Abstract
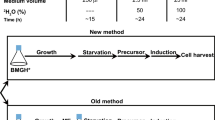
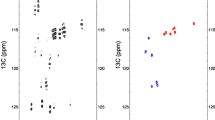
In NMR spectroscopy of biomolecular systems, the use of fluorine-19 probes benefits from a clean background and high sensitivity. Therefore, 19F-labeling procedures are of wide-spread interest. Here, we use 5-fluoroindole as a precursor for cost-effective residue-specific introduction of 5-fluorotryptophan (5F-Trp) into G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) expressed in Pichia pastoris. The method was successfully implemented with the neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R). The 19F-NMR spectra of 5F-Trp-labeled NK1R showed one well-separated high field-shifted resonance, which was assigned by mutational studies to the “toggle switch tryptophan”. Residue-selective labeling thus enables site-specific investigations of this functionally important residue. The method described here is inexpensive, requires minimal genetic manipulation and can be expected to be applicable for yeast expression of GPCRs at large.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
References
Abiko LA, Rogowski M, Gautier A, Schertler G, Grzesiek S (2021) Efficient production of a functional G protein-coupled receptor in E. Coli for structural studies. J Biomol NMR 75:25–38
Alekseev TA, Dergousova NI, Shibanova ED, Azeeva EA, Kriukova EV, Balashova TA, Dubovskii PV, Aesen’ev AS, Tsetlin VI (2003) 5-fluoro-tryptophan-containing N-terminal domain of the α-subunit of the Torpedo californica acetylcholine receptor: preparation in Escherichia coli and 19F NMR study. Bioorg Khim 29:384–390
Anderluh G, Razpotnik A, Podlesek Z, Maček P, Separovic F, Norton RS (2005) Interaction of the eukaryotic pore-forming cytolysin equinatoxin II with model membranes: 19F NMR studies. J Mol Biol 347:27–39
Bai J, Wang J, Ravula T, Im SC, Anantharamaiah GM, Waskell L, Ramamoorthy A (2020) Expression, purification, and functional reconstitution of 19F-labeled cytochrome b5 in peptide nanodiscs for NMR studies. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1862:183194
Ballesteros JA, Weinstein H (1995) Integrated methods for the construction of three-dimensional models and computational probing of structure–function relations in G protein-coupled receptors. Methods Neurosci 25:366–428
Bernstein H, Schneider WG, Pople JA (1956) The proton magnetic resonance spectra of conjugated aromatic hydrocarbons. Proc R Soc Lond 236:515–528
Chen S, Lu M, Liu D, Yang L, Yi C, Ma L, Zhang H, Liu Q, Frimurer TM, Wang MW, Schwartz TW, Stevens RC, Wu B, Wüthrich K, Zhao Q (2019) Human substance P receptor binding mode of the antagonist drug aprepitant by NMR and crystallography. Nat Commun 10:638
Crowley PB, Kyne C, Monteith WB (2012) Simple and inexpensive incorporation of 19F-Tryptophan for protein NMR spectroscopy. Chem Commun 48:10681–10683
Danielson MA, Falke JJ (1996) Use of 19F NMR to probe protein structure and conformational changes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 25:163–195
Didenko T, Liu JJ, Horst R, Stevens RC, Wüthrich K (2013) Fluorine-19 NMR of integral membrane proteins illustrated with studies of GPCRs. Curr Opin Struct Biol 23:740–747
Drazic A, Myklebust LM, Ree R, Arnesen T (2016) The world of protein acetylation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1864:1372–1401
Eddy MT, Lee MY, Gao ZG, White KL, Didenko T, Horst R, Audet M, Stanczak P, McClary KM, Han GW, Jacobson KA, Stevens RC, Wüthrich K (2018) Allosteric coupling of drug binding and intracellular signaling in the A2A adenosine receptor. Cell 172:68–80
Frieden C, Hoeltzli SD, Bann JG (2004) The preparation of 19F-labeled proteins for NMR studies. Methods Enzymol 380:400–415
Ge H, Wang H, Pan B, Feng D, Guo C, Yang L, Liu D, Wüthrich K (2022) G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) reconstitution and labeling for solution nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) studies of the structural basis of transmembrane signaling. Molecules 27:2658
Gerig JT (1994) Fluorine NMR of proteins. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc 26:293–370
Gronenborn AM (2022) Small, but powerful and attractive: 19F in biomolecular NMR. Structure 30:6–14
Harris JA, Faust B, Gondin AB, Dämgen MA, Suomivuori CM, Veldhuis NA, Cheng Y, Dror RO, Thal DM, Manglik A (2022) Selective G protein signaling driven by substance P–neurokinin receptor dynamics. Nat Chem Biol 18:109–115
Johnson CE Jr., Bovey FA (1958) Calculation of nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of aromatic hydrocarbons. J Chem Phys 29:1012–1014
Julius D, Brake A, Blair L, Kunisawa R, Thorner J (1984) Isolation of the putative structural gene for the lysine-arginine-cleaving endopeptidase required for processing of yeast prepro-α- factor. Cell 37:1075–1089
Katritch V, Cherezov V, Stevens RC (2013) Structure–function of the G protein-coupled receptor superfamily. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:531–556
Kim H-W, Perez JA, Ferguson SJ, Campbell ID (1990) The specific incorporation of labelled aromatic amino acids into proteins through growth of bacteria in the presence of glyphosate: application to fluorotryptophan labelling to the H+-ATPase of Escherichia coli and NMR studies. FEBS Lett 272:34–36
Klein-Seetharaman J, Getmanova EV, Loewen MC, Reeves PJ, Khorana HG (1999) NMR spectroscopy in studies of light-induced structural changes in mammalian rhodopsin: applicability of solution 19F NMR. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13744–13749
Koradi R, Billeter M, Wüthrich K (1996) MOLMOL: a program for display and analysis of macromolecular structures. J Mol Graph 14:51–55
Krempl C, Sprangers R (2023) Assessing the applicability of 19F labeled tryptophan residues to quantify protein dynamics. J Biomol NMR 77:55–67
Liu D, Wüthrich K (2016) Ring current shifts in 19F-NMR of membrane proteins. J Biomol NMR 65:1–5
Luck LA, Falke JJ (1991) 19F NMR studies of the D-galactose chemosensory receptor. 1. Sugar binding yields a global structural change. Biochemistry 30:4248–4256
Mohamadi M, Goricanec D, Wagner G, Hagn F (2023) NMR sample optimization and backbone assignment of a stabilized neurotensin receptor. J Struct Biol 215:107970
Pan B, Liu D, Yang L, Wüthrich K (2022) GPCR large-amplitude dynamics by 19F-NMR of aprepitant bound to the neurokinin 1 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 119:e2122682119
Perkins SJ, Wüthrich K (1979) Ring current effects in the conformation dependent NMR chemical shifts of aliphatic protons in the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta 576:409–423
Pervushin K, Riek R, Wider G, Wüthrich K (1997) Attenuated T2 relaxation by mutual cancellation of dipole–dipole coupling and chemical shift anisotropy indicates an avenue to NMR structures of very large biological macromolecules in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:12366–12371
Phillips RS (2004) Synthetic applications of tryptophan synthase. Tetrahedron: Asymmetry 15:2787–2792
Picard LP, Prosser RS (2021) Advances in the study of GPCRs by 19F NMR. Curr Opin Struct Biol 69:169–176
Schöppe J, Ehrenmann J, Klenk C, Rucktooa P, Schütz M, Doré AS, Plückthun A (2019) Crystal structures of the human neurokinin 1 receptor in complex with clinically used antagonists. Nat Commun 10:17
Schuster M, Deluigi M, Pantić M, Vacca S, Baumann C, Scott DJ, Plückthun A, Zerbe O (2020) Optimizing the α1B-adrenergic receptor for solution NMR studies. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1862:183354
Sykes BD, Hull WE (1978) Fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance studies of proteins. Methods Enzymol 49:270–295
Thom C, Ehrenmann J, Vacca S, Waltenspuhl Y, Schöppe J, Medalia O, Plückthun A (2021) Structures of neurokinin 1 receptor in complex with Gq and Gs proteins reveal substance P binding mode and unique activation features. Sci Adv 7:eabk2872
Wang X, Liu D, Shen L, Li F, Li Y, Yang L, Xu T, Tao H, Yao D, Wu L, Hirata K, Bohn LM, Makriyannis A, Liu X, Hua T, Liu ZJ, Wang J (2021) A genetically encoded F-19 NMR probe reveals the allosteric modulation mechanism of cannabinoid receptor 1. J Am Chem Soc 143:16320–16325
Ye L, Wang X, McFarland A, Madsen JJ (2022) ) 19F NMR: a promising tool for dynamic conformational studies of G protein-coupled receptors. Structure 30:1372–1384
Yin J, Chapman K, Clark LD, Shao Z, Borek D, Xu Q, Wang J, Rosenbaum DM (2018) Crystal structure of the human NK1 tachykinin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:13264–13269
Acknowledgements
D.L. acknowledges funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31971153). K.W. is the Cecil H. and Ida M. Green Professor of Structural Biology at Scripps Research. We acknowledge the use of the NMR Core Facilities of the iHuman Institute and help with MS data collection by Dr. Jiakang Chen from the Shanghai Institute for Advanced Immunochemical Studies at ShanghaiTech University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.W. and D.L. supervised the project. B.P. carried out protein production and recorded NMR spectra. B.P., C.G., D.L. and K.W. analyzed the data and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors note no conflicts of interest concerning the research presented here.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, B., Guo, C., Liu, D. et al. Fluorine-19 labeling of the tryptophan residues in the G protein-coupled receptor NK1R using the 5-fluoroindole precursor in Pichia pastoris expression. J Biomol NMR (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-024-00439-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-024-00439-6