bara, B.G., & Adenzato, M. (2019). Theory of Mind, pragmatics, and the brain: Converging evidence for the role of intention processing as a core feature of human communication. Pragmatics & Cognition, 26(1).
Ford, T. C., & Crewther, D. P. (2014). Factor analysis demonstrates a common Schizoidal phenotype within autistic and schizotypal tendency: Implications for Neuroscientific studies. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 5, 117. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2014.00117.
Ford, T. C., Apputhurai, P., Meyer, D., & Crewther, D. P. (2018). Cluster analysis reveals subclinical subgroups with shared autistic and schizotypal traits. Psychiatry Research, 265, 111–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.04.037.
Friston, K. J., Frith, C. D., Liddle, P. F., & Frackowiak, R. S. (1991). Comparing functional (PET) images: The assessment of significant change. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 11(4), 690–699. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.1991.122.
Gillberg, C. L. (1992). The Emanuel Miller Memorial Lecture 1991. Autism and autistic-like conditions: Subclasses among disorders of empathy. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 33(5), 813–842. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.1992.tb01959.x.
Grave de Peralta Menendez, R., Gonzalez Andino, S. L., Morand, S., Michel, C. M., & Landis, T. (2000). Imaging the electrical activity of the brain: ELECTRA. Human Brain Mapping, 9(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(2000)9:1<1::AID-HBM1>3.0.CO;2-#.
Grave de Peralta-Menendez, R., & Gonzalez-Andino, S. L. (1998). A critical analysis of linear inverse solutions to the neuroelectromagnetic inverse problem. IEEE Transactions on Bio-Medical Engineering, 45(4), 440–448. https://doi.org/10.1109/10.664200.
Greicius, M. D., Krasnow, B., Reiss, A. L., & Menon, V. (2003). Functional connectivity in the resting brain: A network analysis of the default mode hypothesis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 100(1), 253–258. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0135058100.
Grinter, E. J., Maybery, M. T., Van Beek, P. L., Pellicano, E., Badcock, J. C., & Badcock, D. R. (2009). Global visual processing and self-rated autistic-like traits. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 39(9), 1278–1290. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-009-0740-5.
Hlinka, J., Alexakis, C., Diukova, A., Liddle, P. F., & Auer, D. P. (2010). Slow EEG pattern predicts reduced intrinsic functional connectivity in the default mode network: An inter-subject analysis. Neuroimage, 53(1), 239–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.06.002.
Horacek, J., Brunovsky, M., Novak, T., Skrdlantova, L., Klirova, M., Bubenikova-Valesova, V., et al. (2007). Effect of low-frequency rTMS on electromagnetic tomography (LORETA) and regional brain metabolism (PET) in schizophrenia patients with auditory hallucinations. Neuropsychobiology, 55(3–4), 132–142. https://doi.org/10.1159/000106055.
Hsiao, M. N., Tseng, W. L., Huang, H. Y., & Gau, S. S. (2013). Effects of autistic traits on social and school adjustment in children and adolescents: The moderating roles of age and gender. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 34(1), 254–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2012.08.001.
Huang, Y., Mohan, A., De Ridder, D., Sunaert, S., & Vanneste, S. (2018). The neural correlates of the unified percept of alcohol-related craving: A fMRI and EEG study. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 923–912. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-18471-y.
Iidaka, T., Kogata, T., Mano, Y., & Komeda, H. (2019). Thalamocortical Hyperconnectivity and amygdala-cortical Hypoconnectivity in male patients with autism Spectrum disorder. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10, 252. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00252.
Imperatori, C., Farina, B., Brunetti, R., Gnoni, V., Testani, E., Quintiliani, M. I., et al. (2013). Modifications of EEG power spectra in mesial temporal lobe during n-back tasks of increasing difficulty. A sLORETA study. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 109. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00109.
Imperatori, C., Della Marca, G., Brunetti, R., Carbone, G. A., Massullo, C., Valenti, E. M., et al. (2016). Default mode network alterations in alexithymia: An EEG power spectra and connectivity study. Scientific Reports, 6, 36653. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36653.
Imperatori, C., Farina, B., Adenzato, M., Valenti, E. M., Murgia, C., Marca, G. D., et al. (2019a). Default mode network alterations in individuals with high-trait-anxiety: An EEG functional connectivity study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 246, 611–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2018.12.071.
Imperatori, C., Farina, B., Valenti, E. M., Di Poce, A., D'Ari, S., De Rossi, E., et al. (2019b). Is resting state frontal alpha connectivity asymmetry a useful index to assess depressive symptoms? A preliminary investigation in a sample of university students. Journal of Affective Disorders, 257, 152–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2019.07.034.
Imperatori, C., Massullo, C., Carbone, G. A., Farina, B., Colmegna, F., Riboldi, I., et al. (2019c). Electroencephalographic (EEG) alterations in young women with high subclinical eating pathology levels: A quantitative EEG study. Eating and Weight Disordrs, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40519-019-00801-w.
Jakab, A., Emri, M., Spisak, T., Szeman-Nagy, A., Beres, M., Kis, S. A., et al. (2013). Autistic traits in neurotypical adults: Correlates of graph theoretical functional network topology and white matter anisotropy patterns. PLoS One, 8(4), e60982. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0060982.
Jung, M., Kosaka, H., Saito, D. N., Ishitobi, M., Morita, T., Inohara, K., et al. (2014). Default mode network in young male adults with autism spectrum disorder: Relationship with autism spectrum traits. Molecular Autism, 5, 35. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-2392-5-35.
Keenan, J. P., Nelson, A., O'Connor, M., & Pascual-Leone, A. (2001). Self-recognition and the right hemisphere. Nature, 409(6818), 305. https://doi.org/10.1038/35053167.
Kennedy, D. P., Redcay, E., & Courchesne, E. (2006). Failing to deactivate: Resting functional abnormalities in autism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 103(21), 8275–8280. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0600674103.
Kirino, E. (2017). Three-dimensional stereotactic surface projection in the statistical analysis of single photon emission computed tomography data for distinguishing between Alzheimer's disease and depression. World Journal of Psychiatry, 7(2), 121–127. https://doi.org/10.5498/wjp.v7.i2.121.
Kreiter, A. K., & Singer, W. (1992). Oscillatory neuronal responses in the visual cortex of the awake macaque monkey. European Journal of Neuroscience, 4(4), 369–375. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.1992.tb00884.x.
Lauriola, M., Panno, A., Tomai, M., Ricciardi, V., & Potenza, A. E. (2011). Is alexithymia related to colon cancer? A survey of patients undergoing a screening colonoscopy examination. Journal of Clinical Psychology in Medical Settings, 18(4), 410–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10880-011-9267-y.
Lever, A. G., & Geurts, H. M. (2016). Psychiatric co-occurring symptoms and disorders in young, middle-aged, and older adults with autism Spectrum disorder. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 46(6), 1916–1930. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-016-2722-8.
Lombardo, M. V., Barnes, J. L., Wheelwright, S. J., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2007). Self-referential cognition and empathy in autism. PLoS One, 2(9), e883. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000883.
Lundstrom, S., Chang, Z., Rastam, M., Gillberg, C., Larsson, H., Anckarsater, H., et al. (2012). Autism spectrum disorders and autistic like traits: Similar etiology in the extreme end and the normal variation. Archives of General Psychiatry, 69(1), 46–52. https://doi.org/10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2011.144.
Lynch, C. J., Uddin, L. Q., Supekar, K., Khouzam, A., Phillips, J., & Menon, V. (2013). Default mode network in childhood autism: Posteromedial cortex heterogeneity and relationship with social deficits. Biological Psychiatry, 74(3), 212–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.12.013.
Mason, R. A., Williams, D. L., Kana, R. K., Minshew, N., & Just, M. A. (2008). Theory of mind disruption and recruitment of the right hemisphere during narrative comprehension in autism. Neuropsychologia, 46(1), 269–280. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2007.07.018.
Mealey, A., Abbott, G., Byrne, L. K., & McGillivray, J. (2014). Overlap between autistic and schizotypal personality traits is not accounted for by anxiety and depression. Psychiatry Research, 219(2), 380–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2014.05.040.
Miraglia, F., Vecchio, F., Bramanti, P., & Rossini, P. M. (2015). Small-worldness characteristics and its gender relation in specific hemispheric networks. Neuroscience, 310, 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.09.028.
Moore, M. R., & Franz, E. A. (2017). Resting-state mu activity modulations are associated with aloofness. Personality and Individual Differences, 116, 366–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.05.026.
Muller, T. J., Federspiel, A., Horn, H., Lovblad, K., Lehmann, C., Dierks, T., et al. (2005). The neurophysiological time pattern of illusionary visual perceptual transitions: A simultaneous EEG and fMRI study. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 55(3), 299–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpsycho.2004.09.004.
Murias, M., Webb, S. J., Greenson, J., & Dawson, G. (2007). Resting state cortical connectivity reflected in EEG coherence in individuals with autism. Biological Psychiatry, 62(3), 270–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.11.012.
Murphy, T. H., Blatter, L. A., Wier, W. G., & Baraban, J. M. (1992). Spontaneous synchronous synaptic calcium transients in cultured cortical neurons. The Journal of Neuroscience, 12(12), 4834–4845. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2009.2028419.
Nichols, T. E., & Holmes, A. P. (2002). Nonparametric permutation tests for functional neuroimaging: A primer with examples. Human Brain Mapping, 15(1), 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.1058.
Oblak, A. L., Rosene, D. L., Kemper, T. L., Bauman, M. L., & Blatt, G. J. (2011). Altered posterior cingulate cortical cyctoarchitecture, but normal density of neurons and interneurons in the posterior cingulate cortex and fusiform gyrus in autism. Autism Research, 4(3), 200–211. https://doi.org/10.1002/aur.188.
Orekhova, E. V., Stroganova, T. A., Nygren, G., Tsetlin, M. M., Posikera, I. N., Gillberg, C., et al. (2007). Excess of high frequency electroencephalogram oscillations in boys with autism. Biological Psychiatry, 62(9), 1022–1029. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.12.029.
Orekhova, E. V., Stroganova, T. A., Prokofiev, A. O., Nygren, G., Gillberg, C., & Elam, M. (2009). The right hemisphere fails to respond to temporal novelty in autism: Evidence from an ERP study. Clinical Neurophysiology, 120(3), 520–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinph.2008.12.034.
Pascual-Marqui, R. D., Lehmann, D., Koukkou, M., Kochi, K., Anderer, P., Saletu, B., et al. (2011). Assessing interactions in the brain with exact low-resolution electromagnetic tomography. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering, 369(1952), 3768–3784. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsta.2011.0081.
Pierce, K., Muller, R. A., Ambrose, J., Allen, G., & Courchesne, E. (2001). Face processing occurs outside the fusiform 'face area' in autism: Evidence from functional MRI. Brain, 124(Pt 10), 2059–2073. https://doi.org/10.1093/brain/124.10.2059.
Pinkham, A. E., Hopfinger, J. B., Pelphrey, K. A., Piven, J., & Penn, D. L. (2008). Neural bases for impaired social cognition in schizophrenia and autism spectrum disorders. Schizophrenia Research, 99(1–3), 164–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2007.10.024.
Pizzagalli, D. A., Oakes, T. R., Fox, A. S., Chung, M. K., Larson, C. L., Abercrombie, H. C., et al. (2004). Functional but not structural subgenual prefrontal cortex abnormalities in melancholia. Molecular Psychiatry, 9(4), 325), 393–405. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001469.
Pop-Jordanova, N., Zorcec, T., Demerdzieva, A., & Gucev, Z. (2010). QEEG characteristics and spectrum weighted frequency for children diagnosed as autistic spectrum disorder. Nonlinear Biomedical Physics, 4(1), 4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1753-4631-4-4.
Posserud, M. B., Lundervold, A. J., & Gillberg, C. (2006). Autistic features in a total population of 7-9-year-old children assessed by the ASSQ (autism Spectrum screening questionnaire). Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 47(2), 167–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.2005.01462.x.
Preti, A., Vellante, M., Baron-Cohen, S., Zucca, G., Petretto, D. R., & Masala, C. (2011). The empathy quotient: A cross-cultural comparison of the Italian version. Cognitive Neuropsychiatry, 16(1), 50–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/13546801003790982.
Puzzo, I., Cooper, N. R., Vetter, P., & Russo, R. (2010). EEG activation differences in the pre-motor cortex and supplementary motor area between normal individuals with high and low traits of autism. Brain Research, 1342, 104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.04.060.
Robinson, E. B., Munir, K., Munafo, M. R., Hughes, M., McCormick, M. C., & Koenen, K. C. (2011). Stability of autistic traits in the general population: Further evidence for a continuum of impairment. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 50(4), 376–384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2011.01.005.
Robinson, E. B., St Pourcain, B., Anttila, V., Kosmicki, J. A., Bulik-Sullivan, B., Grove, J., et al. (2016). Genetic risk for autism spectrum disorders and neuropsychiatric variation in the general population. Nature Genetics, 48(5), 552–555. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3529.
Ruta, L., Mazzone, D., Mazzone, L., Wheelwright, S., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2012). The autism-Spectrum quotient--Italian version: A cross-cultural confirmation of the broader autism phenotype. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders, 42(4), 625–633. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10803-011-1290-1.
Ruzich, E., Allison, C., Smith, P., Watson, P., Auyeung, B., Ring, H., et al. (2015). Measuring autistic traits in the general population: A systematic review of the autism-Spectrum quotient (AQ) in a nonclinical population sample of 6,900 typical adult males and females. Molecular Autism, 6, 2. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-2392-6-2.
Shih, P., Keehn, B., Oram, J. K., Leyden, K. M., Keown, C. L., & Muller, R. A. (2011). Functional differentiation of posterior superior temporal sulcus in autism: A functional connectivity magnetic resonance imaging study. Biological Psychiatry, 70(3), 270–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.03.040.
Skuse, D. H., Mandy, W., Steer, C., Miller, L. L., Goodman, R., Lawrence, K., et al. (2009). Social communication competence and functional adaptation in a general population of children: Preliminary evidence for sex-by-verbal IQ differential risk. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 48(2), 128–137. https://doi.org/10.1097/CHI.0b013e31819176b8.
Sparks, B. F., Friedman, S. D., Shaw, D. W., Aylward, E. H., Echelard, D., Artru, A. A., et al. (2002). Brain structural abnormalities in young children with autism spectrum disorder. Neurology, 59(2), 184–192. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.59.2.184.
Spiker, D., Lotspeich, L. J., Dimiceli, S., Myers, R. M., & Risch, N. (2002). Behavioral phenotypic variation in autism multiplex families: Evidence for a continuous severity gradient. American Journal of Medical Genetics, 114(2), 129–136.
Takarae, Y., Minshew, N. J., Luna, B., & Sweeney, J. A. (2007). Atypical involvement of frontostriatal systems during sensorimotor control in autism. Psychiatry Research, 156(2), 117–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pscychresns.2007.03.008.
Tettamanti, M., Vaghi, M. M., Bara, B. G., Cappa, S. F., Enrici, I., & Adenzato, M. (2017). Effective connectivity gateways to the theory of mind network in processing communicative intention. Neuroimage, 155, 169–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.04.050.
Vicari, G., & Adenzato, M. (2014). Is recursion language-specific? Evidence of recursive mechanisms in the structure of intentional action. Consciousness and Cognition, 26, 169–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.concog.2014.03.010.
von dem Hagen, E. A., Nummenmaa, L., Yu, R., Engell, A. D., Ewbank, M. P., & Calder, A. J. (2011). Autism spectrum traits in the typical population predict structure and function in the posterior superior temporal sulcus. Cerebral Cortex, 21(3), 493–500. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhq062.
Wakabayashi, A., Baron-Cohen, S., & Wheelwright, S. (2006). Are autistic traits an independent personality dimension? A study of the autism-Spectrum quotient (AQ) and the NEO-PI-R. Personality and Individual Differences, 41(5), 873–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2006.04.003.
Wang, J., Barstein, J., Ethridge, L. E., Mosconi, M. W., Takarae, Y., & Sweeney, J. A. (2013). Resting state EEG abnormalities in autism spectrum disorders. Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 5(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.1186/1866-1955-5-24.
Weng, S. J., Wiggins, J. L., Peltier, S. J., Carrasco, M., Risi, S., Lord, C., et al. (2010). Alterations of resting state functional connectivity in the default network in adolescents with autism spectrum disorders. Brain Research, 1313, 202–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2009.11.057.
Whitehouse, A. J., Hickey, M., & Ronald, A. (2011). Are autistic traits in the general population stable across development? PLoS One, 6(8), e23029. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0023029.
Yerys, B. E., Gordon, E. M., Abrams, D. N., Satterthwaite, T. D., Weinblatt, R., Jankowski, K. F., et al. (2015). Default mode network segregation and social deficits in autism spectrum disorder: Evidence from non-medicated children. NeuroImage: Clinical, 9, 223–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2015.07.018.
Yirmiya, N., Sigman, M. D., Kasari, C., & Mundy, P. (1992). Empathy and cognition in high-functioning children with autism. Child Development, 63(1), 150–160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-8624.1992.tb03603.x.
Zumsteg, D., Wennberg, R. A., Treyer, V., Buck, A., & Wieser, H. G. (2005). H2(15)O or 13NH3 PET and electromagnetic tomography (LORETA) during partial status epilepticus. Neurology, 65(10), 1657–1660. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000184516.32369.1a.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Ministero dell’Istruzione, dell’Università e della Ricerca – MIUR project “Dipartimenti di Eccellenza 2018 – 2022” to Department of Neuroscience “Rita Levi Montalcini”. MA and RBA were supported by University of Turin grants (“Ricerca scientifica finanziata dall’Università”).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Chiara Massullo, Claudio Imperatori, Mauro Adenzato, Riccardo Brunetti, Allegra Indraccolo, Giacomo Della Marca, Benedetto Farina and Rita B. Ardito declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (this study was approved by the European University's ethics review board) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Massullo, C., Imperatori, C., Adenzato, M. et al. Abnormal EEG Power Spectrum in Individuals with High Autistic Personality Traits: an eLORETA Study. J Psychopathol Behav Assess 42, 560–569 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-019-09777-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-019-09777-4