Abstract
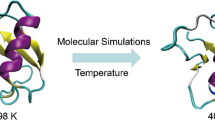
Staphylococcus aureus hibernation promoting factor (SaHPF) is a 22,2 kDa protein which plays a crucial role in 100S Staphylococcus aureus ribosome formation during stress. SaHPF consists of N-terminal domain (NTD) that prevents proteins synthesis by binding to the 30S subunit at the P- and A-sites, connected through a flexible linker with a C-terminal domain (CTD) that keeps ribosomes in 100S form via homodimerization. Recently obtained 100S ribosome structure of S. aureus by cryo-EM shown that SaHPF-NTD bound to the ribosome active sites, however due to the absence of SaHPF-NTD structure it was modeled by homology with the E. coli hibernation factors HPF and YfiA. In present paper we have determined the solution structure of SaHPF-NTD by high-resolution NMR spectroscopy which allows us to increase structural knowledge about HPF structure from S. aureus.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Structural data are available in the Protein Data Bank/BioMagResBank databases under the accession number 6QBZ / 27085.
References
Akanuma G et al (2016) Ribosome dimerization is essential for the efficient regrowth of Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 162:448–458
Akiyama T et al (2017) Resuscitation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from dormancy requires hibernation promoting factor (PA4463) for ribosome preservation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:3204–3209
Bardiaux B, Malliavin T, Nilges M (2012) ARIA for solution and solid-state NMR. Methods Mol Biol 831:453–483
Basu A, Yap MNF (2016) Ribosome hibernation factor promotes Staphylococcal survival and differentially represses translation. Nucleic Acids Res 44:4881–4893
Beckert B et al (2017) Structure of the Bacillus subtilis hibernating 100S ribosome reveals the basis for 70S dimerization. EMBO J 36:2061–2072
Bieri P, Leibundgut M, Saurer M, Boehringer D, Ban N (2017) The complete structure of the chloroplast 70S ribosome in complex with translation factor pY. EMBO J 36:475–486
Brunger AT et al (1998) Crystallography & NMR system: a new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 54:905–921
De Bari H, Berry EA (2013) Structure of Vibrio cholerae ribosome hibernation promoting factor. Acta Crystallogr Sect F 69:228–236
de las Heras A, Cain RJ, Bielecka MK, Vazquez-Boland JA (2011) Regulation of Listeria virulence: PrfA master and commander. Curr Opin Microbiol 14:118–127
Izutsu K et al (2001) Escherichia coli ribosome-associated protein SRA, whose copy number increases during stationary phase. J Bacteriol 183:2765–2773
Kato T et al (2010) Structure of the 100S ribosome in the hibernation stage revealed by electron cryomicroscopy. Structure 18:719–724
Khusainov I et al (2017a) Structures and dynamics of hibernating ribosomes from Staphylococcus aureus mediated by intermolecular interactions of HPF. EMBO J 36:2073–2087
Khusainov I et al (2017b) Structure of the 70S ribosome from human pathogen Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res 45:1026
Laskowski RA, Rullmannn JA, MacArthur MW, Kaptein R, Thornton JM (1996) AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for checking the quality of protein structures solved by NMR. J Biomol NMR 8:477–486
Maki Y, Yoshida H, Wada A (2000) Two proteins, YfiA and YhbH, associated with resting ribosomes in stationary phase Escherichia coli. Genes Cells 5:965–974
McKay SL, Portnoy DA (2015) Ribosome hibernation facilitates tolerance of stationary-phase bacteria to aminoglycosides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:6992–6999
Pettersen EF et al (2004) UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Polikanov YS, Blaha GM, Steitz TA (2012) How hibernation factors RMF, HPF, and YfiA turn off protein synthesis. Science 336:915–918
Puri P et al (2014) Lactococcus lactis YfiA is necessary and sufficient for ribosome dimerization. Mol Microbiol 91:394–407
Russell JB, Cook GM (1995) Energetics of bacterial growth: balance of anabolic and catabolic reactions. Microbiol Rev 59:48–62
Sato A et al (2009) Solution structure of the E. coli ribosome hibernation promoting factor HPF: implications for the relationship between structure and function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 389:580–585
Sharma MR et al (2010) PSRP1 is not a ribosomal protein, but a ribosome-binding factor that is recycled by the ribosome-recycling factor (RRF) and elongation factor G (EF-G). J Biol Chem 285:4006–4014
Tagami K et al (2012) Expression of a small (p)ppGpp synthetase, YwaC, in the (p)ppGpp(0) mutant of Bacillus subtilis triggers YvyD-dependent dimerization of ribosome. Microbiologyopen 1:115–134
Ueta M et al (2008) Role of HPF (hibernation promoting factor) in translational activity in Escherichia coli. J Biochem 143:425–433
Ueta M, Wada C, Wada A (2010) Formation of 100S ribosomes in Staphylococcus aureus by the hibernation promoting factor homolog SaHPF. Genes Cells 15:43–58
Ueta M et al (2013) Conservation of two distinct types of 100S ribosome in bacteria. Genes Cells 18:554–574
Usachev KS, Ayupov RK, Validov SZ, Khusainov IS, Yusupov MM (2018) NMR assignments of the N-terminal domain of Staphylococcus aureus hibernation promoting factor (SaHPF). Biomol NMR Assign 12:85–89
Vila-Sanjurjo A, Schuwirth BS, Hau CW, Cate JH (2004) Structural basis for the control of translation initiation during stress. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:1054–1059
Yoshida H, Wada A (2014) The 100S ribosome: ribosomal hibernation induced by stress. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 5:723–732
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (Grant 16-14-10014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Usachev, K.S., Validov, S.Z., Khusainov, I.S. et al. Solution structure of the N-terminal domain of the Staphylococcus aureus hibernation promoting factor. J Biomol NMR 73, 223–227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-019-00254-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-019-00254-4