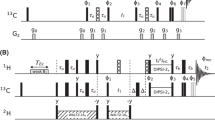
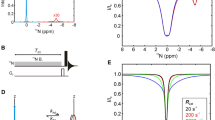
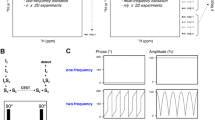
Abstract
EXSY (exchange spectroscopy) NMR provides the residue-specific equilibrium constants, K, and residue-specific kinetic rate constants, k, of a polypeptide chain in a two-state exchange in the slow exchange regime. A linear free energy relationship (LFER) discovered in a log k versus log K plot is considered to be a physicochemical basis for smooth folding and conformational changes of protein molecules. For accurate determination of the thermodynamic and kinetic parameters, the measurement bias arising from state-specific differences in the R1 and R2 relaxation rates of 1H and other nuclei in HSQC and EXSY experiments must be minimized. Here, we showed that the time-zero HSQC acquisition scheme (HSQC0) is effective for this purpose, in combination with a special analytical method (Π analysis) for EXSY. As an example, we applied the HSQC0 + Π method to the two-state exchange of nukacin ISK-1 in an aqueous solution. Nukacin ISK-1 is a 27-residue lantibiotic peptide containing three mono-sulfide linkages. The resultant bias-free residue-based LFER provided valuable insights into the transition state of the topological interconversion of nukacin ISK-1. We found that two amino acid residues were exceptions in the residue-based LFER relationship. We inferred that the two residues could adopt special conformations in the transition state, to allow the threading of some side chains through a ring structure formed by one of the mono-sulfide linkages. In this context, the two residues are a useful target for the manipulation of the physicochemical properties and biological activities of nukacin ISK-1.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and the supplementary information files. The source data underlying Figs. 2b, 3 and 5, and Supplementary Figs. S1 and S3 are provided as supplementary Excel files, which contain executable equations for the HSQC0 and Π analyses.
References
Ashani Y, Snyder SL, Wilson IB (1973) Linear free energy relations in the hydrolysis of some inhibitors of acetylcholinesterase. J Med Chem 16:446–450. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm00263a004
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW et al (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Farrow NA, Zhang O, Forman-Kay JD, Kay LE (1995) Comparison of the backbone dynamics of a folded and an unfolded SH3 domain existing in equilibrium in aqueous buffer. Biochemistry 34:868–878. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00003a021
Farrow NA, Zhang O, Forman-Kay JD, Kay LE (1994) A heteronuclear correlation experiment for simultaneous determination of 15N longitudinal decay and chemical exchange rates of systems in slow equilibrium. J Biomol NMR 4:727–734. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00404280
Fersht AR, Matouschek A, Serrano L (1992) The folding of an enzyme. I. Theory of protein engineering analysis of stability and pathway of protein folding. J Mol Biol 224:771–782. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-2836(92)90561-W
Fersht AR, Sato S (2004) Φ-value analysis and the nature of protein-folding transition states. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7976–7981. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0402684101
Fujinami D, Mahin AA, Elsayed MM et al (2018) The lantibiotic nukacin ISK-1 exists in an equilibrium between active and inactive lipid-II binding states. Commun Biol 1:150. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-018-0150-3
Fujinami D, Hayashi S, Kohda D (2021) Residue-specific kinetic insights into the transition state in slow polypeptide topological isomerization by NMR exchange spectroscopy. J Phys Chem Lett 12:10551–10557. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02387
Fujinami D, Motomura H, Oshima H et al (2020) Mosaic cooperativity in slow polypeptide topological isomerization revealed by residue-specific NMR thermodynamic analysis. J Phys Chem Lett 11:1934–1939. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.9b03591
Hansch C, Leo A, Taft RW (1991) A survey of hammett substituent constants and resonance and field parameters. Chem Rev 91:165–195. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr00002a004
Hu K, Ellinger JJ, Chylla RA, Markley JL (2011a) Measurement of absolute concentrations of individual compounds in metabolite mixtures by gradient-selective time-zero 1H–13C HSQC with two concentration references and fast maximum likelihood reconstruction analysis. Anal Chem 83:9352–9360. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac201948f
Hu K, Westler WM, Markley JL (2011b) Simultaneous quantification and identification of individual chemicals in metabolite mixtures by two-dimensional extrapolated time-zero 1H–13C HSQC (HSQC0). J Am Chem Soc 133:1662–1665. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja1095304
Lee W, Tonelli M, Markley JL (2015) NMRFAM-SPARKY: enhanced software for biomolecular NMR spectroscopy. Bioinformatics 31:1325–1327. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu830
Miloushev VZ, Bahna F, Ciatto C et al (2008) Dynamic properties of a type II cadherin adhesive domain: implications for the mechanism of strand-swapping of classical cadherins. Structure 16:1195–1205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2008.05.009
Palmer AG (2014) Chemical exchange in biomacromolecules: past, present, and future. J Magn Reson 241:3–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmr.2014.01.008
Puglisi R, Brylski O, Alfano C et al (2020) Quantifying the thermodynamics of protein unfolding using 2D NMR spectroscopy. Commun Chem 3:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42004-020-00358-1
Smallcombe SH (1993) Solvent suppression with symmetrically-shifted pulses. J Am Chem Soc 115:4776–4785. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00064a043
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. Kenji Sonomoto and Takeshi Zendo (Kyushu University, Japan) for advice on the production of nukacin ISK-1. We also thank Dr. Daisuke Fujinami (University of Shizuoka, Japan) for productive discussions. This work was partly performed in the Medical Research Center Initiative for High Depth Omics of the Medical Institute of Bioregulation, Kyushu University.
Funding
This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS, Japan) KAKENHI Grant Number JP21H02448 and the Mitsubishi Foundation (Japan) Research Grants in the Natural Sciences Grant Number 202110017 to D.K.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SH conducted material preparation and NMR measurements, SH and DK contributed to the NMR data analyses, and DK wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors note no conflict of interest concerning the research presented here.
Consent for publication
All authors have seen and approved the submitted manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayashi, S., Kohda, D. The time-zero HSQC method improves the linear free energy relationship of a polypeptide chain through the accurate measurement of residue-specific equilibrium constants. J Biomol NMR 76, 87–94 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-022-00396-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-022-00396-y